White sore throat on tonsils and tonsils: reasons for how to treat
Many pathogens can enter the body through the oral cavity. But most of the microbes die here, meeting on their way glands located on the border between the oral cavity and pharynx. They contain a large amount of lymphoid tissue with many immune cells and antibodies that can capture bacteria, viruses, fungi and render them harmless in place, preventing infection of internal organs.
With a massive attack of the body by microbes on the tonsils of a child or an adult, a yellowish or white coating may appear. Most often this phenomenon is noticed when there is a sore throat and fever. But these symptoms do not always accompany each other, because a variety of diseases can be the cause of a raid.
Content
The causes of plaque formation on tonsils and tonsils
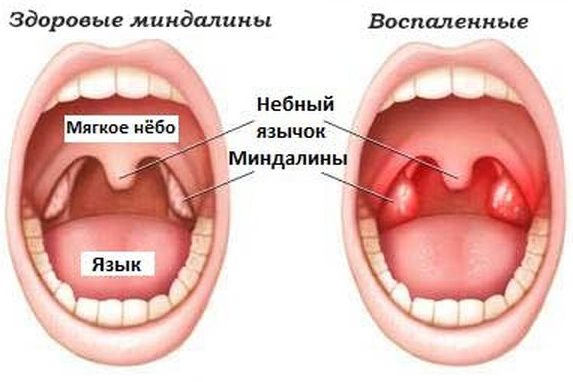
In a healthy person, the entire surface of the mucous membranes in the oral cavity has a pinkish color. In places where there are injuries and inflammatory processes, swelling, redness, and accumulation of plaque of various shades appear.
If plaque between the teeth is more often the result of insufficient hygiene, then its accumulation on the tongue and surface of the tonsils indicates the development of pathology. The exception is cases when a white coating in the throat of a child or adult remains after consuming dairy products. But it quickly disappears with the natural cleansing of the mouth with saliva.
When pathogens massively enter the oral cavity and actively propagate them, a reaction of local immunity is manifested. Lymphocytes formed by the immune system are able to “squeeze” through the epithelium and reach the surface of the tonsils.
Protective cells not only kill germs, but also “get acquainted” with their hereditary information, after which part of the lymphocytes can return into the tonsils to form the immunological memory of the body. If this pathogen again enters the oral cavity, the body can provide a faster and more accurate protective reaction from it.
Many immune cells die when exposed to foreign pathogens and remain for some time on the surface of the throat. Here killed microbes settle. This forms a gray, white or yellow coating on the tonsils and posterior pharyngeal wall. This is not a specific disease and not a particular symptom, but a symptom inherent in many infectious diseases.
Predisposing factors
The appearance of a large amount of white plaque is characteristic of people with weak immunity. Predisposing factors for this phenomenon are:
- Tuberculosis.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Oncological diseases.
- Frequent respiratory infections.
- Taking antibiotics and drugs that suppress the immune system.
- The presence of dental prostheses, under which microbes accumulate.
- Burns of the oral mucosa.
Causes and associated symptoms
It is impossible to determine the cause of the appearance of purulent plaque on the tonsils. For diagnosis, you should always consult a doctor, even if there is no discomfort, fever or other abnormalities. Among the causes of plaque there are very familiar diseases, and there are severe pathologies.
