Causes, symptoms and treatment of periodontitis
In addition to well-known caries, there are other diseases of the oral cavity. Some of them can occur without pronounced symptoms, and for a long time the patient simply does not pay attention to them. Such pathologies include periodontitis, which requires urgent treatment, since The disease affects soft tissues and can lead to tooth loss.
Content
What is periodontitis
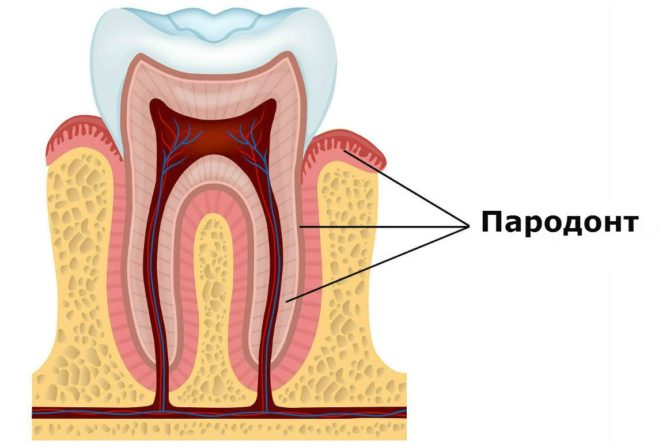
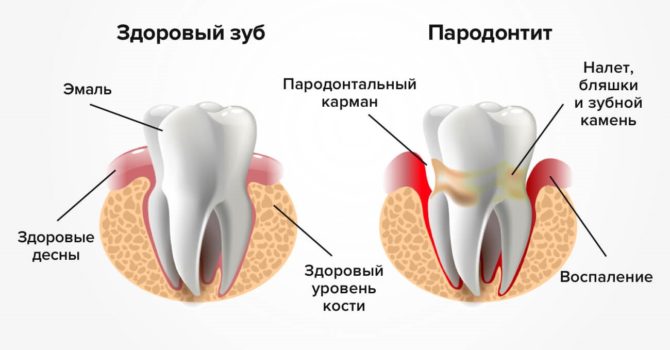
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of periodontium - the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth and holding it in the hole. Periodontium consists of several vessels, canals and nerve fibers that provide protection and nutrition of the tooth.
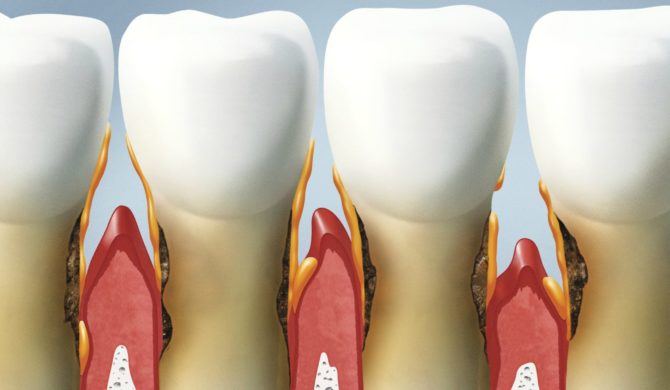
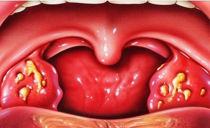
Pathology develops gradually and in most cases appears against the background of other gum diseases. Usually it all starts with gingivitis - gum disease. Tartar provokes it or dense plaque in which pathogenic bacteria actively multiply. If the inflammatory process is not eliminated in time, harmful microorganisms will spread deeper: in the periodontal tissue.
Inflammation contributes to the opening of periodontal pockets through which the infection penetrates closer to the root. The reproduction of bacteria continues, and it is more difficult to stop the process. Gradually, the periodontium becomes loose and lags behind the tooth base, provoking its mobility.
If the treatment of periodontitis is not started in time, it will go into periodontal disease - atrophy of the periodontal structure that is around the tooth. The disease begins with damage to the alveolar process, and bone tissue is gradually involved in the process. The result is the loss of healthy teeth.
Types of Periodontitis
Periodontitis can be divided into several categories, differing in the severity of the disease, the severity of symptoms, the presence or absence of complications. To choose the best treatment, the dentist must establish the form of the disease.
With the course of pathology, two of its forms are distinguished:
- acute: symptoms appear suddenly, the inflammatory process develops quickly, complications in the form of fistulas or damage to teeth and gums occur within two months;
- chronic: periodontitis symptoms are blurry, the inflammatory process is sluggish, tissue destruction occurs slowly and gradually.
Due to the fact that the acute form of periodontitis is characterized by vivid symptoms that cause serious discomfort, treatment usually begins quickly. Chronic disease can proceed unnoticed until it passes into a severe degree.
At the location of the infection, periodontitis can be focal (localized) or generalized. In the first case, a small area of tissue suffers, in the second, a large periodontal area is affected, which greatly complicates the treatment process.
