Tooth cyst: causes, symptoms, conservative and home treatment
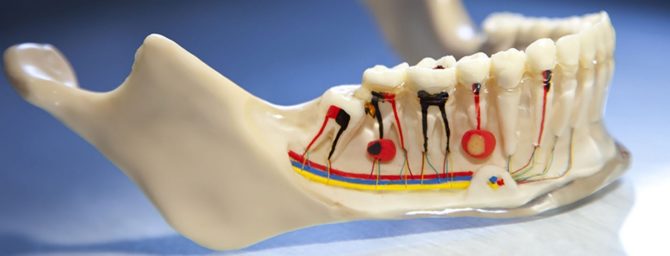
A cyst is a neoplasm at the apex of the tooth root, usually having a rounded shape. A tooth cyst can be treated with both surgical and more gentle methods.
The method of therapy depends on the characteristics of the pathology: cystic formation is always infectious, but is classified by severity, origin, localization and may have a different size, as it is characterized by a tendency to growth. Cysts near the upper teeth grow especially fast - where the bone tissue of the jaw has a very porous structure.
Content
- What is a cyst in dentistry, why is it formed
- Varieties and causes of tooth cysts - table
- How to identify a tooth root cyst: symptoms, signs and photos
- Why is a cyst a health hazard?
- Is it possible to save an affected tooth, methods of treating a dental cyst
- Prevention of tooth root inflammation and cyst development
What is a cyst in dentistry, why is it formed
A cyst is a neoplasm at the apex of the tooth root that looks like a rounded cavity in the bone tissue, lined with a fibrous membrane and filled with purulent contents. The disease develops against the background of inflammation in the dental root canals.
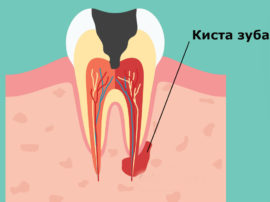 There are several main reasons for the occurrence of a pericarp cyst in a tooth. Pathology develops:
There are several main reasons for the occurrence of a pericarp cyst in a tooth. Pathology develops:
- After a severe course of dental diseases: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis.
- When infection is introduced into the root of the tooth during implantation, filling the canals.
- With complicated teething units, especially wisdom teeth. A teething tooth can injure soft peritoneal tissues, which leads to the development of inflammation and the formation of cystic formation.
- After mechanical damage to the tooth, if an infection has penetrated into an open wound.
- Against the background of ENT diseases: sinusitis, tonsillitis. The consequence of such pathologies can be the penetration of the infection into the oral cavity, and from there - into the soft periodontal tissues.
Cysts in the root of the teeth are also formed under the influence of other factors or under the influence of several of the above. Determining the cause of the development of the pathology and the method of dealing with it should be entrusted to the dentist.
More information about the tooth cyst is described in the video:
Varieties and causes of tooth cysts - table
| Types of Cysts | Subspecies and causes of formation |
|---|---|
| The nature | |
| Inflammatory |
|
| Non-inflammatory |
|
| By origin | |
| Odontogenic | Developing on the background of dental diseases. |
| Neodontogenic | Developing for reasons not related to diseases of the teeth, gums and oral cavity. |
The roots of incisors, fangs, third molars and molars located next to the maxillary sinuses can become inflamed.
Cystic formations can have large and small sizes, their diameter determines the course of treatment: the former must be removed, the latter can be treated.
How to identify a tooth root cyst: symptoms, signs and photos
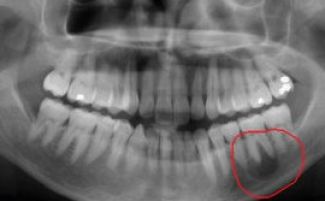
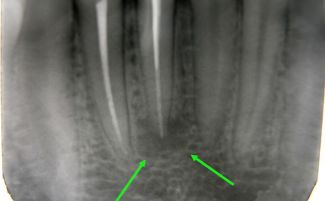
It is problematic to detect the presence of a cystic mass without using an x-ray. Without examination, the patient can detect only a large cyst of the tooth, it acquires such significant dimensions at the final stages of development. During this period, the pain becomes so unbearable and sharp that many patients go to the doctor because of it, and not because of the external manifestations of the disease.