| Diagnosis | Cause of illness | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) | Streptococci, staphylococci, fungi, viruses. | Continuous (with lacunar tonsillitis) or spot (with follicular tonsillitis) white plaque on tonsils, swelling, fever. |
| Chronic tonsillitis | Prolonged inflammation after other diseases. | Purulent plaque on the glands, in gaps. |
| Atypical tonsillitis | Complication of other diseases. | Offensive pale or yellow plaque on one side of the throat, swelling, tenderness of the lymph nodes. |
| Pharyngitis | Pathogenic microbes or throat injuries. | Red throat with white bloom, pain and tickle, fever. |
| ARI | Rhino or adenoviruses. | White plaque on tonsils, often without fever, both in adults and children. |
| Candidiasis | Candida fungus. | Cheesy white coating on tonsils, tongue, cheeks, often without fever. |
| Pharyngomycosis | Candida fungus, mold fungi. | Yellow or white plaque on the glands, accompanied by pain. |
| Diphtheria | Bacillus Leflerra. | Gray or white film coating on the glands against a background of high temperature. |
| Leukoplakia | The reaction of immunity to negative factors. | Horny sore throat. |
| Stomatitis | Bacteria or viruses. | A plaque on one side of the throat, without fever, the mucous membrane is covered with ulcers and hurts. |
Diagnostic Methods Used
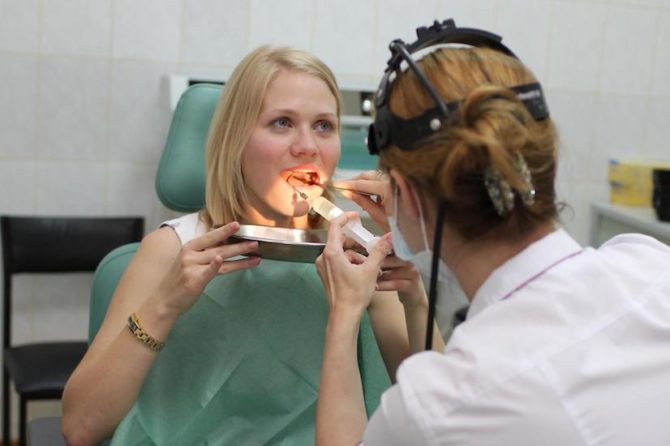
To determine the presence of this symptom, you need to look in the mirror opposite the light source, opening your mouth wide. If there is a film on the tonsils and the back of the throat, you need to go to the doctor. When contacting an otolaryngologist to make a correct diagnosis, you may need these examinations:
- Anamnesis: throat sore or not, whether the body temperature is elevated, how long complaints have arisen.
- Inspection of the oral cavity and the back wall of the throat with the definition of the properties of plaque, its consistency, shade, the nature of the spread in the oral cavity.
- Palpation of the lymph nodes.
- Blood analysis.
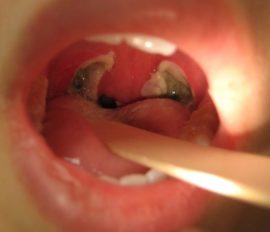
- Taking biological material from the tonsils to identify the causative agent of the disease - a smear with tonsils.
- Analysis of urine.
Often, the disease is quite easily determined by the appearance of the glands. A qualified specialist can make a diagnosis by examining the tonsils and identifying concomitant symptoms. But it is equally important to determine the type of pathogen - that's why a swab from the throat is taken.
Knowing the type of infection, you can choose an antibiotic or antifungal, antiviral agent, to which this pathogen will be susceptible.
Treatment of white plaque on the tonsils and tonsils
With the appearance of plaque on the tonsils, both with pain and without pain, it should be taken into account that this is only a symptom. It will not be possible to get rid of it exclusively by symptomatic therapy, a full-fledged treatment of the disease is necessary, which includes:
- Antibacterial therapy for diphtheria, bacterial tonsillitis, stomatitis of bacterial origin.
- Antiviral therapy for acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis and stomatitis of viral origin.
- Antifungal therapy for pharyngomycosis or thrush.
- Rinse with disinfectant solutions to remove the film from the tonsils and oral cavity.
- Wash off a purulent film from the tonsils using a special syringe with a solution (this removes plaque only in the hospital).
- Antipyretic drugs for fever.
- Pain medication for severe pain in the tonsils.
- Immunomodulators.
- Compliance with the gentle regime for the throat: the exclusion of spicy food, loud and long conversations.
- Drink plenty.
- Taking multivitamins with weak immunity.
It is forbidden to select drugs on your own to remove pus from the tonsils. At home, without diagnosis and consultation with a specialist, it is impossible to determine the type of pathogen, and therefore the direction of treatment.
To treat viral infection with antibiotics is not only impractical, but also dangerous because of a possible decrease in immunity and a long course of the disease with various complications. The same consequences will be from antiviral therapy for mycoses or bacterial infections.
Rinse and rinse
Gland washing is performed by specialists only on an outpatient basis. The procedure requires special care to avoid injuring the tonsils. It is unpleasant and a little painful, so it is especially difficult to wash off a white coating from the baby's throat.
There are contraindications for this procedure: it can not be done during pregnancy, cancer, severe hypertension, open tuberculosis, disorders of the autonomic nervous system. But proper washing effectively clears the white throat for various reasons for plaque.
Rinses can be varied: from cheap home remedies (soda-salt solution, chamomile broth, furatsilinovy solution) to expensive pharmacy. The main condition is the frequency of the manipulations. If the tonsils are rarely washed, the effect will not be achieved, since in a few hours the pus accumulates again.
