Infiltration anesthesia: types, technique, advantages and disadvantages
Therapy of pathologies and injuries of the soft tissues of the face, therapeutic manipulations on the teeth are carried out without the use of medications that block the conductivity of nerve endings in only a few cases: modern medicine has an impressive range of painkillers that facilitate surgical interventions. Among the most effective methods used in the implementation of these actions is infiltration anesthesia in dentistry.
The procedure under consideration is performed by the dentist independently (without involving additional medical staff) and allows you to achieve the desired result in a few minutes.
Content
What is infiltration anesthesia
Infiltration anesthesia is a type of local anesthesia given by injection (using a syringe). A solution of a special drug saturates the required tissue site and interrupts the transmission of nerve impulses. The closer the needle is inserted into the neurovascular bundle, the faster the expected effect occurs.
The procedure is recognized as safe and relatively uncomplicated. Modern anesthetics allow clinic specialists to perform the necessary manipulations within 45-60 minutes without causing discomfort and pain to the patient.
Indications for the use of infiltration anesthesia in maxillofacial surgery and dentistry are:
- suturing;
- extraction (treatment) of teeth - permanent on the upper (less often lower) jaw, milk on both arches;
- opening of abscesses localized under the skin and on the oral mucosa;
- cosmetic manipulations (elimination of minor defects);
- removal of tumors (benign);
- additional support for mandibular analgesia.
To conduct an infiltration type of anesthesia, thin short needles are used; administered drugs - procaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine, ultracaine, trimecaine.
An absolute contraindication to the use of infiltration anesthesia is the presence in the patient's history of individual intolerance to the medicines used.
The fact of a possible manifestation of allergic reactions when using anesthetics is not a reason for refusing treatment with pain relief. In these cases, experts suggest replacing local anesthesia with general.
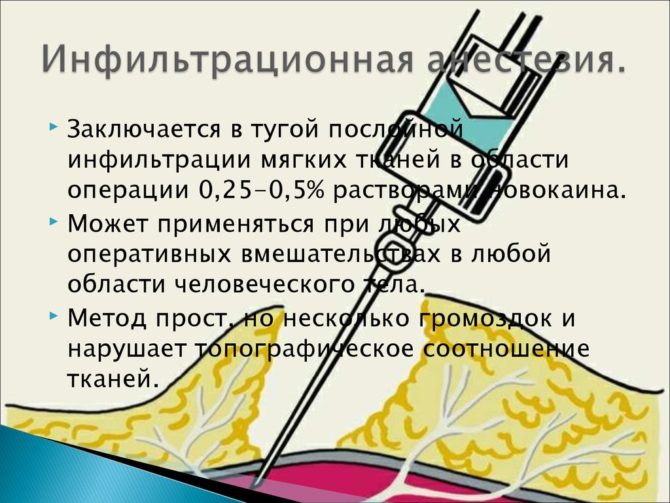
Technique for conducting an infiltration type of anesthesia
When anesthetizing soft tissues of the face, an antiseptic treatment of the skin is performed before applying an infiltration anesthesia.
The introduction of anesthetic passes in layers:
- The procedure begins with injecting the solution with a two-cube (two-milliliter) syringe along the intended line of dissection of the tissues. In the thickness of the skin in this way creates an effect called "lemon peel."
- Repeated injections are carried out using a 5 (10) milliliter syringe through areas already infiltrated by the anesthetic. The solution is released in subcutaneous fatty tissue, covering soft tissues that are outside the area of surgical intervention.
- The specialist conducts further layer-by-layer saturation of tissues by using the introduction technique according to A.V. Vishnevsky (method of creeping infiltrate).
In dentistry, the scheme for conducting the most commonly used type of anesthesia consists of 5 stages:
- Treatment of mucous membranes in the injection area by the use of antiseptics.
- The doctor, sitting to the right of the patient, with the help of a spatula or a mirror pushes the patient's lip (cheek).
- The syringe needle is located on the border between the movable and fixed parts of the gums at an angle of 45º with respect to the alveolar ridge.
- A needle section directed towards the jaw bone is carefully inserted into the soft tissues of the transitional fold until it stops. The level of immersion depends on the injection site and varies from 5 to 15 millimeters.
- Conducting tissue saturation with a drug is carried out smoothly or under pressure (quickly).
The accuracy of the technique of the above scheme allows minimally injuring the area of infiltration.
Classification
Dentistry and facial surgery divide the considered infiltration technique into several types. Classification is determined by the area of influence of the anesthetic.
There are 2 types of infiltration anesthesia:
- Direct - the introduction of a solution into the tissues in the area of which manipulation is planned. The method is recommended for use in facial surgery.
- Diffuse (indirect) - infiltration of an area located at an insignificant distance from the place of dental intervention. By spreading (from the center to the periphery), the active substance reaches the deep layers of tissues. It is more often involved in the treatment of upper jaw teeth.
Depending on the injection site, several types of infiltration anesthesia are distinguished: subperiosteal, intrapapillary, intrapulparic and others.
Submucosal (supraperiosteal)
The type of administration is the most common. Another name for the type of anesthesia is intrapapillary. The main technique of manipulation is discussed above.
A feature of the described type of procedure are the following principles:
- from the palatine side, the injection can be applied at the convergence site of the alveolar and palatine processes of the upper jaw;
- on the lower jaw, the introduction is carried out in the area of transition to the hyoid tissue of the mucous membranes of the alveolar process.
