Inflammation of the tonsils and tonsils in the throat in adults and children: symptoms, causes, treatment, photo
Tonsils protect the body from harmful microbes, but they themselves are susceptible to pathogenic effects. Accompanied by vivid symptoms inflammation of the tonsils in the throat in adults and children is successfully diagnosed in the very early stages.
Content
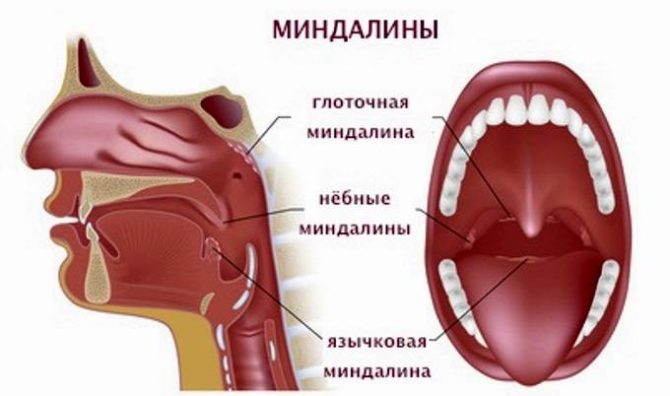
The structure and function of the tonsils
Tonsils are small organs in the form of glands formed from lymphoid tissue. In the human body there are exactly six such glands. They are located in a circle along the pharynx, forming the so-called pharyngeal ring. The main function of this formation is protective. Tonsils prevent harmful microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi) and other pathogens from entering the body. In addition, they take part in hematopoietic activity and help increase immunity, especially in children.
Tonsils are divided into paired and single, and by location at:
- palatine (first and second);
- nasopharyngeal (third);
- lingual (fourth);
- pipe (fifth and sixth).
Tubal glands are located at the openings of the auditory tubes, the lingual - under the tongue, and the nasopharyngeal - at the junction of the nasopharynx with the oral cavity.
Palatine tonsils are often called “tonsils”, although this term is also applicable to other formations.
Inflammation of the nasopharyngeal gland can lead to the formation of an adenoid, but most often paired palatine tonsils bring trouble - these are the main blows for various infections. Particularly dangerous can be diseases associated with an increase in tonsils in the throat in children.
Causes of gland inflammation
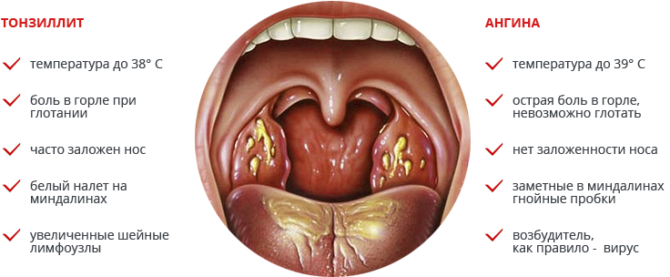
Pain and inflammation of the soft tissues in the throat accompany many diseases: acute respiratory infections, pharyngitis, laryngitis. But the inflammation of the tonsils is most pronounced with tonsillitis and tonsillitis. In fact, this is the same disease, only tonsillitis appears in a chronic form, and tonsillitis - in acute.
Two different sets of causes lead to inflammation of the glands - the effects of pathogens and related factors. Tonsils play the role of a barrier to the path of microbes and viruses into the body, with weakened immunity the pharyngeal ring may not cope with the influx of harmful microorganisms, which leads to inflammatory processes in the glands.
Inflamed glands increase in size and do not cope well with protecting the body from bacteria, which can further provoke various complications. Among the main causes of the disease and associated negative factors are worth mentioning:
- exposure to pathogenic microbes (streptococci, staphylococci);
- complications and weakening of the body after measles, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases;
- contacts with infected people;
- hypothermia of the body;
- inflammation of the nasopharynx, gums, caries, chronic runny nose;
- weakened immune system, low body resistance;
- unbalanced nutrition;
- genetic disorders, hereditary predisposition;
- harmful living or working conditions;
- sharp fluctuations in temperature, adverse environment;
- injuries.
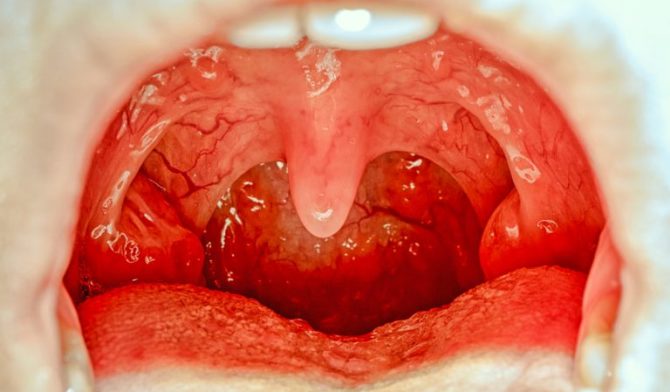
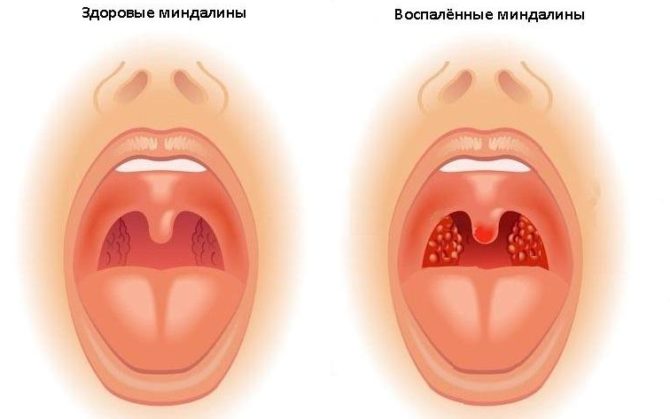
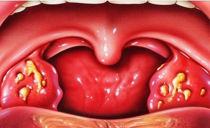
How sore tonsils look
The differences between normal and diseased glands are very easy to recognize. Healthy glands have a smooth pink color, they are quite small in size.Inflamed tonsils look noticeably enlarged, a white coating appears on them, possibly severe redness, the appearance of pustules.
