Tooth periodontitis - what is it and how to treat it
Periodontitis is when pathological process affects the root tissue of the tooth. Successful therapy of an ailment directly depends on the correct classification of the type of inflammation, the establishment of the causes of occurrence, timely contact with a specialist.
Content
- The physiological significance of periodontal
- Pathogenesis
- Localization of periodontitis
- Causes
- How to recognize a periodontal lesion
- What is the difference between pulpitis and periodontitis
- Diagnostic procedures for periodontitis
- Methods and stages of treatment of periodontitis
- Tooth periodontitis is serious
The physiological significance of periodontal
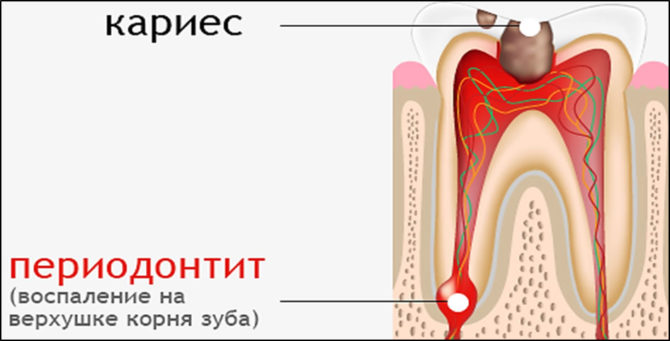
A small anatomical educational program will help to understand what tooth periodontitis is and how to treat it. Any tooth is surrounded by a morphologically complex periodontium. It includes: gums, alveolar processes, root cement, periodontium, the network of blood and lymph vessels, and the neuro-receptor apparatus.
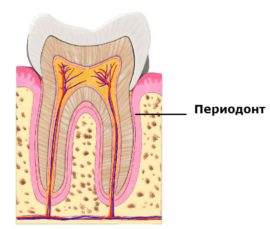 A tooth periodontium is a soft tissue with a width of 0.20–0.25 mm, located in the slit-like space between the alveoli plate and the root cement. It passes through the apical and marginal dental departments, its middle part. Periodontal fibers perform several functions at once:
A tooth periodontium is a soft tissue with a width of 0.20–0.25 mm, located in the slit-like space between the alveoli plate and the root cement. It passes through the apical and marginal dental departments, its middle part. