Glossitis of the tongue: types, causes, treatment
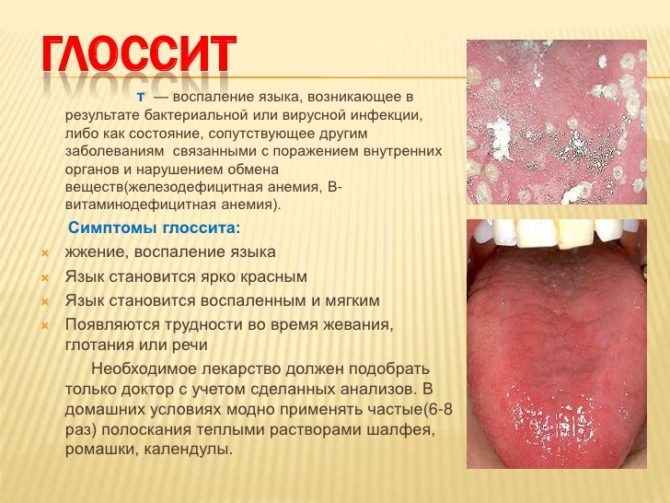
Glossitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tonguewhich is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and may have a different nature. There are many reasons for the development of the disease and types of glossitis, so a professional should be involved in the diagnosis and treatment.
Content
Causes of glossitis
The causes of glossitis can be local and general. Local factors include diseases of the oral cavity. General prerequisites are internal pathologies of the body, the symptoms of which are manifested in the tongue.
The causes of inflammation include:
- Mechanical, chemical or thermal injury. Damage can occur when eating, improper dental treatment, exposure to high temperature.
- The presence of bad habits. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption adversely affect both locally and the entire body.
- Allergic reaction.
- Misuse of drugs (especially antibiotics).
- Infectious, bacterial and fungal infections (candidiasis, herpes, measles, diphtheria, lupus erythematosus).
- Diseases of the internal organs (especially the digestive and cardiovascular systems).
- Genetic predisposition to pathology.
- The lack of vitamins and minerals.
Symptoms of glossitis
Symptoms and treatment of glossitis most often depend on its type, as each type of inflammation has certain signs. The acute process will be characterized by strong pain and spontaneous occurrence. Chronic inflammation exists for a long period, is lethargic and brings discomfort.
Common symptoms of damage are the following symptoms:
- pain
- swelling, swelling;
- limited mobility;
- the appearance of plaque;
- burning sensation;
- bad breath from the mouth;
- impaired speech and eating;
- discoloration of the tongue;
- pathological formations: erosion, ulcers, foci of desquamation, spots;
- violation of taste perception;
- a feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the mouth;
- increase in body temperature;
- enlarged regional lymph nodes;
- weakness and general malaise may occur.
Types of glossitis
There are quite a few types of inflammatory process in the tongue. The disease may have an acute or chronic course. The name of the type of glossitis indicates the main pathological process in the tissues, the most striking symptom or cause of the disease.
| Types of tongue disease | |
|---|---|
| Inflammatory | Non inflammatory |
|
|
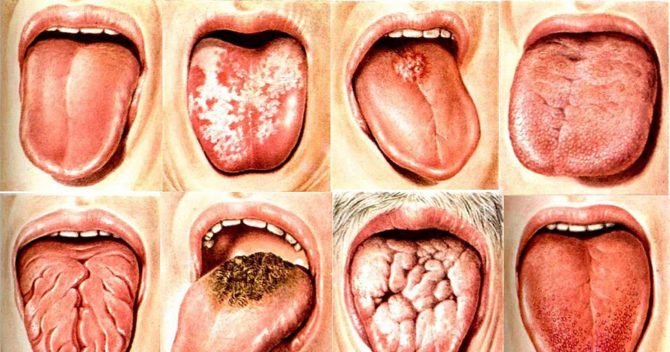
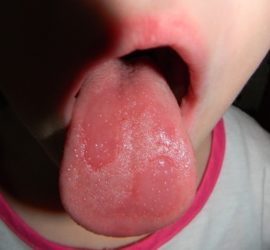
Catarrhal glossitis
Catarrhal glossitis of the tongue is the simplest type of inflammation of the mucous membrane. It arises from local causes: stomatitis, thermal damage during eating, trauma to products or dental structures, biting of the tongue, insufficient level of hygienic care for the oral cavity. With the development of the pathological process, the surface layers of tissues suffer.
The disease manifests itself in one of the sections of the organ at the site of the lesion.The main symptoms are:
- plaque;
- swelling;
- redness;
- sensitivity during meals;
- discomfort.
