Stomatitis in the tongue in adults: causes, symptoms, types, how and what to treat
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. The inflammatory process that is localized in the area of the language is called glossitis.
Most often, the symptoms of the disease appear at the tip or root of the tongue. These include burning, white plaque, sores, pimples or aphthae. In addition to the tongue, ulcers can appear on the inside of the cheeks, lips, and mucous membrane of the gums. Often, the disease interferes with speaking, eating, sleeping. Despite the apparent frivolity of stomatitis in the tongue, every adult should entrust his treatment to a doctor.
Content
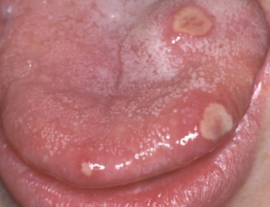
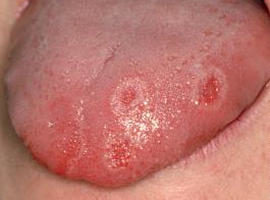
What does the tongue look like with different forms of stomatitis
Depending on the cause of the occurrence and the features of the manifestation, stomatitis in the language is classified into several types.
| A variety and photo of stomatitis in the tongue | The causative agent of the disease, how the tongue looks |
|---|---|
|
Bacterial |
The causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci. It is accompanied by the appearance of rapidly opening abscesses. |
|
Herpetic |
The causative agent is the herpes virus, which can be in the body for a long time without visible manifestations. It is characterized by the formation of vesicles (as in the photo), filled with transparent exudate, which quickly burst and transform into sores. |
|
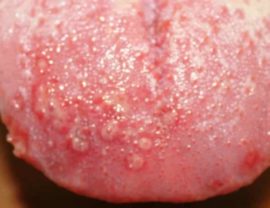
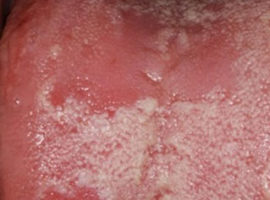
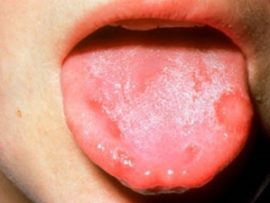
Fungal |
The causative agent of candidal stomatitis is a fungus of the genus Candida, the cause of reproduction of which is weakening of the body's immune functions. It is accompanied by the appearance of a cheesy coating that hides bleeding sores. |
|
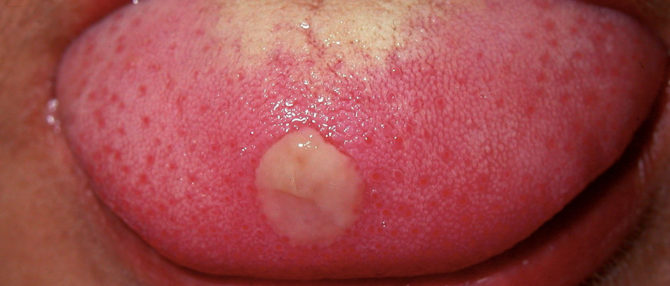
Traumatic |
Possible causes of formation are mechanical damage, burns, exposure to chemicals. It is characterized by the formation of wounds and ulcers. |
|
Allergic |
Possible allergens are dentures, braces, and oral hygiene products. It is accompanied by the appearance of gray or white plaque, the formation of various pathological formations. |
|
Ray |
It develops in patients undergoing radiation therapy. It is characterized by the appearance of pinpoint hemorrhages and ulcerations, hyperemia, swelling and blueness of the organ of taste, an increase in the viscosity of saliva. |
|
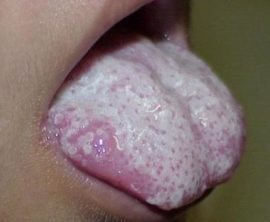
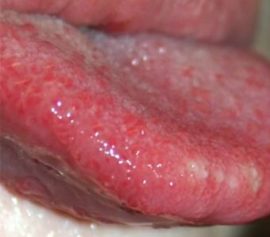
Catarrhal |
A mild form in which superficial damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue occurs. You can cure such a disease quite quickly. |
|
Ulcerative |
Severe form, characterized by a deep penetration of infection into the tissue. Accompanied by severe pain. The cause of the disease lies in the lack of proper treatment for gastric ulcer or catarrhal stomatitis. |
|
