Leukoplakia of the oral mucosa and tongue: forms, causes, symptoms, treatment
Oral leukoplakia is a disease that affects the mucous membrane and is characterized by its visual and structural change. In the initial stages, the pathology is manifested by keratinization and coating with a whitish coating of the mucous membrane of the palate, gums, tongue, and inside of the cheeks. In the future, the disease can "degenerate" into a malignant tumor formation.
Content
Causes
Experts identify several main factors that provoke the development of leukoplakia of the oral cavity. Most often, the cause of the development of the disease is thermal damage or chemical irritation of the mucosa. A similar effect is exerted by smoking (smoker's leukoplakia), drinking, disruption of diet (excess of spicy, excessively hot, sour foods).
The most dangerous is the so-called smoker's leukoplakia, which is common among adult patients. Smoking provokes the occurrence of several forms of pathology at once and increases the risk of cancer.
Other factors provoking the development of leukoplakia include:
- Mechanical injury with damage to the epithelial layer. These include a bruise, a burn of the gums, biting the tongue, malocclusion, chipped teeth, improperly placed correction systems, for example, braces.
- The formation in the oral cavity of an environment favorable for the development of the disease. Such is the galvanic medium that occurs in the presence of metal crowns. Oxidation of the metal provokes persistent irritation of the mucosa and degeneration of the epithelial layer.
- Leukoplakia can be the result of the use of a number of medications, a lack of vitamin A, iron.
- Pathology is provoked by a number of diseases of internal organs: diseases of the digestive tract, pathology of the endocrine system (hormonal disruptions, diabetes). And also the hereditary factor affects the development of the disease.
Symptoms of oral leukoplakia
Symptoms of oral leukoplakia vary depending on the degree of development of the pathology. General symptoms are expressed in the following manifestations:
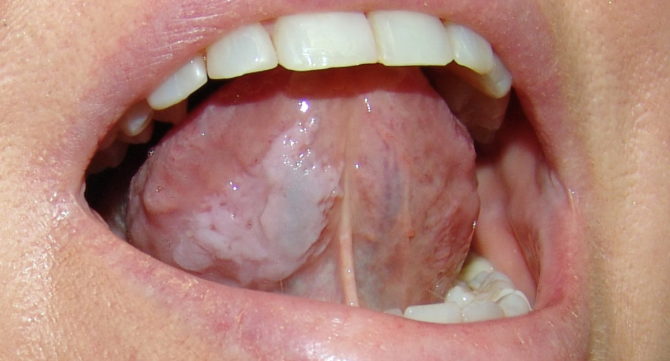
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of gray-white or whitish plaque, which is formed from dead epithelial cells. Foci of lesion in a small amount are concentrated on the tongue, gums, palate, cheeks from the inside, lips, in the hyoid area. On palpation, keratinization of the mucosa is felt, compaction in the area of plaques.
- The development of pathology is accompanied by the proliferation of lesions, their size increases in comparison with a healthy epithelium. Over time, keratinized plaques become more sensitive and painful.
- Spreading of spots is accompanied by a feeling of tightness, dryness and firm roughness. Sensations intensify under the influence of any stimulus.
The uncontrolled course of leukoplakia leads to its steady progression and the appearance of painful ulcerative and erosive lesions.
Varieties and forms of oral leukoplakia
The main forms of oral leukoplakia:
- Flat.
- Verrucous.
- Erosive.
- Leukoplakia Tappeynera.
- Soft.
Oral flat leukoplakia
The most common form of the disease is flat or simple leukoplakia of the oral cavity. It is often characterized as the initial stage of a pathological condition. At this stage of development, pathology does not manifest pronounced soreness.
The initial phase of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of whitish or gray-white plaques, irregular-shaped bands located on the tongue, sky, inner surface of the cheeks, in the corners of the mouth. The plaques are dry and rough, without pronounced elevation and hardening. Often there is a tightness, burning, excessive dryness in the area of damaged areas.
Simple leukoplakia often affects the tongue, resulting in a decrease in its sensitivity and taste perception. Inflammatory processes at this stage of the development of the disease do not occur. In most cases, this kind of pathology proceeds without a deterioration in overall well-being, complications and can accompany a person throughout life.
