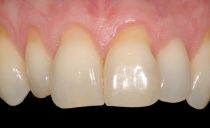
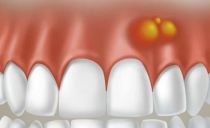
Gingivitis treatment in adults and children
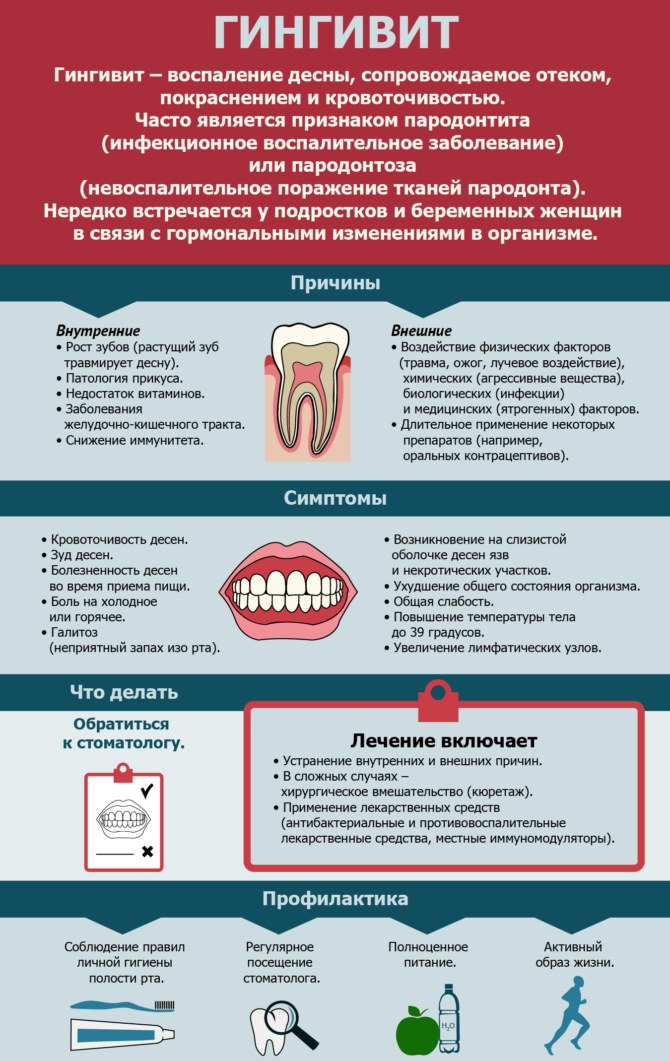
Gingivitis, the treatment of which may seem problematic, is a disease that is manifested by inflammation of the gingival margin and interdental papillae adjacent to the teeth. The most famous symptom of gingivitis is bleeding. Such inflammation follows distinguish from periodontitis, an inflammatory process in which can lead to deformation of bone tissue and tooth mobility (with gingivitis, it is superficial).
Gingivitis occurs in almost the entire adult population, in most schoolchildren, and only in 1/3 of young children.
Content
Causes
The reason for the appearance of gingivitis, dentists call surface hygiene of the oral cavity. Pathogenic diseases contribute to the development of the disease microorganisms that are present in plaque. In combination with concomitant factors, they can cause an inflammatory process of various shapes and severity.
There are people who do not show gingivitis, others suffer from the most common symptom of the disease - bleeding gums.
Usually the process begins with the inflamed papilla of the gum, and then its other parts are involved in it. The disease quickly becomes chronic, in the future periods of exacerbation are replaced by periods of remission. The pathogenic flora of the oral cavity is very aggressive, so people with gingivitis are twice as likely to suffer from cardiovascular ailments and diabetes.
Related factors predisposing plaque congestion include:
- Physiological. The location and shape of the teeth. Crowding, displacement, tooth mobility, malocclusion. All these anatomical features of the structure make it difficult to brush your teeth and contribute to the fact that plaque accumulates. This also includes soft tissue defects - such as a shortened frenum of the tongue and lips, lateral cords, a small vestibule of the oral cavity, which contributes to the separation of the mucous membrane from the teeth during food intake. Arising from this deepening contribute to the accumulation of plaque. Dentists also include oral breathing, which stimulates the development of the inflammatory process, due to insufficient action of the gingival fluid, to physiological factors.