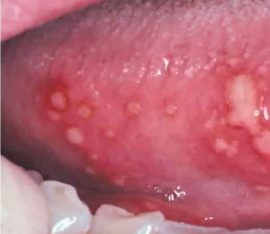
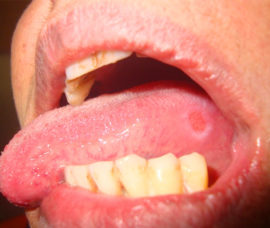
Aphthous |
The specificity of this form of the disease is the appearance of deep ulcers with the right edges. The top of each aft is covered with white or yellow bloom. Pathology proceeds in acute and chronic form. |
Self-treatment of stomatitis in the tongue rarely leads to a positive result. In order to completely recover from an illness, you need to undergo a course of complex drug therapy, the success of which depends on the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if painful ulcers appear on the tongue, you should contact your therapist or dentist and take all the tests necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease.
Symptoms of stomatitis in the tongue
The main symptoms of stomatitis in the tongue are pain and burningfelt almost constantly. In addition, signs of intoxication appear, the temperature rises (37–38 ° C).Symptoms of intoxication include headaches and muscle pain, fatigue.
A temperature exceeding 38 ° C occurs only with the herpetic form of stomatitis.
The tongue for stomatitis is as follows:
- The tip and sides blush and swell.
- The surface is covered with ulcers, aphthae or pustules.
- The mucous membrane is lined with white or grayish plaque.
- The papillae become inflamed and enlarged.
The auxiliary symptoms of the disease include:
- Increased bleeding gums.
- Repulsive breath.
- Increased salivation or dry mouth.
Diagnostic Methods
Before you fight the disease at home, you need to go through a diagnosis in the clinic, as you can get rid of stomatitis in the tongue only after eliminating the cause of its occurrence. Diagnosis begins with a survey of the patient, who informs the doctor about the features of the course of the disease.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Analysis of smears from the lesion.
- Blood analysis.
- Determination of allergen (if necessary).
- Examination of the digestive tract.
- Biochemical research (study of the working capacity of internal organs).
- Glycemic study (screening for diabetes).
- Syphilis test.
- Vitamin B deficiency test
Causes of stomatitis in the tongue
Stomatitis in the tongue develops under the simultaneous influence of two factors: lowering the body's resistance + infection of the soft tissues of the oral cavity or trauma to the mucous membrane of the tongue + infection. A healthy person has his own microflora in his mouth, consisting of various bacteria and fungi that do not harm health under normal conditions (one of the components of saliva, lysozyme is a powerful antiseptic). However, with a decrease in protective functions, the microflora balance is disturbed, which leads to the appearance of stomatitis in the tongue.
There are two main types of stomatitis. At the first, inflammation of the tongue is an independent disease, at the second - a symptom of another pathology. External manifestations in both cases are almost the same, but the causes of development are different.