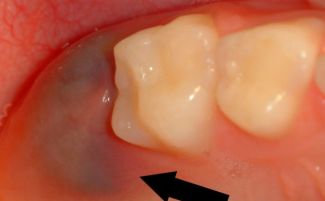
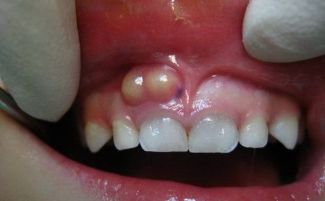
A tooth brush can be recognized by such signs:
- Swollen and reddened gums in the area of the affected tooth.
- The appearance on the surface of the gum formation, which has a pale yellow or grayish tint and a red rim at the edges.
Auxiliary symptoms
Treatment of a tooth cyst is complicated by the absence of symptoms in the early stages of its development. The formed purulent bladder may not manifest itself for a long time, during such a period the disease can be detected only by accident - when examining an X-ray of neighboring molars, canines or incisors.
With the development of the inflammatory process, symptomatology also progresses: first there is a slight pain when pressing on the gum or biting, then the pain sensations intensify and begin to give to the jaw.
Auxiliary symptoms of a tooth root cyst:
- Swelling of the cheeks, redness and swelling of the gums in the area of the cyst cavity. With localization of the cyst at the root of the anterior tooth, a slight swelling of the lip is possible.
- Aching dull pain in the gums.
- Headaches that occur when the cyst is located in the area of the roots of the upper teeth - next to the maxillary sinus. With this localization of the cystic formation, accumulation of pus in the nasal passages is possible.
- The formation of a fistula is a channel between the purulent cavity and the gingival surface, which gives an outlet to the accumulated purulent masses. Fistula is formed in the late stages of the development of the disease - when a purulent capsule bursts.
- Possible increase in body temperature.
How to identify a tooth cyst using x-rays, a difference from granulomas
A tooth cyst is easily confused with a granuloma - a dangerous neoplasm similar to the cystic infectious nature of origin, the presence of purulent contents and localization at the tooth root. But these diseases can be distinguished using an x-ray: with a cyst, a capsule with purulent exudate is formed, and with a granuloma, there is no capsule, since it represents focal inflammatory proliferation of connective tissue - that is, its borders are not so clearly visible on x-rays.
Why is a cyst a health hazard?
Cyst not removed in time, constantly growingAs a result, inflamed bone tissue is destroyed and replaced by connective tissue. At this stage of the development of the disease, complications can occur that lead to tooth loss.
The main consequences of a tooth cyst:
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- The development of chronic sinusitis, which is manifested due to the germination of a cyst in the maxillary sinus.
- The development of sepsis.
- Penetration of infection into the bloodstream and spread to internal organs.
- Fracture of the jaw, which can occur spontaneously due to an increase in cystic formation and thinning of bone tissue at the base of the jaw.
- Purulent inflammation of the cystic neoplasm, in which fistulous passages, an abscess on the gum or cheek, phlegmon of the neck, periostitis or osteomyelitis can form - inflammation and fusion of the jaw bone, developing in proportion to the growth of the cystic capsule.
If the patient notes the appearance of a purulent smell in the nose, then the usual inflammatory process has turned into a purulent one.In addition, such a dangerous symptom may indicate the germination of a cystic neoplasm in the maxillary sinus.
Is it possible to save an affected tooth, methods of treating a dental cyst
Previously, the cystic formation was removed together with the tooth, but today the pathology is treated with new traditional methods, which allows to save the dental unit. It is necessary to remove a diseased tooth only in extreme cases, most often the pathology is treatable.