According to the severity of the disease is divided into:
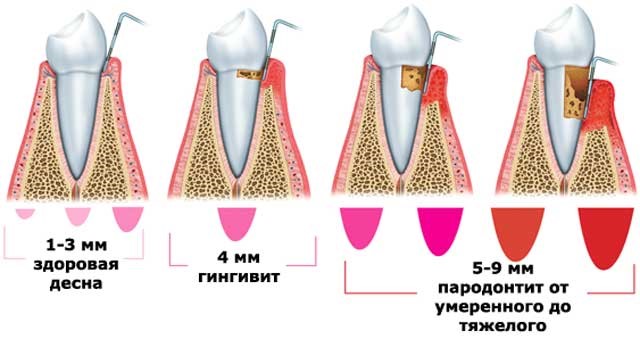
- mild: symptoms are mild and do not cause much anxiety, pockets up to 3 mm deep may appear, bone destruction is negligible;
- middle: the gaps in the pockets are doubled, the root cover is half destroyed, tooth mobility appears;
- severe: rapid deformation of the interdental septum begins, the pockets become large, the food penetrating them provokes purulent abscesses.
Severe periodontitis is practically untreatable, and most often it is impossible to repair damaged tissue.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
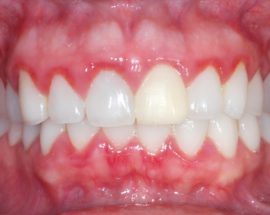
Signs of the disease depend on the localization of the inflammatory process and the degree of neglect of periodontitis. Patient expect:
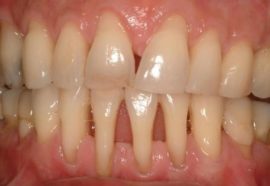 increased sensitivity of enamel;
increased sensitivity of enamel;- bleeding gums during brushing;
- foul odor from the mouth;
- cracks between the teeth in the pockets;
- pain while brushing or chewing;
- exposure of the tooth root;
- increased saliva viscosity;
- minor inflammation of the lymph nodes under the jaw.
The basal part of the enamel darkens, a yellow or brownish dense plaque appears. After the onset of the inflammatory process, the problem area of the gums becomes a dark red hue. Signs of periodontitis increase as the disease progresses.
The inflammatory process affects the general condition of the body. Signs of mild intoxication appear: weakness, headache and dizziness, possibly a slight increase in temperature. Together with inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes, periodontitis may be mistaken for acute respiratory viral infections, so diagnosis is necessary.
Causes of Periodontitis
The main reason for periodontitis is the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria that provoke infection. Various factors can contribute to this pathological process, these include:
-
advanced gingivitis;
- diseases that weaken the immune system;
- hypertonicity of the jaw muscles;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- tartar;
- stress and bad habits;
- improper hygiene;
- diseases affecting the acid-base balance in the body;
- genetics.
One of the factors contributing to the onset of periodontitis is poor nutrition. A lack of vitamins weakens the immune system, and an insufficient amount of solid food leads to a slow depletion of bone tissue.
A rare examination by a dentist increases the likelihood of developing advanced periodontitis. Prior gingivitis often occurs without pronounced signs, and only a professional can notice the pathological process. A timely visit to the doctor allows you to notice the violation in time and quickly eliminate it.
Periodontitis often develops in adults, in the zone of particular risk - people from 16 to 30 years old. Frequent use of alcohol or smoking increases the likelihood of a rapid development of the inflammatory process in the gums. If the dentist can accurately determine the origin of the pathology, it will be easier to treat, but there will be no transition to periodontal disease.
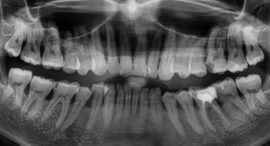
Periodontitis Diagnosis
The first obvious sign of gum problems is the appearance of blood during brushing. It is advisable to consult a doctor at this stage, before other symptoms of periodontitis occur. The specialist must listen to all patient complaints and examine the oral cavity. Tissue changes will be noticeable during a routine examination.
Additionally, can be assigned:
- reoperodontography;
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- X-ray of the jaw.
Only after carrying out all diagnostic procedures, making a diagnosis and determining the severity of the disease, the doctor selects the optimal methods of treatment of periodontitis.
Periodontitis treatment
The treatment of periodontitis depends on the cause of its development and should be carried out by a specialist, since self-medication is extremely dangerous. Incorrectly selected medications or procedures at best will not give any effect, at worst, inflammation will continue to develop, and the result will be the rapid onset of complications.
To completely remove the symptoms of a tooth disease such as periodontitis, and stop a pathological tissue change, the following methods are used:
- use of local or general medicines;
- physiotherapy;
- hardware treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- correction of orthopedic type.
Doctors try to preserve the tooth, removal is the most extreme method that is used when other types of treatment are impossible or ineffective.
