Dental fluorosis in children and adults: symptoms, treatment, enamel whitening methods, prevention
The content of all structural components in dental tissues should be balanced. An excess of various substances, as well as a deficiency, is very harmful to enamel and can lead to the development of serious diseases. One of those dental fluorosis, the treatment of which is to reduce the amount of fluorine entering the body and restore the appearance of enamel.
Content
Causes of dental fluorosis
The development of dental fluorosis is caused by an excess of fluoride in the body. This trace element is necessary for tooth tissue, but in moderation. Fluoride can enter the body from such sources:
- Drinking water is the main source of fluoride necessary for the body. But in some regions, water contains an excessive amount of water, which is why an endemic form of the disease forms in the local population.
- Food. Seafood is especially rich in this substance.
- Fluoride-containing toothpastes and medicines.
- Contaminated air. In the Russian Federation, there is an increased incidence of fluorosis among the population living near coal-fired TPPs, near glass and metallurgical plants, and fertilizer manufacturing enterprises.
Fluorine most actively affects the forming enamel of molars, which is one of two reasons for the wider spread of fluorosis among children. The second reason is that the daily intake of this substance for a child is much lower than for an adult.
If in a particular region drinking water will contain fluorine in an amount of about 1.5 mg per 1 liter, an adult will consume about 3 mg of this substance every day, which is an acceptable norm and may not affect the state of health in any way. However, people who are more susceptible to fluoride may notice a manifestation of fluorosis even when such an amount of substance is ingested.
An increase in fluorine concentration to 2.5 mg per 1 liter of water is fraught with the development of the disease in almost half of the population. Safe is the content of 1 mg of fluorine per liter of drinking water.
In Moscow, the fluorine content in water is from 0.41 to 1.6 mg / l, the lower value does not reach the norm, the upper one corresponds to it. In Odintsovo, the amount of element in water exceeds the permissible norm and is 1.8 mg / l.
Dental fluorosis in children
Milk teeth can have signs of fluorosis only in rare cases. Doctors believe that for the defeat of this disease of the milk dentition, the water consumed by the child should contain at least 10-15 mg of fluorine per 1 liter.
The rare development of fluorosis in the milk teeth is due to the fact that the mineralization of the dental primordia occurs in the womb, and the placenta is able to retain the main amount of fluoride. But if the baby regularly drinks water with a high content of this substance, then he may develop fluorosis at 3-4 years of age. The likelihood of manifestation of the disease is higher in children who suffer severe diseases or have weakened immunity.
Strengthening of enamel enamel occurs much later, and during this period, fluorine in high concentration can freely act on them.If a teenager or an adult with formed enamel regularly drinks water with a fluorine concentration of more than 6 mg / l or is exposed to the harmful effects of the chemical industry, fluorosis can also affect fully formed enamel.
Symptoms of fluorosis and its form
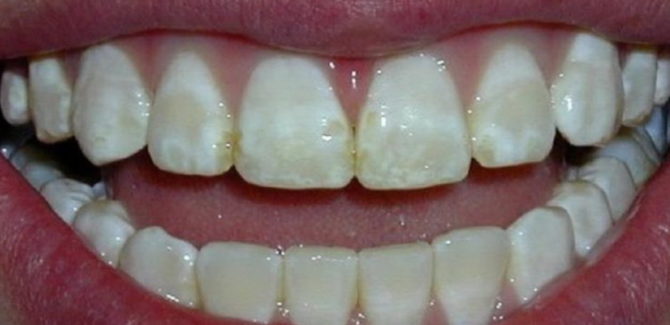
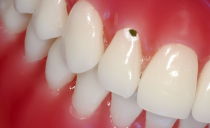
The external manifestations of fluorosis are quite clearly indicated by its old folk names: speckled enamel, spotted enamel. This disease is really accompanied by the appearance of various forms of spots on the teeth. Depending on the features of the location of the spots and the degree of exposure to fluorine on the enamel, these forms of fluorosis are distinguished:
| Fluorosis form | Characteristic properties of spots | Tissue damage |
|---|---|---|
| Dashed line | The spots look like light stripes, hardly noticeable. Incisors and fangs are more often affected. | The disease is not accompanied by loss of dental tissue. |
| Spotted | Yellowish spots in the center of the crowns, similar to a carious lesion. | |
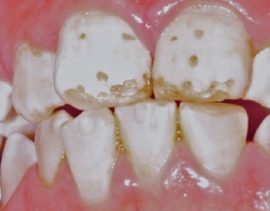
| Cretaceous-mottled | Spots with dots and splashes from light yellow to brown in color and with a rough surface. All teeth may be affected. | |
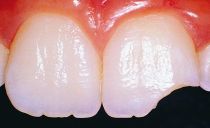
| Erosive | The spots are clearly visible, have signs of erosion and abrasion of enamel, tooth sensitivity is increased. | The disease is accompanied by tooth decay. |
| Destructive | Corresponds to the last stage of the disease, manifests itself not only in pronounced areas of tooth decay, but also in various bone diseases. |
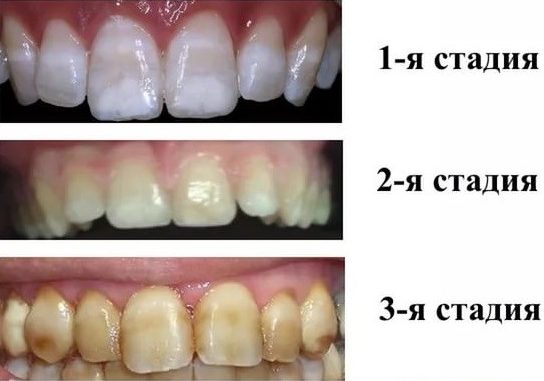
Already during the examination, the dentist can determine the stage of enamel damage: a very mild degree is characterized by almost imperceptible spotting, a severe degree is characterized by more than half deformation and destruction of crowns.
