Why is a lump formed on the gum and how to get rid of it
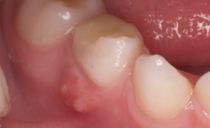
The surface of a healthy gum is pink and smooth. When talking or chewing food, a person should not feel pain. If a white bump appears on the gum, it means that some kind of inflammatory process develops in it. The causes of the appearance of neoplasms can be different, as well as the accompanying symptoms.
Content
Probable reasons
Among the reasons for the appearance of cones on the gums in adults and children, the leading position is occupied by non-compliance with hygiene. When brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth with disinfecting solutions, plaque is removed not only from the enamel, but also from the soft gingival tissues. If you do not clean the oral cavity, food debris and the microbes living in them accumulate in the form of a film, under which even more favorable conditions are created for the propagation of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Gum patches near such deposits can become inflamed and swollen.
If a lump appears on the jaw, then one of the following diseases has developed in the oral cavity:
- Periodontitis
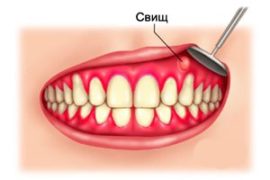
- Intraday fistula.
- Periodontitis.
- Periostitis.
- Gingivitis.
- Epulis.
Sometimes gum tissue densification is formed for non-infectious reasons:
- Exostosis.
- Jaw injury, hematoma.
- Chemical or thermal burn.
- Side effect of drugs.
- Oncological diseases.
In children, bumps in the mouth, localized on the upper or lower jaw, can be a completely natural phenomenon - a harbinger of teething of milk or molars.
Swelling and redness of the gums in the absence of infection is a sign of immunity, for example, leukocyte utilization of damaged or regenerated cells. An infectious process can occur as a complication of non-infectious inflammation, when pathogens enter through a burn or wound.
A lump on the gum from the inside or outside can be a sign of flux, gingivitis, periostitis. Therefore, you will have to go to the dentist to clarify the diagnosis, and for quick quality treatment to avoid dangerous consequences.
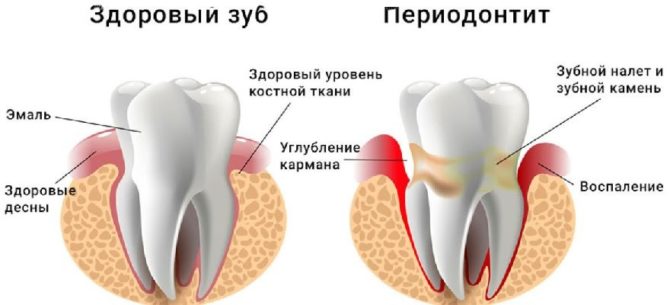
Periodontitis and intra-gingival fistula development
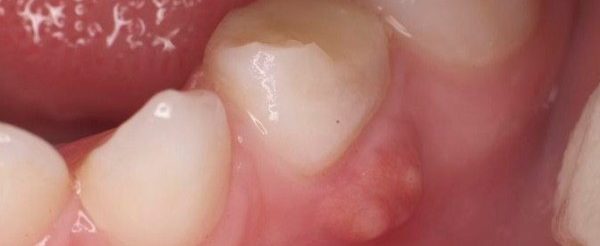
The destruction of the complex of tissues that hold the tooth in the gum, accompanied by the formation of a bump on the jaw under the tooth, is called periodontitis. The disease is accompanied by damage to the ligaments of the tooth, partial resorption of hard tissues.
The infectious form of this disease is most often associated with the progression of caries, although such processes can also develop with injuries or exposure to toxic medications on the dentition. Manifestations of the disease can be diverse: from a slight soreness to a sharp pain syndrome with loosening of the tooth and fever.
Hyperplasia of the gingival tissue can lead to suppuration. If a cone with pus appears on the gum, it may be a fistula, which is the path of purulent contents outward. If it is closed and pus does not leak, the feeling of pain can be unbearable. As the fluid gradually escapes from the open fistula, the person feels relief.
The treatment of periodontitis is carried out in stages: from the complete cleansing of the jaw from pus to the filling of the dental canals or the removal of an excessively shattered or damaged tooth. Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents are used, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
If periodontitis remained untreated and went into a chronic form, get rid of the fistula is possible only through surgical treatment.
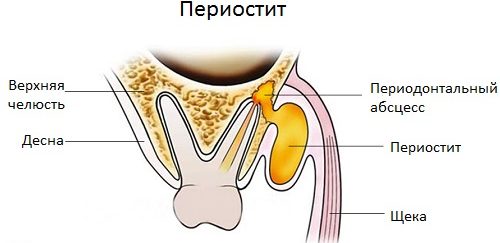
Periostitis
The appearance of a red compacted cone on the gum, which is very painful and causes swelling of the neighboring lymph nodes and cheek, indicates periostitis or the development of flux. This disease can lead to an outflow of purulent contents into the oral cavity, in which a white ball appears on top of the gum. In addition, pus can break through to the internal tissues of the tooth, which can cause very violent inflammation, fraught with tooth loss and the spread of infection throughout the body.
Therapy for periostitis includes the removal of inflammation and the disinfection of dentition. As well as long-term (up to 2 months) phased filling of seals of temporary and permanent type.