The healing process usually begins with professional ultrasonic toothbrushing. During the procedure, all tartar and dense plaque are removed, which reduces the likelihood of inflammation moving to other areas of the oral cavity. Also, the doctor must find out the causes of periodontitis in order to eliminate them and reduce the likelihood of relapse.
Medicines
Topical preparations help to remove the symptoms of inflammation and suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Throughout the treatment, the patient should regularly treat the oral cavity with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs. Used for these purposes:
 solutions: Maraslavin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Rotokan;
solutions: Maraslavin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Rotokan;- gels: Holisal, Metrogil Denta, Traumeel, Levomekol;
- special toothpastes: Parodontax, Lakalyut-active.
Most drugs are suitable for the treatment of adults, but are prohibited for children.
With the rapid development of periodontitis or a neglected form, antibiotics may be needed: Klindomycin, Tarivid, Linkomycin. It is recommended to use tablet preparations: injections are not used due to the too high concentration of the active substance in the problem place, since it contributes to the destruction of the gingival attachment.
Additionally, vitamin-mineral complexes are selected to increase immunity and improve the body's resistance to the inflammatory process. If necessary, an immunomodulator Immudon is prescribed.
Physiotherapy
For serious periodontal problems in adults, the following procedures are additionally recommended:
- UHF therapy;
- darsonvalization;
- ultrasonic waves to strengthen the gums;
- aerosol therapy;
- gum massage;
- light therapy;
- diathermocoagulation.
All procedures are painless and performed in a dental clinic. In Moscow, the demand for such services is much higher than in small cities.
Orthodontics
Chronic gum disease or periodontitis may result from malocclusion, lack of tooth, or failed implantation. If the cause of the disease is this, experts recommend replacing the implant, prosthetics or installing a bracket system.
Hardware correction
Hardware methods for treating periodontitis are considered the most effective and safest. They are notable for their high price, but they allow you to quickly and reliably restore the condition of soft tissues.
Are used:
- Laser. It allows you to painlessly remove problem areas of the gums to stop inflammation and destroy bacteria. The risk of re-inflammation is minimal.
- Vector. This is a directional ultrasound machine that flushes out toxins, heals the gums and eliminates stone and dense plaque.
- Ultrasound. Allows you to remove the subgingival stone, cleans periodontal pockets of food debris.
Any hardware methods are used in combination with drug therapy.
Surgery
If local or general treatment with medicines does not bring the desired result and the development of periodontitis cannot be stopped, dentists recommend treating the problem surgically. Conducted:
- Gingivectomy - purification of periodontal pockets, partial removal of inflamed areas. It is used for a localized form of the disease.
- Bone growth. Essential for significant tissue loss.
- Patchwork operation. It is carried out with exposure of the tooth root. Pockets are cleaned, with a healthy mucosa a small piece is cut off, which fits on the problem area and is connected by sutures. The method allows you to hide the root and strengthen the gums.
- Splinting. Crowns are being restored to prevent tooth loss and to keep the tooth in the socket.
- Gingivoplasty - cleansing pockets, covering the roots with protective substances. If necessary, bone transplantation or renewal of the epithelium occurs.
Surgical intervention can cure even advanced periodontitis and prevent possible complications.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes are usually used as adjuvants and cannot completely replace drug therapy or surgical treatment. They allow you to quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms and accelerate the healing process of tissues.
With the approval of a doctor, you can apply:
 Massage. Fir and sea-buckthorn oils (the optimum proportion is 1: 1) are mixed, they are impregnated with a sterile bandage, which can easily massage problem gums for 5-10 minutes. The procedure needs to be done twice a day.
Massage. Fir and sea-buckthorn oils (the optimum proportion is 1: 1) are mixed, they are impregnated with a sterile bandage, which can easily massage problem gums for 5-10 minutes. The procedure needs to be done twice a day.- Rinse aid. A tablespoon of dry comfrey root is poured with 250 ml of water, brought to a boil over low heat. The mixture is infused for 30 minutes, cools, filtered.
- Rinse solution. A teaspoon of chopped oak bark is poured with 200 ml of boiling water, brought to a boil over low heat. It is infused to room temperature, filtered. Rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours.
With severe pain, you can use an antiseptic solution: a teaspoon of soda and sodium chloride in a glass of warm water. They need to rinse their mouth every hour, after several applications the pain subsides.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of inflammation in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, hygiene must be carefully observed. For cleaning, it is recommended to use medium hard brushes and pastes without aggressive abrasive particles. The procedure is carried out at least twice a day, and if possible after each meal.
You need to visit the dentist at least once every six months. It is also necessary to go to the doctor when the first symptoms of inflammatory diseases or caries appear. Timely diagnosis of periodontitis and proper treatment can avoid complications and eliminate the disease immediately after it occurs.