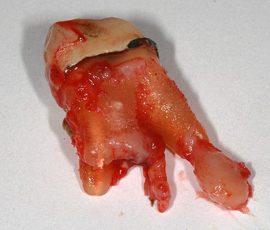
How is the surgical treatment performed? What does a removed tooth look like with a cystic capsule?
Usually, cystic lesions are treated surgically, since in the early stages of the disease is rarely determined. Removal of the neoplasm is indicated in such cases:
-
If the root of the tooth is inflamed with a pin.
- If a crown is placed on the affected tooth.
- If the cyst has a size larger than six millimeters in diameter.
- If the patient's jaw is inflamed, or other consequences have developed.
- When the patient is often bothered by toothache, and if the gums in the area of the affected tooth unit are swollen.
A tooth cyst is removed under local anesthesia, so patients do not experience pain. There are several methods of surgical treatment of cystic education:
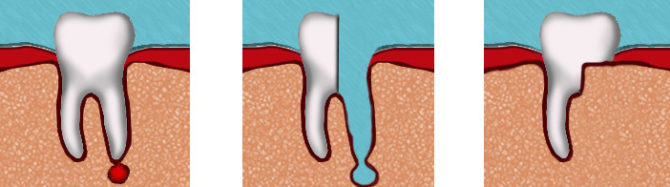
- Cystectomy The cystic bladder is removed with a shell from the connective tissue and the apex of the tooth root. If the inflamed tooth has one root, it is filled. And if several - delete. After the operation, the dentist closes the wound and prescribes antibiotics and antiseptic drugs to the patient to continue therapy at home. Typically, a cystectomy is performed if the cyst has developed in the upper jaw and has grown to a large size.
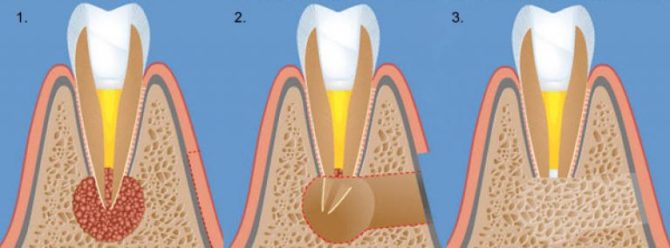
- Cystotomy. A surgical treatment method in which only the anterior wall of the cystic cavity is removed. The disadvantage of cystotomy is the long healing time of tissues after surgery. Such an intervention has to be carried out in two cases: if the base of the jaw has thinned (provided that the cyst appeared near the lower tooth), if the bone bottom of the nasal cavity is destroyed or the palatine plate (when the cyst is near the upper tooth).
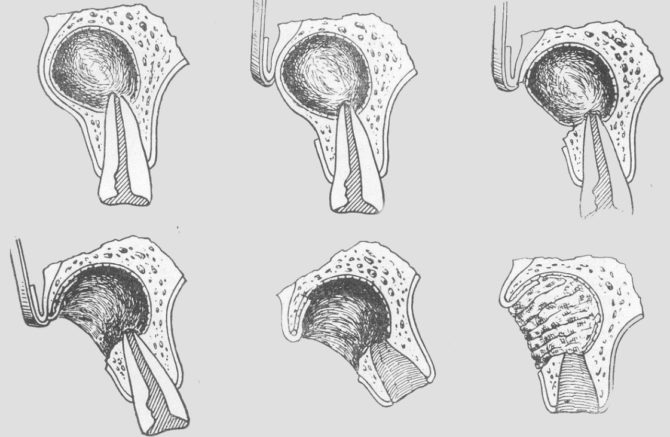
- Hemisection. With this method of surgical intervention, the dentist must remove the cyst, tooth root, and part of the affected crown.
What to do after surgery
The condition of the patient after these operations improves after about a day, if after this period acute pain persists in the area of the incision, you need to visit dentistry again. Swelling in the operated area begins to subside only by 2-3 days.
After removal of the cystic formation, it is impossible to make warming compresses and be treated with aspirin. Under the influence of heat, inflammation can occur in the operated area, since under such conditions pathogenic microbes multiply faster. And acetylsalicylic acid can provoke bleeding.