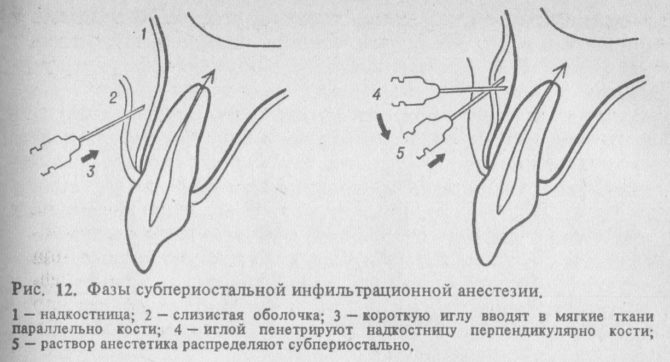
Subperiostal
A type of anesthesia is also called subperiosteal. The technique is recommended to be used if it is necessary to obtain deep analgesia. The engagement technique consists of 4 stages:
- the introduction of a needle under the mucous membrane at the border of the gum parts (in the transitional fold);
- saturation of tissues with a part of the drug;
- periosteum piercing;
Before introducing the rest of the solution, the experts advance the needle at an angle of about 45 ° to the root of the tooth.
Spongy Intraceptal
The second name of the procedure is intraosseous.
Infiltration anesthesia is performed by inserting a needle into the base of the gingival papilla, at an angle to the axis of the molar. At the level of the interdental septum, a small amount of the substance is released. When the syringe passes through the cortical plate, the rest of the active substance is excreted.
In the absence of the expected effect, the method is recommended to be used on the opposite side of the tooth.
Intraligamental
The technique involves the introduction of a solution into the region of the periodontal gap. The duration of the injection is up to 2 minutes, since the injected liquid meets significant resistance. Experts advise using computer syringes in combination with ultra-thin needles - this greatly simplifies the procedure.
Intrapulpar
One of the most reliable types of infiltration method. To conduct it, the dentist opens the pulp chamber (the diameter of the hole should correspond to the cross section of the needle).
The success of the method is determined by the absence of leaks of the active substance around the injection tool.
Additional views
In addition to the above, the types of anesthesia considered also include:
- “Block field” - it is used in case of presence of foci of inflammation in the area of the periandibular soft tissues;
- plexual - the necessary manipulation to achieve pain relief - injection into the alveolar anterior and upper middle plexus;
- intrapapillary - the introduction of an anesthetic solution is carried out directly into the base of the gingival interdental papillae;
- Druk anesthesia - placement in a carious cavity of a tampon moistened with an antiseptic solution.
Maxillary Infiltration Anesthesia
Anesthesia according to the infiltration principle is often used in the treatment of the upper jaw, since its bone is characterized by a relatively small thickness, high porosity.
For the purpose of anesthesia of one incisor or the first premolar, a needle is inserted between the stationary and moving parts of the gum slightly above the apex of the tooth root.
For infiltration blocking of the nerve endings of the second premolars and molars, the anesthetic is fed to the root base. The injection of a syringe is carried out between requiring treatment (removal) and the adjacent teeth.
Additionally, it is recommended to stop the nerves located in the corner of the convergence of the palatine and alveolar processes. When the latter is anesthetized, up to 0.3 milliliters of the drug solution is injected under the mucosa (the direction of entry is from bottom to top)
Anesthesia of the lower jaw
Infiltration anesthesia on the lower jaw is rarely used. This is due to the peculiarity of the bone structure: its tissues are more dense than the upper.
The maximum micropores contains the anterior part of the jawbone; therefore, the type of anesthesia considered is more often used in the treatment (removal) of incisors.
Anesthetic is injected into the crease of the transition to the base of the roots of the problem tooth.
If necessary, stop the nerve endings of all incisors, the needle is inserted similarly, after which it is given an almost horizontal position. Saturating the tissue with a solution, injection tools slowly move left and right (to the side of the fangs).
In order to infiltrate anesthetization of the lingual nerve, the tissue under the mucosa in the area of the transition to the bottom of the oral cavity of the alveolar ridge is saturated with medication (next to a diseased tooth). This type of anesthesia is auxiliary for small surgeries, before removal
Conductor infiltration anesthesia
 The conduction type of anesthesia is used in dental practice if a direct effect on the nerves is necessary (during serious surgical procedures, in case of emergency intervention in the gum tissue).
The conduction type of anesthesia is used in dental practice if a direct effect on the nerves is necessary (during serious surgical procedures, in case of emergency intervention in the gum tissue).
The procedure is based on the introduction of an anesthetic (a solution of novocaine, novocaine-containing drugs) directly into the nerve trunk or into the tissue surrounding it.
The active substance is introduced extremely slowly, in order to avoid injury.
When blocking the nerve endings of the lower jaw, 3 types of conduction anesthesia are used:
- mandibular;
- torusal;
- submental (mental).
Conduction anesthesia is one of the most difficult types of anesthesia.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any type of nerve fiber blockage, infiltration anesthesia has positive and negative sides.
Among the advantages of the technique:
- simplicity of engagement technique;
- rapid anesthesia;
- the possibility of using anesthetics in minimal concentrations;
- long period of action of anesthesia;
- the possibility of introducing new doses of the drug.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- the likelihood of damage to blood vessels and nerve trunks;
- insufficient pain relief with the rapid administration of the drug;
- the risk of allergic reactions;
- accidental breaking of the needle;
- an overdose of anesthetic with an incorrect therapy regimen.
Most of the above disadvantages of the anesthesia method can cause complications.
According to statistics, up to 90% of the population of our country postpone a visit to the dentist because of fear of possible pain. The anesthesia method considered is one of the best ways to ensure proper analgesia.