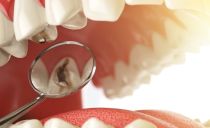
How to distinguish fluorosis from caries
You can distinguish fluorosis from caries by the following signs:
- A carious lesion can affect one or several teeth, and fluorosis always affects the dentition symmetrically: both central incisors or all incisors and both canines.
- Stains with an excess of fluorine can have a whitish color or a brown tint, the enamel can become speckled. Caries does not spread along the surface of the tooth with specks and dots; it affects the tooth enamel with a single spot.
- Sites with signs of excess fluoride can be located on either side of the crown, and tooth decay often develops in depressions and in places where adjacent teeth come into contact.
- Excess fluoride leads to skeletal bone diseases, osteoporosis, and dysfunction of the joints.
Caries can occur with a lack of fluoride, and fluorosis with an excess of it, but these diseases can develop in humans at the same time.
It is quite difficult to distinguish fluorosis from other dental diseases, for example, from enamel hypoplasia, therefore, for accurate diagnosis and competent medical treatment, you need to contact dentistry.
Treatment of dental fluorosis in adults and children
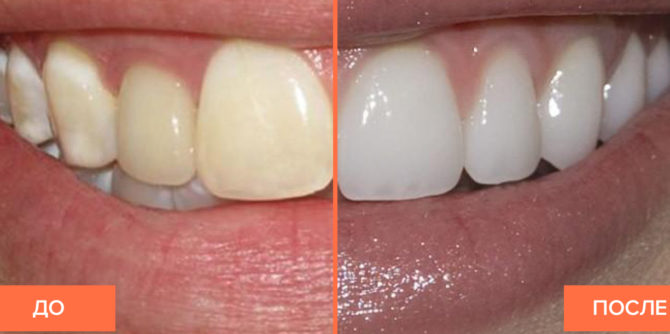
The consequences of an excess of fluoride can be eliminated only through complex therapy. On the one hand, it is necessary to stop the further development of the disease by reducing fluoride intake, on the other hand, to correct the appearance of the dentition. Effectively enamel can be whitened and damaged teeth can be cured only in dentistry using special procedures. To improve the appearance of the dentition at home, you can use special toothpastes, but they only help in the initial stages of the disease.
To effectively treat dental fluorosis, you need to find a source of better drinking water that meets sanitary and chemical standards. People working in hazardous chemical industries may need to change jobs. If endemic fluorosis is common in the area, your doctor may recommend moving to another region. With fluorosis, you must definitely stop using fluorinated toothpastewhich saturates the enamel with excess fluoride.
In the treatment of fluorosis, especially in children, it is very important to diversify the diet by including products that will saturate the dental tissues with other important elements - calcium and phosphorus. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of seafood and fish, you should drink as little green and black tea as possible.
Different forms and degrees of the disease require different approaches to treatment:
- With initial stage fluorosis, teeth whitening is performed. The procedure is performed either at home with the help of special toothpastes (in the treatment of children), or by professional methods in the dentist’s office (in the treatment of adults). To whiten a tooth affected by fluorosis, the doctor treats it with an acid solution, rinses it and thoroughly dries the tooth surface. On a repeat visit, only blemishes are whitened in the same way, without affecting healthy enamel.
After enamel clarification with an acid solution, a side effect occurs - increased tooth sensitivity to irritants.
- Whitening can be done with a laser. Previously, a gel containing hydrogen peroxide is applied to the enamel, and then it is treated with a laser beam.
- Remineralization helps to treat light spots with fluorosis that affects children's teeth. This procedure is carried out in dentistry. Under the influence of electrophoresis, calcium and phosphorus, necessary for the restoration of its structure, penetrate tooth enamel from gel applications. To return to the teeth a natural appearance, 10 to 25 remineralization procedures are performed.
- If the disease managed to cause severe damage to adult tooth enamel, micro-prosthetics with veneers can be used. The installation of light composite fillings on affected teeth is often unsuccessful: they fall out due to an altered tissue structure. Heavily damaged teeth are prosthetized with artificial crowns.
- To prevent tooth decay, both adults and small patients are prescribed preparations containing calcium, vitamins.
Fluorosis Prevention
To prevent fluorosis, it is necessary to suspend the intake of a large amount of fluoride in the body:
- You can use water for drinking and cooking only after a preliminary chemical analysis. Its fluorine content should not exceed 1–1.5 mg per liter.
- Residents of areas with a high prevalence of endemic fluorosis should not abuse seafood, fish, lard, and various varieties of green and black tea.
- For the prevention of the disease, it is better not to use toothpastes containing fluoride compounds. Their presence or absence is indicated on the packaging of the product.
- If the symptoms of an excess of fluoride are already showing up, stop tooth decay. To do this, it is necessary to carry out all the treatment procedures that the doctor recommends - whitening, remineralization, micro prosthetics or prosthetics.
The prevalence of fluorosis in the Russian Federation is high, which is associated with the development of industry, environmental pollution and the lack of quality drinking water. Therefore, it is necessary to control the intake of fluorine in the body, and if there is already an excess, timely measures should be taken to reduce it and to treat developing fluorosis.