Periodontitis
A purulent lump on the gum above the tooth can be a sign of a very insidious disease with a long course and irreversible consequences - periodontitis. With a degenerative change in the alveolar process, which provides fixation of the root in the alveolus, suppurations over the teeth may appear, from which fetid fluid is constantly released. Tissue degradation can be associated with inadequate hygiene, and with internal diseases of the connective tissues.
In the treatment of periodontitis in the initial stages, it is enough to carry out professional toothbrushing and to ensure that the patient continues to regularly observe oral hygiene. The advanced stages of the disease, accompanied by loosening of the dentition and accumulation of pus, can only be treated by removing the teeth or surgical restoration of the alveolar processes.
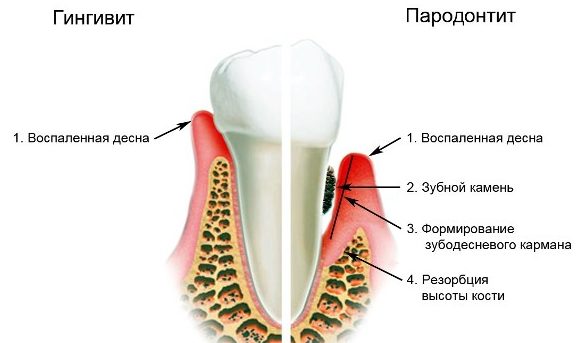
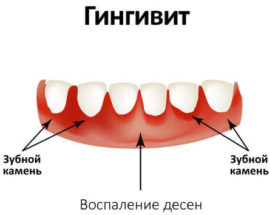
Gingivitis
If a lump appears on the gum, but it does not hurt, then its appearance is caused by gingivitis. This is an inflammatory process in which only the gum is involved, and the periodontal apparatus around the tooth remains unaffected.
The main symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding, swelling, desquamation of the epithelium. The disease is often accompanied by halitosis, it is provoked by a biofilm from accumulated pathogenic microbes, which may be the root cause of gingivitis. In rare cases, the causes of pathology lie in internal malfunctions of metabolic and endocrine origin.
When treating gingivitis, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of its occurrence. Therefore, professional cleaning of the oral cavity, diagnosis and treatment of metabolic disorders. To relieve inflammation and limit the spread of pathogens, antibiotics are prescribed. If severe pain appears, analgesics are used.
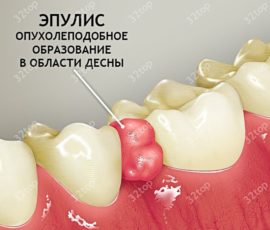
Epulis
Epulis is a small ball connected to the gum leg and arising due to prolonged mechanical stress on one of the sections of the dentition. More often, such a lump appears on the lower jaw, inside it there may be different histological elements.
In young children, cutting teeth provoke this pathology, and in adults it occurs when wearing poor-quality and uncomfortable prostheses, the presence of the sharp side of a broken tooth. Among patients with this diagnosis, there are much more women.
No matter how fast the epulis grows, whether there is pain and bleeding when pressed, it can only be cured surgically. First, the formation is excised under local anesthesia, then the damaged area is cauterized. In modern dentistry, this is done with a laser. A very important condition for treatment is the removal of the factor that provoked the pathology.
Exostosis
A solid bump on the gum, similar to a bone, can be exostosis - a continuation of bone tissue, slightly protruding outward. This is either a congenital anomaly of the bone, which crawled out even during development in the womb, or an acquired defect.During life, these abnormal bones can grow after injuries of the dentition in the home or after unsuccessful dental procedures.
Such a hard lump on the gum (exostosis) may not hurt, but there is no guarantee that in the future it will not degenerate into a malignant formation. Therefore, it must be shown to the doctor, it is impossible to treat this pathology at home. If the dentist counts a bone that has come out near a tooth that is suspicious of an oncological plan, an operation will be necessary.
Hematoma on the gum
When you hit the jaw on the gum near the tooth, a red or blue cone may occur. Such a lump can jump up after tooth extraction. Inside, it is filled with blood pouring out of damaged blood vessels.
A hematoma is usually not particularly dangerous, because there are special mechanisms in the body to cleanse tissues of blood clots. Therefore, after some time, the seal should disappear, but if the bump remains, you should go to the doctor.
Oncological diseases
A lump that jumped on the upper or lower gum under the tooth should not be underestimated, since such a lump may be a sign of cancer. Men are more susceptible to this pathology, but it can occur in any person with risk factors.
Oncological diseases are predisposed by addiction, radiation, chemical pollution, malnutrition, genetic predisposition and age-related changes.
At first, the cancerous cone on the gum above the tooth does not hurt, because of which patients may not be aware of the seriousness of the disease or not notice it at all. Over time, pain appears that spreads to the tongue, jaw tissue, cheeks, and any parts of the head. New bumps may appear - the growth of those that were previously. Tissues in the area where the tumor formed begin to break down.
The bumps on the gum around the tooth can have a very different origin, so it is almost impossible to determine why this seal appeared at home. In dentistry, they not only examine the formation, but also evaluate its consistency when pressed, bleeding when pressed, tooth mobility.
It is necessary to appoint additional examinations, of which X-ray and CT are very informative. If the inflammatory process is diagnosed, it is necessary to achieve complete disinfection of the oral cavity and relieve inflammation. With bone abnormalities, neoplasms in the soft tissues, a very thorough treatment should be carried out, which is not available at home.