Gum and tooth cancer: symptoms and first signs in the initial stage
Oncological diseases are a sore subject in dentistry. Many patients completely deny the presence of a dangerous pathology and do not go to the dentist, and especially to the oncologist. But awareness can save a person’s life. If you detect cancer of the tooth or gingival tissue at an early stage and consult a doctor in time, you can permanently recover from a deadly disease.
Content
Gum cancer
Gum cancer is a dangerous disease that is difficult to diagnose at an early stage. Often they confuse her with other diseases, prescribe the wrong treatment, which is not characteristic of oncology, and only aggravate the situation.
Causes of Gum Cancer
The causes of an oncological tumor in the mouth include:
- bad habits: alcoholism, smoking, chewing tobacco, drug addiction;
- jaw injuries of varying severity;
- lack of oral hygiene;
- adentia not cured by prosthetics;
- piercing
- the presence of infections in the body in a vegetative state;
- weak immunity;
- poor-quality dentures or their improper installation;
- caries, periodontal disease, pulpitis and other inflammatory processes in the mouth;
- chemical or thermal burns of the oral mucosa;
- medical errors during the extraction (removal) of the tooth.
Most often, oncological pathologies are diagnosed in people over 45 years old. Moreover, men suffer from cancer of the oral cavity more often than women. This is due to the fact that many men of pre-retirement age are negligent in oral hygiene, smoke a lot and abuse alcohol.
Symptoms and first signs of gum cancer
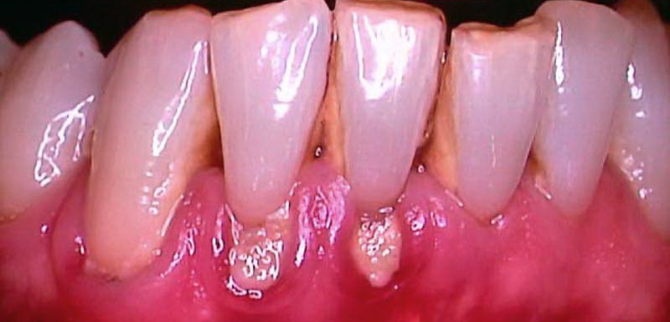
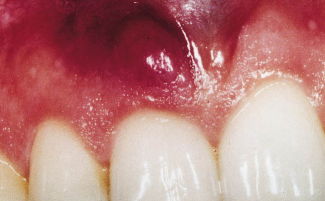
At the initial stage of gum cancer, a small swelling forms near the teeth, from which blood oozes when pressed. The tumor grows until it reaches 2–2.5 cm in diameter. Near or directly inside the tumor, the first small ulcers form, the gums continue to bleed. Most often, at this stage, the cancer is confused with gingivitis or stomatitis and therefore do not seek medical help.
Over time, the seal spreads to the nearest areas of the gums and the inside of the cheeks. White spots form on the seal, a local pain of an impulsive nature appears, the lymph nodes often increase, and the temperature rises to 38–39 ° C. It becomes difficult for the patient to speak and swallow, the first signs of disturbance in the salivary glands appear, because of which the patient often feels dry in his mouth.
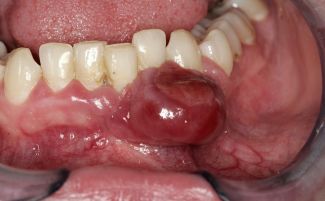
The seal turns red and increases to 4 cm. At this stage of the disease, the doctor can easily make a mistake and remove the tooth located in the affected area, but extraction will only lead to tumor progression.
With the further development of pathology, a sharp weight loss is observed. The patient feels a constant weakness and breakdown. Due to the growth of the tumor, a sore throat may appear, which neither antibiotics nor anti-inflammatory drugs can cope with.
An oncologist or dentist should be consulted when the first signs of gum cancer develop, without waiting for the appearance of vivid symptoms of pathology. There is no need to be afraid of the diagnosis; at the initial stage, oncological diseases are really treated.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosis of cancer is carried out by a dentist and oncologist. Typically, the diagnosis includes the following measures:
- history taking by interviewing the patient;
- histological analysis to detect cancer cells;
- fluorescence analysis of the gingival mucosa;
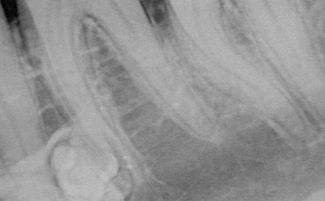
- X-ray and MRI of the jaw;
- tissue biopsy to determine the type of tumor;
- radioisotope analysis;
- PET - positron emission tomography.
In addition to local diagnostics, additional studies are often conducted to determine the presence of metastases in other organs and tissues. To this end, X-rays of the lungs, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and CT of the brain are done. The earlier a cancerous tumor is detected in the gum, the greater the patient's chances of a full recovery.
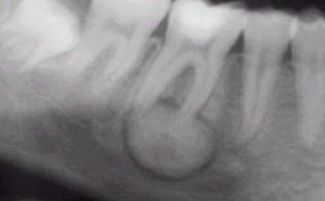
What does gum cancer look like at the initial stage?
Cancer treatment
The treatment of cancer is:
- Radical surgical removal of pathological cells.
- Radiation therapy - exposure to tumor tissue with highly active radiation.
- Chemotherapy - cytostatic destruction of cancer with special drugs. The method of therapy is used in cases where it is not impossible to carry out a surgical operation.
Oncology treatment is carried out in several stages. Most often, to achieve the best effect, a combination of different treatment methods is practiced.
Gum cancer treatment is carried out by medical staff in a hospital after diagnosis. Taking medications without a doctor’s prescription is unacceptable and can be fatal.
Folk therapy
Traditional medicine does not cure cancer. Some home remedies can stop the symptoms of the disease or slow down the division of cancer cells, but they are not able to completely defeat the disease. Many patients simply lose time trying to cure herbal infusions. The tumor still continues to grow, capturing healthy cells and body tissues.
Tooth cancer
Few people know that in oncology, in fact, there is such a thing as tooth cancer. This is a rare disease that affects dentin, enamel, other dental tissues and, like other oncological pathologies, leads to death. On milk teeth, the disease practically does not occur.
Tumor classification
The following types of tooth cancer are known:
- adamantinoma - a tumor of enamel cells, divided into massive and cystic ameloblastoma;
- odontogenic fibroma - a cancer in the lower jaw;
- cementoma - a tumor of the premolars of the lower jaw;
- odontoma - hard ameloboastofibroma, which forms in the jaw, and soft amelobastofibroma, which is formed in periodontal and enamel tissues.
Symptoms and photos of tooth cancer
Symptoms of a tumor in the tooth at the initial stage are erased. Indirect marker signs of the disease include:
- frequent trauma to the jaw and the presence of fistulas on the gums;
- malocclusion;
- difficulty swallowing;
- loosening of molars and premolars;
- bleeding gums;
- constant aching pain;
- a crunch that occurs when pressure is applied to a tooth.
Disease treatment
Treatment of a tumor involves surgical removal of the tooth and resection of the jaw (if necessary). In parallel with this, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is performed. To avoid a relapse of the pathology, it is necessary to undergo dental examinations and avoid injuring the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Malignant neoplasms in the teeth and gums are curable only with timely diagnosis. You should not delay going to the doctor until stage 4 of the disease, when all methods of treatment become useless.