This form of ailment proceeds uncomplicated and passes after a few days. Treatment of catarrhal glossitis is aimed at eliminating the cause of the occurrence, suppressing inflammation and unpleasant symptoms. Therapy is recommended after consultation with a doctor.
Folded glossitis
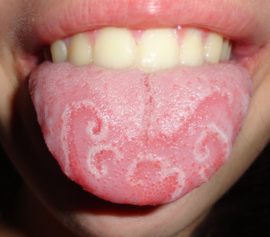
This is a congenital disease that can be inherited. Pathology is characterized by the presence of folds in the tongue. Most often there is a large longitudinal wrinkle, from which small transverse furrows extend. The appearance of the organ will depend on the severity of the pathology.
Very often, patients do not suspect the presence of an ailment, since it does not cause complaints. But with an insufficient level of hygiene, food debris, pathological microorganisms that can cause an inflammatory process, as well as a catarrhal form of the disease, accumulate in the folds. The pathology is treated symptomatically.
Candidiasis glossitis
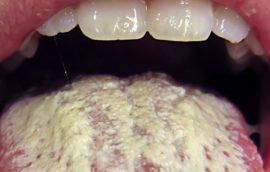
Candidiasis glossitis of the tongue is a disease that occurs with fungal invasion in the oral cavity. It manifests itself with a significant decrease in immunity, prolonged use of medications, and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Candida fungi, which are normal in the mouth and cause a decrease in the body's defenses, cause pathology.
Symptoms of the disease will be the appearance of a white cheesy plaque on the mucous membrane, which is tight to the tissues. Under the deposits are red, inflamed sores. The disease manifests itself in pain, burning, an unpleasant odor.
If untreated, candidiasis of the tongue can turn into a chronic form. Most often, this process is observed in children and the elderly.
Hunter glossitis
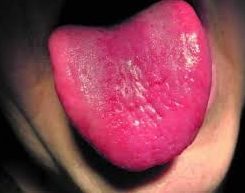 The Hunter language is also called glosser Hunter. It manifests itself when anemia occurs in the body, namely, with a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12. Atrophy and smoothing of the papillae occur, the surface of the tongue becomes smooth and has a bright crimson color.
The Hunter language is also called glosser Hunter. It manifests itself when anemia occurs in the body, namely, with a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12. Atrophy and smoothing of the papillae occur, the surface of the tongue becomes smooth and has a bright crimson color.
The patient complains of a feeling of pain, burning, discomfort in the oral cavity. The disease is easily diagnosed, as it has characteristic symptoms. Manifestations disappear after treatment of anemia.
Atrophic glossitis
The pathogenesis of this form of the disease has an infectious nature. Candida fungi, viral agents, streptococci, oncological diseases provoke its occurrence. When the organ is damaged, the papillae die off and atrophy, the tongue decreases in volume. With the disease, a deficiency of vitamins A and E is noted, which also plays a role in the development of the pathological process.
The main symptoms are:
- organ reduction;
- smoothing the surface of the mucosa;
- discomfort, discomfort and pain while eating.
When diagnosing, the main cause of the disease is established and eliminated. The earlier the pathology was identified, the greater the chances of a successful treatment.
Ulcerative glossitis
Ulcerative glossitis is very painful and unpleasant. It occurs in the absence of treatment of other types of ailment. This form differs in the appearance of round or oval formations - ulcers. Depending on the severity, their number on the mucosa can be different.
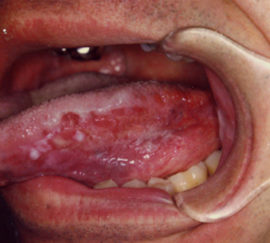 The patient is worried about acute pain, the inability to talk and eat normally. Ailment is characterized by severe swelling, the presence of bacterial plaque, a violation of salivation, an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
The patient is worried about acute pain, the inability to talk and eat normally. Ailment is characterized by severe swelling, the presence of bacterial plaque, a violation of salivation, an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
When injured, aphthae bleed and cause additional discomfort. The general condition of the patient may be disturbed:
- body temperature rises;
- regional lymph nodes are enlarged;
- weakness and migraine appear.
Villous glossitis
The villous glossitis is distinguished by its specific appearance.With the pathological process, changes in the papillae occur, which begin to resemble villi or hair. Over time, the papillae become saturated with pigments and become brown or black. Most often, the lesion is located in the middle or in the posterior third of the organ. People are not bothered by painful symptoms - only an unusual appearance.
They provoke an ailment of the pathology of the digestive tract (gastritis, ulcer, colitis), infectious processes, metabolic disorders, lack of vitamins and minerals, taking medications, and the presence of bad habits.
Allergic glossitis
It is an organism reaction to an allergen. Occurs with hypersensitivity to any substance. Most often develops with local exposure (food, hygiene products), but can also act as a general reaction in the body. The clinical picture of the disease will depend on the type of allergic manifestation.
