Neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia: causes, symptoms and treatment
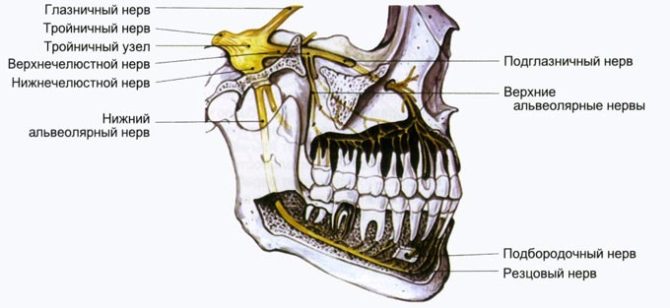
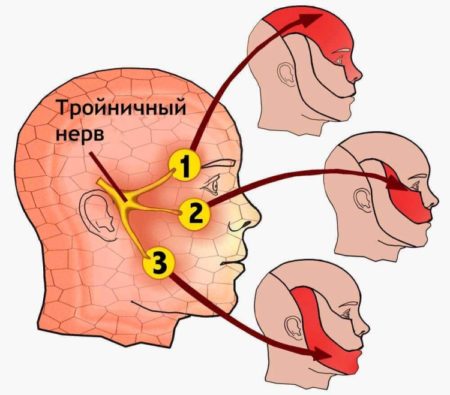
Trigeminal neuralgia (NTN) - a chronic disease provoked by compression, irritation or inflammation of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve and manifested by sharp shooting pain in the zones of his innervation. Treatment of trigeminal neuritis is aimed at eliminating the symptoms and the causes of their appearance.
Content
Neuralgia or trigeminal neuritis - how to
According to the International Classification of Diseases 10 revision (ICD-10) a chronic disease that manifests itself in bouts of excruciating pain in the trigeminal nerve innervation zones is called neuralgia. Patients often confuse such concepts as neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis, but there is one significant difference between them - neuralgia is not characterized by motor disturbances and structural changes in the area of nerve damage.
The second name of the disease is trigeminal neuralgia. It belongs to the group of pathologies of the somatic nervous system and is most often diagnosed in people over 50 years old, most of whom are women. Sometimes the disease is found in young people suffering from multiple sclerosis.
According to WHO statistics, trigeminal neuralgia occurs in one person out of 15 thousand, but the numbers can be underestimated due to incorrect diagnosis.
Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
In practice, doctors are more likely to experience peripheral trigeminal neuralgia, the cause of which is the compression factor (compression). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are continuously compressed with:
- some diseases of the teeth;
- neoplasms in the maxillary sinus;
- purulent sinusitis.
In addition to the compression factor, pain in the facial area can provoke injuries, psycho-emotional stress, chronic foci of infection, and a change in weather.
Diagnosis of the disease
If suspected of trigeminal neuralgia, the neurologist interviews the patient - clarifies the nature and frequency of the manifestation of the pain syndrome, asks what preceded these pains, what diseases had been transferred shortly before they appeared, if there were any chronic diseases at the moment, whether injuries had occurred in the face.
By palpation (palpation), areas of reduced / increased sensitivity, local pain are detected.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
Diagnosis by a neurologist is not difficult, because the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis are typical:
- Complaints of burning, shooting and unbearable pain in the areas of trigeminal nerve innervation. Some patients compare these sensations with current discharges.
- On average, a pain attack lasts 20 seconds, sometimes longer - up to one and a half minutes.
- There are gaps between bouts of pain.
- An attack can be triggered by pressing on certain parts of the face in the nerve innervation zone.
- During an attack, the patient is constrained, almost motionless. Mimic, chewing muscles can twitch.
- Clear localization of pain that does not change.
Even during remission, many chew food on only one side of the jaw, due to which seals are formed on its “inactive” half, signs of which are detected by palpation. A long-running disease passes into a dystrophic stage, as evidenced by atrophic changes in the masticatory muscles.
In adult patients, postherpetic neuralgia occurs. A typical symptom of this type of trigeminal neuritis is periodically arising painful pain that first appears no less than three months after curing shingles.
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis
Trigeminal neuralgia is peripheral and central. In the first case, the disease may be associated with a violation of blood circulation in the nucleus of the nerve (the area of plexus of all branches), and in the second it is the result of a negative effect on a specific area of one of its branches. Peripheral neuritis can provoke diseases of the paranasal sinuses, various facial injuries, neoplasms.