Treatment of tooth cysts without removal
Therapeutic treatment of the affected tooth is performed without removing the cyst and involves antiseptic treatment, cleaning and filling of the tooth. An alternative method of therapy with which dentists preserve a dental unit is the introduction of a calcium-copper suspension into the root canal and exposure to it with an electric current of low power.
You can save a tooth through therapeutic treatment in such cases:
- If the root canals of the affected dental unit are not sealed, and the doctor does not need to unseal them to gain access to the cyst.
- If the root canal is not completely filled.
- If the diameter of the cyst is less than six millimeters.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of cysts on the root of the tooth is carried out in several stages:
- First, the dentist must make a hole in the tooth crown to gain access to the canal and cystic cavity.
- Then, certain drugs are introduced into the cavity that affect the cystic capsule.
- Pus in the cavity is pumped out. And the vacated place is filled with special paste, which is needed to accelerate the regeneration of bone tissue.
- At the end of the procedure, the dental canals are filled, and the cavity in the crown is closed with a seal.
A few months after the procedure, the patient must come to the clinic for an examination, which will show if the bone tissue has recovered and if a secondary infection has developed in the tooth. After therapeutic treatment of cystic formation, relapses are more common than after surgery.
Laser treatment
A tooth with a cyst can be cured with a laser method. Thanks to this method of therapy, doctors manage to remove the cystic cavity, save the tooth and prevent its repeated inflammation. Healing after laser treatment is faster than after drug treatment of the channels. In addition, such therapy will protect the patient from the development of complications.
Stages of laser therapy:
- Removing the filling or opening the crown and expanding the dental canals.
- Introduction to the channels of a special dental laser.
- Disinfection of inflamed tissues and "destruction" of the cyst with a laser.
- Antiseptic treatment.
- Canal filling and crowns.
The advantages of laser exposure to the root cyst of the tooth include the impossibility of introducing infection into the canals due to the non-contact procedure, the absence of pain, disinfection and prevention of inflammation in the oral cavity, the possibility of complete preservation of the tooth, rapid healing and rare development of complications.
Among the shortcomings of the therapeutic method are its high cost and low prevalence: the procedure is carried out only in clinics in Moscow and some other large cities.
Within 4 hours after the treatment of dental roots with a laser, you should not eat or drink. In the early days, it is necessary to use antiseptics that prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
What to do to eliminate a tooth cyst at home
The cyst cannot be cured with folk remedies, home therapy is applicable only in relation to granuloma, since such a formation does not have a purulent capsule and can dissolve without medical intervention. You can get rid of a cyst only in the dental office, and it’s better not to delay visiting it so that you don’t have to pull out a bad tooth due to the growth of the tumor.
Treatment of tooth cysts at home with folk remedies can be carried out only after removal of the affected tissues in the clinic, such therapy will help prevent secondary infection of the tooth root. You can relieve soreness, swelling and prevent inflammation with the help of such folk remedies:
- Herbal infusions of eucalyptus, sage, calendula. The medicine for rinsing the oral cavity should be made from 2 tablespoons of raw materials and 100 ml of water.
- Alcoholic extracts of propolis, calamus root, calendula, aloe.
- Applications for gums in the localization of puffiness with the use of aloe or garlic gruel.
- Saline and sesame oil for rinsing the mouth.
Prevention of tooth root inflammation and cyst development
It is 100% impossible to protect yourself from the appearance of a cyst, but there are preventive rules, adhering to which you can reduce the likelihood of its development:
- A regular visit to the dentist - at least twice a year.
- Good oral hygiene.
- Attentive to general health and maintaining immunity.
- Avoidance of injuries to the jaw and teeth.
- Fast caries treatment.
If the cystic formation still developed, you need to start tooth treatment as soon as possible, since pathology diagnosed in the early stages is subject to drug therapy and does not entail tooth loss.