Diseases of the oral cavity and tongue: types of pathologies and methods for their treatment
WHO statistics show: various types of oral diseases are diagnosed in 90% of the world's population. The pathologies under consideration are susceptible to patients of all ages. Anomalies are localized in soft and hard tissues, reappear after an apparent recovery, in the absence of therapy cause the development of severe complications.
Content
General concepts
According to medical literature, diseases of the oral cavity include pathologies of the teeth, gums, tongue and mucous membranes. Diseases have a viral, infectious or fungal etiology, arise as a result of the development of inflammatory processes in the body, the appearance of oncological neoplasms. There is no unified classification of anomalies: most scientists differentiate diseases detected in the oral cavity according to heterogeneous signs.
Causes of occurrence
The list of the main factors affecting the appearance of pathologies in the oral cavity includes weakened immunity, nutritional errors, hormonal disruptions, bad habits, taking antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs without a doctor's prescription, and a genetic predisposition. In addition, abnormalities can be caused by a special condition of the body - pregnancy and lactation.
Additional factors that can provoke the development of oral diseases are:
- hypothermia;
- frequent stress;
- vitamin deficiency and lack of trace elements;
- allergic reactions;
- pathology of the internal systems of the body;
- mechanical injuries of hard, soft tissues in the mouth;
- increased saliva viscosity;
- poor hygiene measures;
- refusal of timely visits to the dentist.
Diseases of the oral mucosa of an infectious etiology are frequent companions of HIV and AIDS.
Symptoms of Oral Infections
The diseases in question are characterized by the presence of a number of common symptoms. Usually, at the doctor’s appointment, patients complain of dryness and discomfort in the mouth, manifested during communication with the interlocutor, while drinking or eating food.
Additional signs of the development of the pathological process include:
- prostration;
- decreased performance;
- insomnia;
- increase in body temperature;
- violation of taste perception;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- unpleasant aftertaste of a temporary or permanent nature.
Inflammation of the tongue is accompanied by swelling of the affected organ, a feeling of numbness. The presence of infectious diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is indicated by pain at the site of localization of the disease, the appearance of ulcers, wounds, ulcers, a dense film and a curdled white plaque, difficulty in salivation. Gum bleeding, discomfort during hygiene - signs that indicate the development of pathologies of the teeth or gums.
Types of pathologies
Depending on the type of microorganism that caused the appearance of the abnormal condition, all diseases detected in the oral cavity are conditionally differentiated into infectious and fungal. In addition, dental problems, allergic reactions and cancer, the etiology of which has not received clinical confirmation, are distinguished.
Infectious diseases of the oral cavity and their symptoms
The infectious group of diseases combines diseases arising from the growth and development of bacterial, viral colonies in the affected tissues. The list of the most common diseases includes stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, pharyngitis. The main reasons for their appearance are poor-quality procedures for the care of gums, tongue and teeth, as well as the progression of pathologies of internal organs, mainly gastrointestinal disorders - peptic ulcer, gastritis, enterocolitis.
In order to avoid the appearance of infectious diseases, regular preventive medical examinations should be taken, and a dentist should be visited.
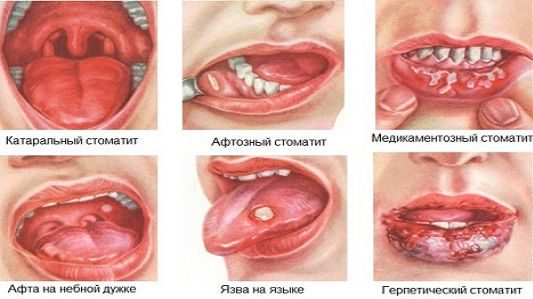
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is one of the abnormalities that develop in patients of different ages. There are several types of disease. In the list of common stomatitis:
- Aphthous. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus. The primary symptoms of this oral infection are swelling of the mucous membrane, tissue hyperemia. As they develop, painful, covered with fibrinous deposits of erosion (aphthae) appear. The second name of the lesion is herpetic stomatitis.
- Vesicular. Symptoms are similar to the above symptoms. It is detected by the presence of small vesicular rashes that are transformed in erosion. Pathology has a herpetic nature.
- Catarrhal. When an infection gets into the oral cavity, swelling of the mucous membranes develops, a plaque of a light yellow hue appears.