- Pathological. The presence of tartar makes it difficult to cleanse teeth from plaque and is a place of accumulation of microorganisms. Injury to the teeth through aggressive brushing, exposure to cold and hot food on tooth enamel, and chemical damage also contribute to the development of gingivitis. Open caries is a bacterial reservoir that causes deposits to build up.
- Incorrect medical tactics. Mechanical damage to the oral cavity during inaccurate dental procedures. An improperly placed, unpolished or unpolished seal with an overhanging edge, contributing to the fixation of pathogenic flora. Complications of tooth extraction.
- Installation of dentures and orthodontic appliances. Both of them can damage the gum, make it difficult to brush your teeth.
- System factors. This includes taking medications and body diseases that reduce immunity.Also in this group include factors such as: age, stress, severe genetic and endocrine dysfunctions, blood pathologies, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, severe chronic diseases, intoxication of the body and bad habits.
Causes of the development of the disease in children
The main reason for the development of childhood and adult gingivitis is no different. The pathological process in the oral cavity causes plaque. Children's gum tissue is immature, unlike adults, they continue to grow and develop. Therefore they especially vulnerable to the effects of harmful factors.
If a child’s defenses are weakened, he suffers from infections or gastrointestinal upsets, is prone to allergic reactions, endocrine dysfunctions, heart and blood vessel diseases, doesn’t get enough vitamins with food, then the optimal conditions for the development of inflammation are created.
A key predisposing factor to gingivitis in a child is a violation of self-cleaning of teeth, which can lead to:
- early removal of primary teeth;
- treatment at the orthodontist;
- pathological structure and fixation of the frenum of the lips and tongue;
- viscous composition of saliva;
- malnutrition;
- the presence of carious teeth and inflamed dental vessels and nerves;
- congenital defects of the salivary glands;
- uneven load on the dentition;
- prolonged teething.
Causes of gingivitis in pregnant women
The main reason for the development of the disease in pregnant women remains the same. The main role in the appearance of the inflammatory process plays plaque. The bearing of a child is accompanied by a change in the hormonal background and the work of all vital organs and systems of a woman. This almost always provokes bleeding gums.
Doctors have shown that under the influence of an increased amount of hormones, the gums become more susceptible to the pathogenic flora of dental plaque. This, in turn, contributes to the occurrence of edema and inflammation. The composition of plaque in expectant mothers is somewhat different, because some types of microbes instead begin to use female hormones as nutrients.
Manifestations of gingivitis
Gum disease is characterized by symptoms such as:
- hyperemia;
- bleeding gums;
- swelling of the oral mucosa;
- proliferation of gum tissue;
- the appearance of wounds on the gums;
- pain during meals;
- itchy gums.
Additionally, gum disease can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- general weakness and fatigue;
- strong pain when eating food;
- hyperthermia up to 39 ° C;
- bad breath;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- soreness in case of ingestion of cold or hot products, air in the mouth.
Diagnostics
To diagnose gingivitis, doctors conduct a comprehensive examination.
The main methods:
- Poll. The patient finds out the timing of the appearance of the first unpleasant sensations, their features, with which he connects their appearance, changes in sensations, whether there was a treatment for any gingivitis. External visual examination: the dentist notes the patient's behavior, appearance, palpates the lymph nodes.
- Oral examination. The doctor examines the space between the lips and teeth to assess the bite, condition of the frenulum of the lips, palate, throat, tongue and mucous membrane of the cheeks. Such an examination suggests the presence of diseases of the internal organs. Next, the doctor examines the patient's teeth and finds out the presence of caries, pulpitis, microbial plaque and tartar, pathological pockets inside the gums. Their appearance (color, shape, swelling, bleeding) is also evaluated.
- Index score. The specialist, using special formulas, calculates the severity of the disease.
Additional diagnostic methods include:
- Roentgenography. It makes it possible to differentiate between gingivitis and periodontitis.
- General blood analysis. Allows to detect blood diseases.
Types of disease
Doctors distinguish the main forms of the disease:
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative necrotic;
- hypertrophic.