Verrucose form
The uncontrolled course of leukoplakia with a constant traumatic effect on the mucous membrane - irritation by chips on the teeth, irregular dentures, the use of excessively hot food and fluid - provokes its development and the transformation of the simple form of the disease into a verrucous one.
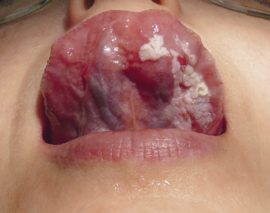 The dominant sign of the conversion of simple leukoplakia to verrucous is a pronounced keratinization and elevation of the upper layer of epithelial cells of the affected area. At this stage of the disease, the plaques significantly rise above the healthy epithelium, with palpation, a compaction is clearly felt.
The dominant sign of the conversion of simple leukoplakia to verrucous is a pronounced keratinization and elevation of the upper layer of epithelial cells of the affected area. At this stage of the disease, the plaques significantly rise above the healthy epithelium, with palpation, a compaction is clearly felt.
Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity is accompanied by a pronounced feeling of tightness and dryness, the occurrence of painful sensations during meals.
By external signs, leukoplakia is of two types:
- Plaque. Plaque patches appear on the oral mucosa. Plaques are characterized by pronounced roughness, density, elevation above a healthy epithelium. Their color varies from milky to cyanotic.
- Warty. Foci of lesion appear on the mucosa, similar to warts. Compared with the plaque form of the disease, the wart is characterized by the appearance of more keratinized, tuberous seals. Formations rise above healthy epithelial cells by 2-3 mm, most often have a gray-white hue.
Verrucous form of the disease more often than others turns into a malignant lesion of the epithelium of the mucosa.
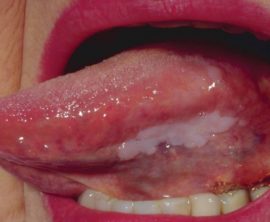
Erosive stage
The erosive form of the disease occurs with its progression, prolonged exposure to negative factors on epithelial tissues. This stage of leukoplakia of the oral cavity is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
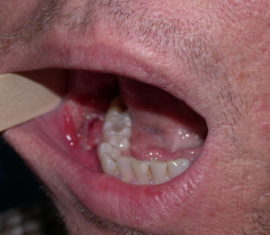 There is a pronounced soreness, which is amplified when any type of irritant enters the lesion. Eating food, alcohol and hot drinks provokes the occurrence of pain.
There is a pronounced soreness, which is amplified when any type of irritant enters the lesion. Eating food, alcohol and hot drinks provokes the occurrence of pain.- Externally, the disease is manifested by the appearance on the affected areas of cracks and ulcers, erosive foci. Around erosive lesions localized inflammatory foci, often accompanied by bleeding.
- Unpleasant sensations persist even at rest. Burning, excessive dryness and roughness are felt. The development of a lesion at the base of the tongue causes a sore throat, impaired speech (coughing occurs).
This type of pathological condition has the highest risk of relapse. The erosive stage of the disease can be treated with great difficulty, ulcerative lesions heal for a very long time.
Mild oral leukoplakia
This type of pathology is a benign neoplasm. The main prerequisites for the development of mild leukoplakia of the oral cavity are hormonal disruptions, a violation of the psychoemotional background, chronic overwork.
Visually, a slight elevation of white plaques over a healthy epithelium is noted. The lesions are rough and painless. There is a slight compaction and dryness of the affected tissue. With damage to the lateral surfaces of the tongue, sensitivity to temperature influences decreases, taste perception is disturbed.
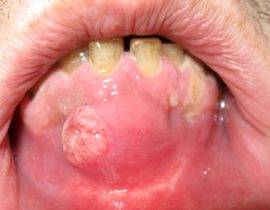 The mild form of pathology is divided into several varieties:
The mild form of pathology is divided into several varieties:
- Partial (focal), manifested by the occurrence of affected areas in the form of foci localized in certain places.
- Diffuse variety, characterized by "spreading" of plaques over the entire surface of the mucosa. Formations have a spongy, porous surface, loose structure, increased size. The lesions are painless, but interfere with the conversation, eating, creating a feeling of "excess" tissue.
Leukoplakia Tappeynera (smoker)
This form of the disease is most susceptible to adult patients, especially smokers with experience. Tappeiner's leukoplakia is provoked by the decay products of tobacco and chemical irritation of the mucosa with tobacco smoke.