It is impossible to determine the type of stomatitis on your own. At the first signs of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
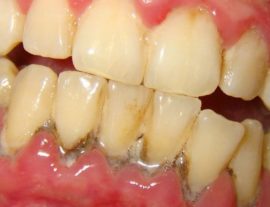
Gingivitis
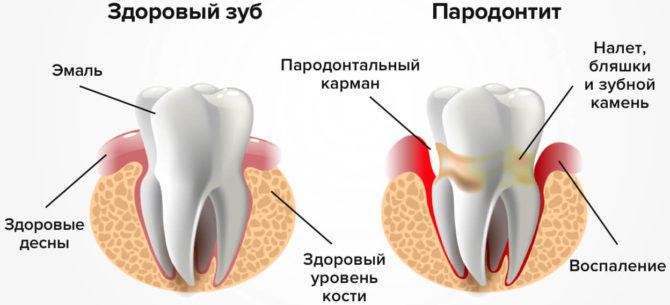
Gum disease is provoked by chemical, mechanical, and infectious factors. Gingivitis, activated as a result of the vital activity of pathogenic agents, occurs mainly in children and young people and either manifests as independent pathologies or signals the development of other ailments, including periodontal disease.
- swelling;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gingival margin;
- bad breath;
- bleeding of tissues.
Dentists highlight the acute and chronic form of gingivitis. The latter is characterized by the duration of the course, the weakness of the symptoms.
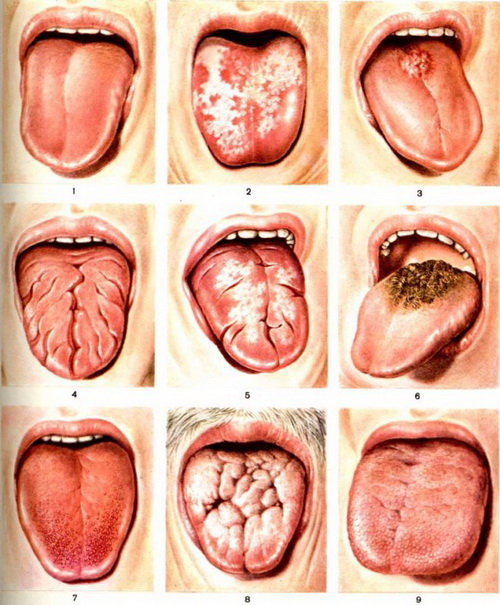
Glossitis
Glossitis is a large group of pathologies that cause structural disruption and discoloration of the tongue. At risk are people who refuse regular hygiene procedures. Infection penetrates the thickness of the tissues of the tongue in the presence of injuries, inflammation in the oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract.
Glossitis can be prevented through the daily use of flosses, hygienic rinses, and high-quality toothpastes.
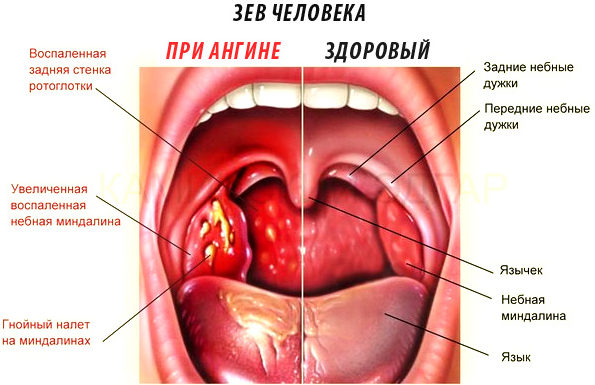
Laryngeal diseases
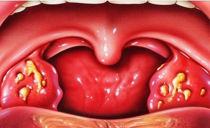
Chronic and acute forms of pharyngitis, tonsillitis (tonsillitis), laryngitis are accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition of the patient, the appearance of dry mouth, discomfort and sore throat. The most susceptible to the development of these pathologies are children and people with weakened immunity. Avoiding the appearance of anomalies will help hardening, playing sports, taking vitamins.
Other abnormalities of viral etiology
Unprotected oral-genital contacts are the cause of infection of the oral cavity with sexually transmitted infections. With the indicated type of intimate relationship from the patient to a healthy partner, the following are transmitted:
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- cytomegalovirus;
- chlamydia
- human papillomavirus;
- HIV
The presence of the disease is indicated by a plaque on the tonsils, an increase in lymph nodes. When swallowing, the root of the tongue hurts, the throat. In the absence of treatment, the pathogen spreads rapidly, and the disease becomes chronic.
Fungal lesions
The causative agents of fungal diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are yeast-like microorganisms Candida, penicillas, aspergillus. Infectious agents belong to the group of saprophytes that acquire pathogenic properties and cause mycotic process only under certain conditions.Among the factors that activate their livelihoods are weakened immunity, treatment with corticosteroids and antibiotics, and the presence of diseases.
Mold damage occurs in 2% of the total number of patients examined. The most common ailment localized on the mucous membranes is candidiasis.