| Cause of disease | additional information |
|---|---|
| Drug treatment | The disease develops after prolonged antibiotic therapy, taking immunosuppressants. |
| Lack of oral hygiene | Inadequate care of the oral cavity leads to the active reproduction of bacteria. |
| Injuries | Chronic injury to the tip or lateral surfaces of the tongue with an incorrectly selected bracket system, prosthesis, tooth fragment, solid food increases the risk of infection of its mucous membrane. |
| Tooth diseases | Diseases such as periodontitis and tooth decay can lead to stomatitis. |
| Disorders in the digestive tract | Frequent relapses of chronic stomatitis may indicate the presence of stomach ulcers, colitis, gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. |
| Helminthic infestations | The activity of helminths leads to the cyclical appearance of stomatitis. |
| Hormonal disorders | Characteristic for women during pregnancy. |
| Mouth breathing | Mouth breathing is practiced with sinuses blocked due to colds. As a result, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is drained, which increases its susceptibility to infections. |
| Decreased immunity | It is provoked by emotional stress, overwork, malnutrition. |
| Allergy | The allergen may be food, cosmetics, household and hygiene products. |
| Bad habits | The use of alcohol, drugs, smoking leads to exacerbation of symptoms of stomatitis. In this case, it is not necessary to treat the disease, it is enough to abandon bad habits. |
| Heredity | The appearance of aphthous stomatitis is often associated with an inherited predisposition. |
| Lack of iron, folic acid, vitamin B12 | The lack of nutrients in the diet leads to a decrease in immunity. |
| Harmful substances poisoning | Even a single poisoning with harmful chemical elements is fraught with frequent relapses of stomatitis. |
How and what is the treatment of stomatitis in the tongue in adults
Stomatitis in the tongue in adults should be treated comprehensively. The goal of therapy is to relieve the symptoms and causes of the disease. Sometimes drugs are prescribed that accelerate the healing process of erosion. To relieve pain, local anesthetics are used: Anestezin, Asept, Lidocaine, Lidochlor.
 Injections are rarely prescribed, since stomatitis in the tongue can be treated with local medicines with anesthetics: tablets, gels, ointments, sprays. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs include:
Injections are rarely prescribed, since stomatitis in the tongue can be treated with local medicines with anesthetics: tablets, gels, ointments, sprays. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs include:
- Holisal.
- Stomatidine.
- Ingalipt spray.
- Eucalyptus M.
- Evkarom.
- Hexoral spray.
Quickly cure stomatitis in the language of an adult, these medications will help:
- Herpetic stomatitis - Acyclovir, Zovirax, Interferon or Oxolinic ointment.
- Fungal stomatitis - Mykozon, Levorin, Dactarin.
- Allergic stomatitis - Tavegil, Tsetrin, Loratodin.
- Bacterial stomatitis - Penicillin, Lincomycin, Gentamicin.
Preparations that accelerate the healing process of ulcers include Shostakovsky balm, Solcoseryl. The course of treatment of stomatitis in the tongue may include the use of immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, sedatives.
Stomatitis can be completely cured only after getting rid of concomitant diseases, the treatment tactics of which are determined by highly specialized doctors: dentist, otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, immunologist.
How to treat stomatitis in the tongue at home
If the cause of the appearance of ulcers in the tongue is not identified, treatment is based on the relief of symptoms. To get rid of discomfort in the mouth and protect the body from secondary infections, you need to perform the following steps:
- Refuse to drink hot drinks, salty, spicy and citrus products.
- Rinse your mouth with cool water or dissolve ice cubes.
- Rinse your mouth with saline several times a day.
- Use a toothpaste with triamcinolone acetonide.
- Drink more water.
To quickly get rid of stomatitis in the tongue at home, you need to rinse your mouth with decoctions and herbal infusions based on calendula, chamomile or sage, a solution of potassium permanganate, Furacilin, iodine, propolis tincture. Apply aloe juice or Kalanchoe to the affected areas of the tongue.
Preventive actions
The development of stomatitis can be avoided by observing the following rules:
- Brush your teeth twice a day, rinse your mouth after each meal.
- Use a suitable toothbrush and toothpaste.
- Use high-quality prostheses and braces, follow the rules for caring for them.
- Monitor the general condition of the body, nutrition.
- Take walks in the fresh air, organize a full sleep.
Do not try to establish a diagnosis by photo, it is better to consult a doctor so that he conducts clinical trials and determines the exact cause of the disease. The lack of proper treatment can lead to the transition of stomatitis into a chronic condition, which is fraught with gangrenous inflammation of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers.