Submandibular lymphadenitis: causes, stages and symptoms, treatment, prevention
In the maxillary lymph nodes, lymph is circulated in the cells and capillaries of the oral cavity and head area. Submandibular lymphadenitis refers to polyetiological diseases: both chronic diseases and infections in the acute stage can cause its development. The disease requires compulsory treatment by a specialist, it is impossible to cure lymphadenitis yourself.
Content
What is submandibular lymphadenitis, stages of development
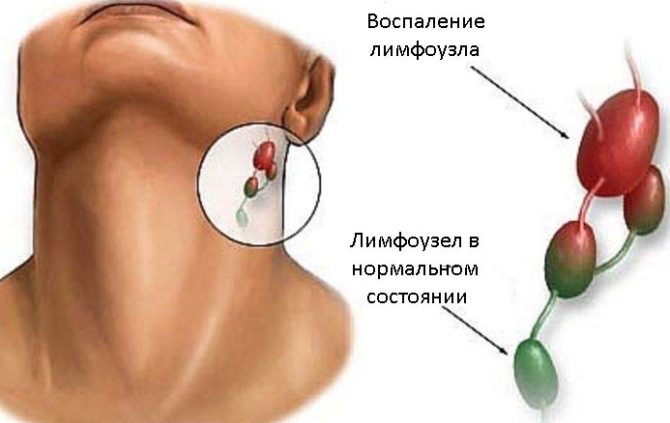
Submandibular lymphadenitis is called inflammation of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes, which is acute and chronic. Often the disease is secondary, that is, it does not occur on its own, but as a symptom of a primary infection.
Acute stage
In the acute form of the disease, one or several lymph nodes can become inflamed. Depending on what exudate is contained in the inflamed node - pus or serous fluid - lymphadenitis is divided into purulent and non-purulent. An acute form of the disease is treated by removing pus from the lymph node and eliminating the root cause of inflammation.
If there is pus inside the lymph node, there is a danger of its breakthrough and infection of surrounding tissues.
Chronic stage
The transition of the disease to the chronic phase is a consequence of the lack of adequate treatment. The node no longer grows in size and hardens. The pain syndrome intensifies, and severe intoxication of the body occurs. The skin around the knot becomes crimson.
Compared to the acute phase of the disease, in chronic lymphadenitis, an increase in the area of inflamed tissues around the lymph node is clearly noticeable. The danger of this form of pathology is that removal of the lymph node may be required.
Causes of submandibular lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the cervical and maxillary lymph nodes is associated mainly with diseases of the oral cavity and respiratory organs. The main causes of submandibular lymphadenitis are:
- Respiratory infection in acute form of viral or bacterial origin without characteristic localization.
- Dental diseases. Especially often, the cause of the inflammatory process in the submandibular lymph nodes is advanced caries or one of its complications: pulpitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontitis.
- The presence in the history of throat diseases: tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, adenoiditis.
- Acute otitis media.
- Chronic or acute inflammation of the sinuses: frontal sinusitis, sinusitis, sinusitis.
- Mechanical damage to the submandibular lymph node caused by trauma.
- The presence in the body of foci of chronic inflammation characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis, STDs, HIV.
- Infection of the body with a Koch stick. The presence of a microorganism does not necessarily entail the development of a tuberculosis process, so the patient may not be aware of infection. But even in a depressed state, Koch's wand can infect lymph nodes.
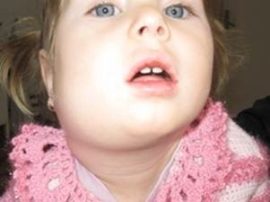
Symptoms, photos and diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis
To distinguish submandibular lymphadenitis from the usual enlargement of the lymph nodes that occurs with lowered immunity, it is possible by the presence of painful sensations and compaction.If, when touching the knot, pain does not occur and compaction is not felt, its increase can be triggered by reduced immunity. Sealing of the lymph node can signal the development of oncology, therefore, if it is detected, it is urgent to be examined by a doctor.
Submandibular lymphadenitis is characterized by an increase in lymph nodes, but it is not the main symptom. In order for a doctor to suspect lymphadenitis, at least one of the following symptoms should appear:
- Pain syndrome. In the early stages of the development of the disease, aching pulling pains of high intensity are noted in the lower part of the head - under the lower jaw. Severe pain is felt with a light pressure on the lymph node, during chewing, with yawning, turning the head. As the disease progresses, pain during palpation increases, and then at rest. Patients fail to self-relieve pain.
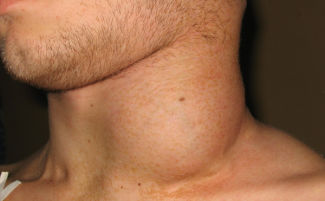
- A significant increase in the lymph node and severe swelling, which makes swallowing difficult and provokes a sensation of fullness in the sublingual region. When swallowing, it feels like a piece of food is too large. Difficult speech.