Due to the various root causes leading to the development of neuralgia, the therapeutic approach to the treatment of this disease is individual in each case. Therefore, the fidelity of the diagnosis and the correct determination of the root cause of the pathology are the main conditions for the quick and effective treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
The basis of therapy for trigeminal neuritis is taking medication, with the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, the question of surgical intervention is raised. In some cases, physiotherapy is prescribed - therapeutic galvanotherapy, ultraphonophoresis.
Drug treatment
If there is no need for surgical treatment, medication is carried out. Drugs for the treatment of trigeminal neuritis are listed in the table:
| Carbamazepine
|
Gabapentin
|
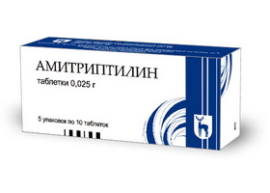
Amitriptyline
|
|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine is the basis of drug treatment of neuritis, the most effective and affordable remedy. Carbamazepine reduces the amplitude of potentials in the sensitive nuclei of the spinal cord and diencephalon, disrupting susceptibility to pain stimuli, therefore, after a few days, patients notice the effect of pain relief, which lasts several hours.
In a dosage that allows you to maintain a normal lifestyle (talking, chewing), the drug is taken for 30 days. Then the dose is gradually reduced. Stop taking the drug only when achieving stable remission - at least 6 months without exacerbations. Treatment lasts from several months to several years. |
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with an analgesic effect. Effective for neuropathic pain. It is indicated for increased facial pain caused by multiple sclerosis. Also effective in chronic pain, postherpetic and traumatic neuralgia.
Of the three drugs examined, Gabapentin is the safest, especially in comparison with Amitriptyline. |
Amitriptyline is an antidepressant tricyclic, a serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Available in tablet form.
Effective against postherpetic neuritis. Patients note improvement in well-being 10-14 days after the start of the drug. In order to avoid a pronounced sedative effect, at first the medicine is taken only at night for 10 mg. Then a single dose is increased, but only the one that is taken before bedtime is not morning or afternoon. |
Also, in the treatment of trigeminal neuritis, antihistamines and antispasmodics are used.
With a sharp cessation of medication, there is a high probability of a repeated exacerbation of the inflammatory process. The risk of increasing the intensity of pain increases the use of electrophoresis.
B vitamins
Patients tend to be skeptical about vitamin complexes and often ignore the recommendations of a neurologist on their use in trigeminal inflammation.This is a big mistake. Vitamin preparations should not be underestimated.
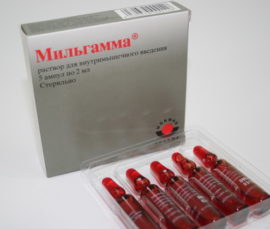 Treatment of trigeminal neuritis involves the intake of B vitamins in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration or dragees. The use of the drug Milgamma is shown - a multicomponent drug, which includes cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12), thiamine (B1), pyridoxine (B6). The effect of the drug is to inhibit the input of nerve pain impulses into the brain and to stimulate tissue regeneration.
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis involves the intake of B vitamins in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration or dragees. The use of the drug Milgamma is shown - a multicomponent drug, which includes cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12), thiamine (B1), pyridoxine (B6). The effect of the drug is to inhibit the input of nerve pain impulses into the brain and to stimulate tissue regeneration.
Milgamma in the form of a solution for i / m is used for two weeks, 2 ml each. Then, three times a day for 40 days, the Milgamma compositum is taken orally - a drug in the form of dragees. This treatment regimen for trigeminal therapy is highly effective, which has been repeatedly proved in practice.
Surgery
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the question arises of the advisability of surgical intervention, which is carried out in three ways:
- Decompression.
- Percutaneous radiofrequency destruction.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery.
Microsurgical operation (decompression) is contraindicated in severe concomitant diseases, especially in people over 65 years of age.
Alternative treatment
No alternative treatment is effective against trigeminal neuralgia. Alternative therapy takes precious time that can be spent on conservative treatment. Thus, the forecast worsens.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis depends on the underlying cause of the disease and the age of the patient. The recovery of young people with neuritis caused by trauma occurs quickly. Relapses do not bother them. Persons older than 60 years have metabolic disorders in the body, and therefore trigeminal neuritis tends to recur. But this does not mean that treatment is not necessary.
Prevention of trigeminal neuritis
In many cases, the root cause of damage to the trigeminal nerve is dental diseases - complications of caries in the form of pulpitis and periodontitis, as well as ENT diseases - sinusitis, frontal sinusitis. If these diseases are treated on time, the risk of developing neuralgic diseases is reduced.
To prevent exacerbation of neuritis, it is necessary to treat infectious pathologies in time, especially diseases of the teeth and sinuses. You should also protect your face from hypothermia and avoid emotional outbursts.