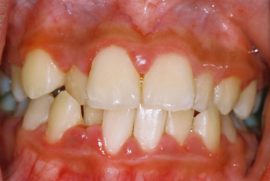
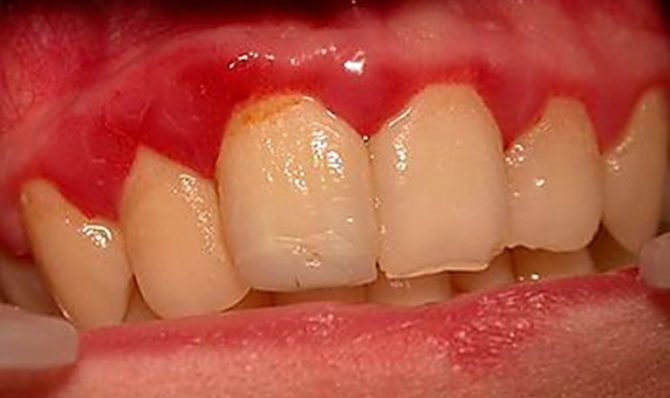
Catarrhal gingivitis
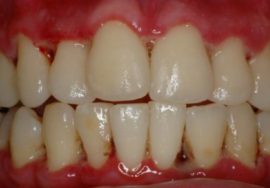
The main reason for this form of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which causes an accumulation of microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Especially a lot of pathological contents accumulate in the area of the necks of the teeth, where they interact with the gum, provoking the appearance of signs of inflammation in it. This is the most common form of the disease.
The causes of this form of pathology, dentists include a deficiency of vitamin C, diseases of the blood coagulation system and blood formation, hormonal imbalance.
Signs of the disease include:
- swelling of the edge of the gums and papillae between the teeth;
- hyperemia of the visible periodontal period or its blueness;
- bleeding gums during brushing;
- pain during oral hygiene;
- accumulations of plaque and tartar are visible on the dentition.
Types of Catarrhal Gingivitis
Catarrhal gingivitis can conditionally have several types. Doctors distinguish the following types of disease:
- Generalized. The inflammatory process affects a significant surface of the gums on the upper and lower jaw. This form is usually caused by internal health problems.
- Localized. The disease is characterized by the fact that the mucous tissue covering the roots of the teeth becomes inflamed only in the area of several of them, and the causes of the pathological process are local in nature.
The course of catarrhal gingivitis can be acute and chronic. Treatment options may vary. It is imperative to follow the doctor's instructions!
The acute nature of this form of the disease is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, rapidly progressing development, severe bleeding and pain during hygiene procedures in the oral cavity. Gums, however, are usually highly hyperemic. Often, patients suffering from acute catarrhal gingivitis generally refuse to brush their teeth twice a day, which only complicates the situation.
Acute catarrhal gingivitis usually develops once and does not recur if adequate therapy is carried out in time. It can develop in young children during teething. Often, gum disease is associated with childhood infectious diseases. Sometimes this form of gingivitis is a harbinger of viral stomatitis or a manifestation of an allergic reaction.
If you do not pay attention to the treatment of acute gingivitis in time, the pathological process can go to the chronic stage, which is characterized by systematic flaccid inflammation of the gum tissue with periodic exacerbations.
The chronic nature of this form of the disease is characterized by mild manifestations over a long time period. Gingivitis in this form has moderate signs of bleeding gums, slight pain during brushing, the color of the gums is almost unchanged, with the exception of slight cyanosis. When the body's defenses are reduced, the symptoms of the disease worsen. As a rule, this occurs during periods of colds.
Treatment of catarrhal gingivitis
Treatment of the disease should be aimed at eliminating soft microbial plaque and hard tartar. The first is easily removed during ordinary oral hygiene procedures. And you can get rid of tartar and partially mineralized plaque only with the help of a dentist.
If the necessary hygiene measures are absent, the microbial coating is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus salts, which are present in saliva.As a result, the plaque hardens, attaches tightly to the tooth and is no longer removed with a toothbrush.
How to treat catarrhal gingivitis? After removing the dental plaque, the dentist will prescribe medications for gingivitis, rinsing with anti-inflammatory drugs and special gel applications that can be done at home. Such anti-inflammatory therapy should last at least ten days, and then you need to visit the dentist for a second examination.
Important: remember that just stopping gum disease is not enough. It will reappear very soon if you do not start brushing your teeth correctly. To avoid relapse of gingivitis, it is important to sanitize all carious teeth, as they are breeding grounds for infection.
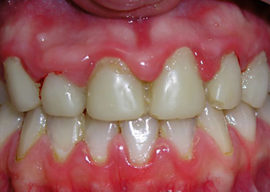
Ulcerative necrotic gingivitis
This form of the disease can also be acute and chronic. It develops due to poor oral hygiene. The mass of bacterial plaque on the teeth increases greatly, as a result of which the mucous membrane is necrotic and ulcerated. Most often, this form of inflammation occurs against the background of a sharp weakening of the body's defenses or severe chronic diseases.