- redness;
- swelling;
- pain;
- burning;
- itching
- discomfort;
- discomfort.
The patient is concerned about acute pain symptoms, the inability to fully talk and eat food. To treat glossitis, you need to take antihistamines and eliminate the allergen.
Herpetic glossitis
It occurs when the mucous membrane of the tongue is affected by the herpes virus. The form of the disease is characterized by the occurrence of acute pain and can be contagious. Viral particles are able to activate with a decrease in immunity, acute respiratory viral infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases.
When the tongue is damaged, bubbles with liquid appear, which eventually open and form ulcers. The lesions can be of various shapes and sizes, characterized by soreness, burning, itching.
It is difficult for the patient to open his mouth, talk and eat food. Therefore, therapy will be aimed at suppressing the virus and analgesia.
Diamond Glossitis
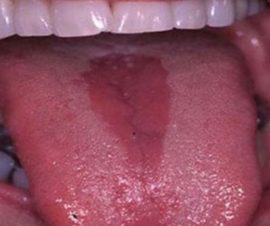 It differs by the appearance of a diamond-shaped formation on the back of the tongue. It occurs due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with a lack of vitamins, the presence of bad habits. The etiology is unclear to the end.
It differs by the appearance of a diamond-shaped formation on the back of the tongue. It occurs due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with a lack of vitamins, the presence of bad habits. The etiology is unclear to the end.
Doctors distinguish three forms:
- Smooth. The affected area in the form of a rhombus is characterized by atrophy of the papillae and the appearance of a flat surface. Papillae of the tongue are absent, and the organ itself is painless.
- Lumpy. It is distinguished by the presence of tuberous formations that arise due to the growth of papillae. The keratinization of the mucosal epithelium is observed.
- Hyperplastic. It is characterized by proliferation of papillae. When injured, the disease can turn into malignant.
Interstitial glossitis
This is a rather rare type of language pathology that occurs due to the tertiary period of syphilis. The superficial and deep layers of the organ are affected, compaction occurs. If untreated, muscle tissue is replaced by connective tissue, and the tongue loses mobility.
Desquamative glossitis
This type of pathology is also called geographical language. With damage to the mucous membrane, rounded foci of desquamation of the epithelium appear, which constantly change their boundaries. The pathology is based on inflammatory-dystrophic processes.
Glossitis occurs due to diseases of internal organs, hormonal disorders, poisoning, chronic allergies. In addition to the specific type of language, it is manifested by its sensitivity during the intake of hot, spicy food. There may be discomfort, tingling.
Manifestations in children
Glossitis in children is rare, but most babies under 3 years old suffer from herpetic stomatitis. Ailment is not dangerous, but requires professional treatment by a dentist.
With trauma, teething, a catarrhal form of the disease can occur, with internal pathologies of the body - bacterial, and with atypical dermatitis, gastrointestinal disorders - desquamative.
Glossitis treatment
The treatment of glossitis in adults depends on the symptoms and form of the disease. Therefore, it is important to correctly identify the cause of the disease and classify it. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since only a doctor can carry out the correct diagnosis.
To cure glossitis of the tongue, you need to resort to local and general therapy. Depending on the prerequisites that led to the development of the disease, it is necessary:
 visit a doctor, undergo examinations and find out the cause of the disease;
visit a doctor, undergo examinations and find out the cause of the disease;- get rid of pathologies of internal organs;
- boost immune defense;
- eliminate anemia;
- restore hormonal balance;
- protect the patient from allergens;
- sanitize the oral cavity.
Glossitis is an inflammatory disease of the tongue, so you need to treat it with such medicines:
- painkillers;
- local anesthetics;
- antiseptic solutions;
- antiviral, antimicrobial or antifungal drugs;
- healing gels, vitamins.
The dentist conducts local therapy and eliminates all the unpleasant symptoms. It consists of the following stages:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- professional toothbrushing;
- removal of plaque from the tongue;
- antiseptic treatment;
- medical applications;
- the use of antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic applications;
- prescribing drugs for use at home.
As additional measures, you can treat glossitis of the tongue at home with folk remedies. To rinse and make oral baths decoctions of medicinal herbs: sage, chamomile, oak bark, St. John's wort, mint, calendula.
You need to follow the doctor’s recommendations, take the necessary medications, rinse your mouth with drugs (Vinisol tablets, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine bigluconate).
The decision on how and with what to treat glossitis in the tongue in adults and children should be made by a doctor. You can only get rid of the catarrhal type of the disease yourself. But since the patient is not able to diagnose, with the first symptoms it is necessary to consult a dentist.