Regular, frequent rinsing (once an hour or as prescribed by a doctor) allows you to remove both microbes and food debris, immune cells, which eliminates the formation of a favorable environment for the life of microorganisms. The tonsils will become less red and painful.
These procedures will be even more effective if the patient regularly carries out brushing. The plaque accumulating on them also contains bacteria, from there they can spread to the tonsils, to the larynx and even the lungs.
White plaque on tonsils in a child
White plaque on the tonsils of the baby does not always indicate something pathological and terrible. For babies who are breastfed, inconsequential light deposits in the oral cavity are completely natural. If there are no concomitant symptoms, the child is cheerful and eats well, there is nothing to worry about.
It is much worse when a white coating covers the tonsils of a child older than a year, whose diet consists not only of dairy products. Plaque itself is not dangerous, but it is a symptom of a disease, so you need to carefully monitor the condition of the child and take him to the doctor as soon as possible.
On the glands of children, white plaque appears for the same reasons as in adults.
How to identify
 Gland deposits do not occur as a single symptom. The baby can cough, spit out food due to the fact that it hurts to chew and swallow, to breathe through the mouth due to nasal congestion. It is imperative to measure the temperature and examine the baby's throat.
Gland deposits do not occur as a single symptom. The baby can cough, spit out food due to the fact that it hurts to chew and swallow, to breathe through the mouth due to nasal congestion. It is imperative to measure the temperature and examine the baby's throat.
For inspection, use a small flashlight and a teaspoon. Place the child by the window so that light falls on him, and push the spoon on the tongue, but slightly, as this can provoke a gag reflex. It is enough to slightly press the tip of the tongue to the teeth. If during the examination a plaque on the tonsils is detected, consult a doctor.
Treatment features
It is impossible to take a child to the clinic, as some of the diseases are very contagious. It is better to call a doctor at home. The doctor will examine the baby, listen to complaints and, if necessary, issue a referral for a smear from the tonsils. Such an analysis is needed to identify the causative agent of the disease, since treatment tactics depend on its type. In addition to a smear, a blood test, urine, feces are given.
If the disease is bacterial in nature, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. Ampicillin and Augmentin are the safest for the child’s body, but it is strictly forbidden to take them without a doctor’s test, since any medications can be dangerous to the health and life of the child.
If the doctor determines that the plaque is caused by a viral infection, he will prescribe antiviral agents and drugs for local treatment of the tonsils: Vinilin balm, rinses with furatsilin solution, Miramistin antiseptic. Fungal diseases in children are treated comprehensively: with the help of local treatment and antifungal drugs.
If the cause is an enlarged tonsil, the doctor will determine the stage of damage to the adenoids.The first does not need surgery, but adenoids of the second degree are an individual case: if breathing is slightly disturbed, the doctor will try to eliminate the disease on an outpatient basis. With adenoids of the third degree, the child is hospitalized.
Regardless of the prerequisites that led to the appearance of white plaque, the child will be assigned general strengthening physiotherapy. The method of treatment of inflamed tonsils with ultrasound has also established itself.
Possible complications
If the disease is not treated and the plaque on the tonsils is not removed, even if the adult or baby does not have a fever, serious complications can occur. Severe infections, such as diphtheria, can lead to the death of the patient. Improperly cured sore throat is fraught with negative consequences for various body systems and immunity.
When the throat hurts, and white plaque appears on it, it becomes a source of infection that can penetrate the lower parts of the respiratory system, digestive organs, and with the blood flow into any, even the most distant organ. If the pathology cannot be cured in time, in advanced cases, the following complications are possible:
- Inflammation of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs.
- The development of otitis media.
- Abscesses and mediastinitis in the pharynx - the spread of pus in deep tissue.
- Arthritis
- Heart diseases.
- Pathology of the kidneys.
- The transition of the disease into a chronic form.
- With swelling of the larynx, a voice may hoarse.
- Children may lose weight by refusing to eat if it hurts to swallow.
The appearance of white or gray plaque on the tonsils can be a very dangerous signal. This non-specific symptom, characteristic of many infections and some non-communicable diseases, can even harm the body without a fever if it is not eliminated in time.
When the throat is red and very sore, a person immediately pays attention to it. In cases where there is no pain and fever, the pathology remains hidden, and until the patient notices it, it continues to negatively affect the immune system. Therefore, it is worth periodically inspecting the oral cavity to identify any violations on time and prevent dangerous consequences.