- Labored breathing. It occurs gradually, accompanied by cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and pallor of the skin of the face.
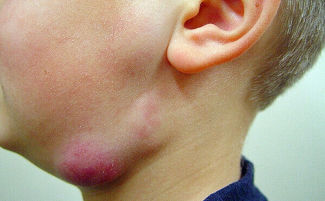
- Visually noticeable swelling under the cheek. The size of the seal depends on the severity of the ongoing pathological process, the amount of serous fluid and pus.
- An increase in body temperature to 39–40 ° C, which may be accompanied by severe headache and sweating. This temperature does not go well with conventional antipyretic drugs.
- Redness of the skin over the node and around it. If pus has accumulated in the node, the skin around it will acquire a pronounced crimson hue. You can detect the accumulation of pus upon palpation, pus is palpated even through the texture of the skin and node.
If there are signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph node, you should consult a doctor. Therapists, otolaryngologists and surgeons are involved in the treatment of lymphadenitis.
In addition to visual inspection and palpation of the node, doctors use several more methods of clinical diagnosis:
- General blood analysis. With the development of submandibular lymphadenitis, a significant increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood is noted.
- Ultrasound procedure. It allows to detect the presence of pus and serous fluid inside the lymph node.
- Bacteriological analysis of fluid from the lymph node. Allows you to determine the type of bacteria that caused inflammation, and choose the most effective antibiotics.
- Conducting a complete differential (excluding other diseases) diagnosis. It is necessary in connection with the similarity of the symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis with other diseases: inflammation of the salivary glands, adenoiditis.
To prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to identify the form of the disease and determine the severity of the pathological process.
How to treat submandibular lymphadenitis
Fully cure inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes is possible only with an integrated approach. The doctor determines the treatment regimen for submandibular lymphadenitis in a child or adult, having studied all the symptoms and the patient’s history.
The first stage of treatment is carried out by dentists and surgeons and may include medical and surgical methods of therapy. At this stage, two main tasks should be solved - sanitation of the focus of infection and relief of pain. The main groups of prescribed drugs are:
- Antibiotics. In the vast majority of cases, the disease is bacterial in nature, therefore treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis requires antibiotics. Penicillin-type antibiotics are usually used, since streptococci or staphylococci are the characteristic causative agents of the disease.To choose the most effective drug, the doctor can prescribe a puncture to the patient, which allows you to determine the resistance of bacteria to a particular drug. Ampicillin, Ampiox, Oxacillin, Bicillin, Amoxicillin or Ticarcillin are usually prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Used to relieve inflammation. The medicine should be selected by the attending physician taking into account the course of the disease and anamnesis.
- Analgesics. They are necessary solely in order to eliminate acute pain syndrome. Analgesics are a concomitant medication, the main medicine for submandibular lymphadenitis in adults is antibiotics.
In parallel with drug therapy, the doctor reorganizes the foci of infection. If the cause of the disease is inflammation of the oral mucosa, then the dentist will treat it.
To quickly remove inflammation and accelerate the healing process with a purulent form of lymphadenitis, the node is opened surgically, after which accumulated pus is removed from it.
When the primary source of inflammation is eliminated, and the acute period of the disease passes, the doctor will prescribe physiotherapy to the patient. Electrophoresis is especially effective. At this stage of treatment, you can use folk remedies for an early recovery.
Submandibular lymphadenitis in children
In children, submandibular lymphadenitis occurs less frequently than in adults. In children under three years of age, the disease cannot develop at all, which is due to the peculiarities of the formation of the lymphatic system.
If the child is worried about pain in the cervical or jaw area, parents should carefully probe his nodes. Healthy lymph nodes are quite soft and mobile, and the procedure itself is completely painless. If you experience pain or if a seal is found, you should immediately contact a pediatrician.
The main cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes of the children are dental diseases, gums and an infection in the nasopharynx. The doctor determines the treatment regimen for submandibular lymphadenitis in a child individually, taking into account the patient's age and the admissibility of taking medications.
Prevention of submandibular lymphadenitis
Prevention of submandibular lymphadenitis is to carry out measures to prevent the development of diseases that can cause the onset of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes:
- During periods of an acute respiratory infection epidemic, crowded places should be avoided and all preventive measures for respiratory diseases should be carried out.
- It is necessary to undergo a timely examination by a dentist and carry out all the necessary medical measures.
- It is necessary to properly and completely treat nasopharyngeal diseases, to prevent the transition of acute forms of ENT pathologies to chronic ones.