In most cases, formations affect the sky and gingival tissues located next to it. Large folded plaques of brown or grayish color appear in the oral cavity. Affected areas are painless.
The appearance of formations leads to blockage of the salivary glands, the appearance of reddish nodules. This condition causes excessive dry mouth, "thick" saliva.
It is not difficult to treat this kind of leukoplakia in the oral cavity. It is necessary to give up smoking, first reducing its consumption, and then completely stopping smoking. Getting rid of a negative habit leads to the complete disappearance of the pathological condition.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made on the basis of examination and questioning of the patient. Mandatory diagnostic tests confirming the diagnosis include:
- Cytology - the collection of epithelial cells to detect cancerous lesions.
- A histology fence for biopsy, which allows the examination of affected epithelial tissues for the detection of cancer cells.
- Blood from a vein.
Additional clarifying studies can distinguish leukoplakia from other pathologies.
The classic treatment for leukoplakia of the oral cavity
The choice of treatment for leukoplakia of the oral cavity depends on the symptoms, the form of pathology, its severity. Initially, it is necessary to eliminate the negative factors that trigger the onset of the disease: giving up bad habits, changing the diet.
A productive treatment of the disease in the hospital allows a number of physiotherapy procedures. Such events include:
- Diathermocoagulation intervention to remove keratinized plaques. After a course of procedures, healing of the mucosa occurs within 10 days.
- Freezing the affected epithelial layer of the oral cavity (cryodestruction) for 1 minute. The course of treatment is 1 week.
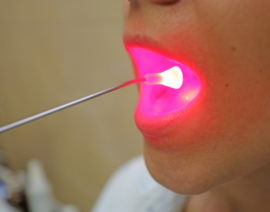
- Carrying out photodynamic therapy (FTD). Pathogenic cells are destroyed by exposure to a light wave.
The treatment regimen includes taking medications aimed at stopping infectious processes and inflammation. Be sure to carry out local treatment of the mucous membrane.
Features of the treatment of leukoplakia of the tongue
With the localization of the disease in the tongue, an oral cavity sanitation is necessarily carried out. In the presence of improperly installed prostheses, fillings, chips on the teeth, polishing of fillings, prostheses (or their replacement), restoration of chipped teeth are carried out. Affected areas are treated with antiseptics and wound healing solutions.
A flat form of the disease is easily treated. Sometimes it is possible to eliminate the pathological plaque by means of laser or radio wave therapy. But if a patient has malignant tumors, the treatment will be carried out in two stages - first they perform an operation, then a long-term radiotherapy is performed.
Upon completion of the treatment course, the patient should remain under outpatient supervision, since leukoplakia of the tongue is characterized by a sluggish course, and symptoms of the disease can appear for several years.
Treatment of leukoplakia of the oral cavity at home
 At home, the treatment of leukoplakia of the oral cavity and tongue must begin with proper hygiene procedures. Use soft bristled toothbrushes. Brushing your teeth and tongue should go smoothly, without excessive intensity. After each meal, rinses, applications with anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties are used. Particularly careful hygiene is required in the treatment of leukoplakia of the tongue.
At home, the treatment of leukoplakia of the oral cavity and tongue must begin with proper hygiene procedures. Use soft bristled toothbrushes. Brushing your teeth and tongue should go smoothly, without excessive intensity. After each meal, rinses, applications with anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties are used. Particularly careful hygiene is required in the treatment of leukoplakia of the tongue.
Affected areas must be treated with antiseptics: Chlorhexidine, Furacilin. Irrigation with antiseptic solutions is carried out up to 5 times a day. The cure of the pathological condition at home is helped by the intake of vitamin complexes containing vitamins A and B groups.
As an additional treatment, folk remedies can be used. Especially effective are decoctions of sage, chamomile, calendula, which have anti-inflammatory and soothing effects. A positive result is achieved when treating the affected areas with sea buckthorn oil and Kalanchoe juice.
Adult patients are advised to consume natural juices, which have a general strengthening effect that enhances immunity. Such drinks include juices from apples, carrots, cabbage. Freshly squeezed drinks are recommended to be diluted with water.
Oral leukoplakia is a pathological condition that should not be allowed to drift. When the first signs of pathology appear, it is necessary to consult a specialist, self-medication is fraught with the development of serious complications and consequences.