The increase in tonsils with inflammation often occurs on an increasing basis. At first, they swell relatively slightly, with the further development of the disease and the transition to more serious stages of the gland, they continue to increase, and the picture of the course of the disease changes. To avoid complications, treatment should be started as early as possible.
Enlarged glands can be observed on one or both sides of the larynx. In the first case, the course of the disease is usually milder than with bilateral inflammation.
Enlarged tonsils and tonsils in children
Children are much stronger than adults are susceptible to inflammation of the glands. Essential point: Tonsils are almost the only formed organ of the children's immune system, therefore, their normal functioning is very important for the full development of a growing and emerging organism. Therefore, you should be extremely careful about the diseases of these glands in children. At the first sign of enlarged tonsils in a child, you should consult a doctor.
In newborns, tonsils are present only in their infancy (in the form of follicles). Their full formation with the normal development of the baby ends by about six months of age. Since that time, serious inflammations are possible, although problems with the forming tonsils may occur earlier. For young children, prevention of tonsillitis is especially important - optimal indoor temperature, proper nutrition, the complete exclusion of too cold, hot food and drink.
If the child has enlarged glands from one or two sides, it is advisable to immediately conduct an examination. You cannot start the situation, as this can contribute to the occurrence of chronic diseases.
In itself, an enlargement of the palatine glands is not yet a symptom of the disease; it can also indicate normal functioning of the immune system. Therefore, instead of self-medication, you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Tonsil inflammation treatment
Until recently, the surgical method of treating tonsils was very popular. It was believed that removal of the tonsils in childhood could permanently solve the problem of the occurrence of tonsillitis, tonsillitis and a number of other diseases. Today, the understanding has come that these glands perform the most important task of protecting the body. Their role is especially great in childhood, when the child’s immunity is still insufficient to successfully resist infections.
Therefore, now doctors prefer medical methods of treating inflamed glands. A large number of various drugs have been developed that successfully resist tonsillitis, tonsillitis and the complications caused by them. The main thing in the treatment of inflammation of the tonsils is to consult a doctor in a timely manner. The sooner a person begins to treat inflamed glands, the more effective the use of medicines.
The main tool in the treatment of tonsils are antibiotics. It should be understood that they are not always able to bring success. This is due to the different etiology of the disease. In addition to bacteria, laryngeal inflammation is also caused by fungi and viruses, against which antibiotics can be ineffective. Therefore, you should not be treated on your own, you should entrust the choice of the drug to a specialist. Moreover, different antibiotics have an unequal degree of effectiveness even against various groups of pathogenic bacteria.
Another significant point in the treatment of tonsillitis and tonsillitis is a certain difference in the methods used in the treatment of inflamed tonsils in children and adults.
Treatment of inflammation of the tonsils and tonsils in adults
In adults, immunity is usually much higher than in children.The course of tonsil disease is much easier if it is not complicated by a number of the above negative factors.
The choice of drugs for inflammation of the tonsils in adults can be approached with less concern. Antibiotics and other potent medicines have a less negative effect on the formed body than on children. The use of such drugs is especially effective in the treatment of tonsillitis and tonsillitis:
 antibiotics: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Doxicillin, Cephalexin;
antibiotics: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Doxicillin, Cephalexin;- aerosol: Ingalipt, Hexaspray;
- lozenges: Faringosept, Strepsis;
- rinse preparations: Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt.
In severe forms of the disease, the use of antibiotics in the form of injections is possible. Aerosols and tablets under the tongue should be used if antibiotics are contraindicated to the patient. Rinses help relieve symptoms of the disease.
A number of folk remedies are quite effective. Useful drinks from raspberries, currants, honey, aloe, propolis, elecampane, rinses from chamomile, clover, sage. Vitamin complexes that enhance immunity will also help to cure the disease faster.
Treatment of inflammation of the tonsils and tonsils in children
In the treatment of inflamed tonsils in a child, basically the same means are used as for adults. But it should be understood that the effect on the children's body of potent drugs (especially antibiotics) can be very negative, so it is advisable to put more emphasis on soft methods of treating a sick child, including inhalations and various folk remedies.
Symptoms characteristic of a sore throat (sore throat, redness, white plaque) are also associated with other diseases, including such dangerous ones as diphtheria. Sore throat can look almost the same with different diseases, so treating a child yourself is highly discouraged. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of the ailment and prescribe the right treatment.
If with acute angina, the main drugs are still antibiotics, then in chronic tonsillitis it is more important to take drugs designed to strengthen the immune system. But resorting to surgery should only be in extreme cases.
Surgical intervention and other treatment methods
If the tonsils become inflamed very often, then the only method for their treatment may be surgical removal. The operation itself is harmless and practically painless, its undesirability is to eliminate the glands, which play a rather important role in protecting the body. Therefore, resorting to this method should be done only as a last resort - if the other methods with which you can treat inflammation of the tonsils in the throat of a child or adult have been ineffective. Removal of inflamed glands is performed under local anesthesia directly from the mouth.
Today, a number of modern methods of treating inflamed tonsils are used, some of them were almost unknown earlier. Among them are worth mentioning:
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound methods;
- physiotherapy.
In addition, herbal medicine is used, more modern methods of inhalation are used. If the tonsils continue to increase in size, only then it makes sense to decide on an operation.