By the nature of the course, the disease differentiates into 3 forms:
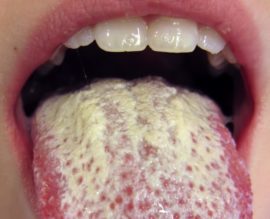
- Pseudomembranous or acute. The main signs of its development include dryness of the inner surfaces of the palate, lips, cheeks, tongue and the formation of white curd in these zones. The patient feels itching, burning.
- Hyperplastic or chronic. It differs by the appearance of plaques tightly soldered to tissues. Attempts to remove plaque cause bleeding of the mucous membranes.
- Atrophic. It is detected in patients using removable orthopedic structures. The list of symptoms includes drying out, inflammation of the surface of the oral mucosa.
Yeast-like microorganisms can cause fungal glossitis, tonsillitis, angular infectious cheilitis. The last of these ailments affects the red border of the lips. When opening the mouth, patients experience severe discomfort. Superficial erosion, detected at the beginning of the disease, as cheilitis progresses, spreads to the skin of the chin.
To avoid the development of fungal pathologies, experts recommend strengthening immunity, avoiding stress and hypothermia.
Dental problems
Diseases in the oral cavity are also detected in patients who refuse regular visits to dentistry. Periodontitis and periodontosis in the absence of treatment worsen the condition of the gums, expose the neck of the teeth, and disrupt the structure of the jaw. The list of additional signs of the presence of diseases includes swelling and bleeding of tissues. With a constant postponement of a visit to the doctor, you can lose teeth located at the site of localization of inflammation.
The development of carious processes is accompanied by a change in the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity. Plaque is formed in the carious openings, which plays a significant role in the activation of the previously listed diseases. The progression of the problem can only be avoided by visiting the clinic.
Diseases of unclear etiology
Among the diseases observed in the oral cavity is lichen planus, an anomaly, the causes of which are not clear. The clinical picture of the manifestation of the disease differs in a number of features:
- In the initial stage, rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity - small papules.
- The progression of the pathology leads to an increase in the affected areas, their fusion.
- Stripes, plaques with keratinized grayish-white surface, protruding above the level of the mucous membranes, form on the tissues.
Treatment regimens are selected individually, taking into account the patient's condition.
Other pathologies
Among the ailments that alter the structure of the oral mucosa are diseases that result from allergic reactions. Among them - Reiter, Lyell syndromes, exudative erythema. The provoking factors that cause abnormal conditions are microbial, contact and drug allergies. Disease treatment regimens include the study of allergological status, elimination of the source of negative effects.
The incidence of oral cancer varies from 2 to 4% of the total number of oncopathologies detected in Russia. At an early stage, the disease is hidden. Its further development is accompanied by the appearance of local pains, bleeding, ulcers. In a later period, uncomfortable sensations intensify, they begin to give to the cheekbones, temples, forehead. The outcome of oncopathologies depends on the stage of the identified process, the general condition of the patient.
Treatment regimens for diseases of the oral cavity and tongue
Treatment of infections in the mouth involves the use of a complex of drugs.Health workers recommend treating the resulting foci of inflammation with antiseptics (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Hexoral) and infusions of raw medicinal plants (calendula, chamomile, sage).
The development of viral ailments in the oral cavity is suppressed by the use of Famvir, Valaciclovir, Acyclovir. When identifying a chronic pathology, antibiotics are used - Ciprofloxacin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav. For the treatment of mycotic diseases of the oral cavity and tongue, Nistatin and Levorin are used.
To speed up the regeneration process, doctors include rosehip and sea buckthorn oils, propolis ointment, and Solcoseryl in the treatment regimen. Itching, burning and swelling are minimized with the help of antihistamines (Tavegil, Tsetirizin), pain - analgesics and NSAIDs (Nise, Aspirin, Ibuprofen).
Dental pathology should be treated upon detection of their first signs. The teeth affected by caries are filled, the units of the dentition that cannot be restored are removed.
Additional measures
To stop the development of pathologies, adherence to a special diet helps. The patient's menu should not consist of excessively hot dishes, hot sauces, sour dressings. Alcoholic drinks are not allowed.
The list of allowed products includes milk, vegetables (boiled), cereals in the form of cereals. Multivitamin complexes and herbal medicine will help to consolidate the achieved effect.
Prevention
Preventive measures to help avoid the development of pathologies in the oral cavity include:
- high-quality hygiene procedures;
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- compliance with the basic rules of healthy lifestyle;
- regular visits to dispensary examinations.
At the first signs of the development of an oral disease, you should immediately consult a doctor: timely diagnosis and adequate therapy will help stop the development of the disease at an early stage.