Signs of ulcerative gingivitis include:
- plaque on the gum white or yellow;
- ulcerated sections of the mucosa covering the edges of the jaws;
- papilla necrosis;
- hyperthermia;
- lack of appetite;
- headache;
- bad breath from the mouth;
- bleeding gums and pain in them.
If the disease is chronic, these gingivitis symptoms are less pronounced.
How to treat ulcerative necrotic gingivitis
Therapy of this form of gingivitis is carried out urgently in the dentist's office. First of all, the doctor removes necrotic plaque and dental deposits. Then the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial therapy, rinsing with antiseptics and application. It should be treated strictly in accordance with its requirements.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
This is a chronic form of the inflammatory process in which the gums increase in volume. The cause of this phenomenon can be both its fibrous growth and its edema. Usually this kind of pathology is found at the gingival margin in the area of the outer surface of the upper and lower teeth.
Pathology most often traditionally develops with functional disorders of the endocrine system, hormonal disorders in pregnant women and adolescents, with malocclusion, inaccurate fillings and crowns. Sometimes gingivitis is the result of long-term chronic catarrhal gingivitis.
Symptoms of this inflammatory disease differ depending on its form. Edematous hypertrophic gingivitis is manifested by swelling of the gingival papillae. Therefore, they have a loose structure (most often this form of gingivitis develops against a background of hormonal imbalance). At the first stage of treatment, the doctor will remove the dental deposits and prescribe treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of insignificant results, the doctor will apply sclerotherapy.
How to treat advanced gingivitis in adults? The fibrous form of such an inflammatory process is characterized by the dense structure of the gingival papillae. The doctor will begin treatment of fibrous gingivitis with the elimination of traumatic factors and the removal of soft and hard deposits from the teeth. In the next step, treatment will include:
- Tissue excision.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy (treatment of gingivitis with dressings with hormonal drugs).
For a long time, the current edematous form of the inflammatory process can turn into hypertrophic.
Treatment of gingivitis with drugs at home in adults
Treatment of gingivitis in adults at home involves the treatment of anti-inflammatory drugs with a catarrhal form of the disease. And then only after the dentist removes hard dental deposits in the clinic. It is impossible to carry out this procedure yourself and at home.
How to cure gingivitis? Complicated forms of gingivitis are strictly forbidden to be treated independently. With an ulcerative necrotic or hypertrophic process, it is not enough to treat only the manifestations of the disease, for example, bleeding gums, it is necessary to eliminate the cause. Otherwise, the disease will return again.
The advertised toothpastes and rinses with chamomile decoctions and infusions in the treatment of gingivitis in adults at home will not help if you do not first remove the soft coating and hard deposits from the teeth. Therefore, this is not a cure for acute or chronic gingivitis.
Treatment for gum disease during pregnancy
Catarrhal gingivitis in expectant mothers can be treated in the same way as in other patients, with the exception of ingestion of pharmacological preparations not approved by the gynecologist. If there is a hypertrophic form, only local symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Traditional medicine recommends that pregnant women drink more milk, take a rosehip broth, fruit juices and rinse their mouth with saline solutions. These funds should help expectant mothers deal with bleeding gums.
Treatment of gingivitis in children
The dentist conducts professional oral hygiene for children. In severe cases, treatment of childhood gingivitis is carried out by the same methods as adult gingivitis. If one of the causes of the disease was a malocclusion, the child is referred to an orthodontist.
In order to prevent inflammation of the gums in the child, it is necessary to teach him oral hygiene. In children's dental clinics, such lessons are held in a playful way.
Treatment of gingivitis folk remedies
 Treatment of the inflammatory process with folk remedies is not excluded, but they can be used only as an additional anti-inflammatory treatment. In no case can such remedies be independent therapeutic methods and cannot cure the disease.
Treatment of the inflammatory process with folk remedies is not excluded, but they can be used only as an additional anti-inflammatory treatment. In no case can such remedies be independent therapeutic methods and cannot cure the disease.
As a means of traditional medicine, decoctions and infusions of St. John's wort, eucalyptus and other medicinal plants are used to rinse the oral cavity.
It is preferable to use store-bought medicines with herbs of factory production, which can be bought in the pharmacy chain.
Do not run your teeth so that you do not subsequently suffer from manifestations of gingivitis.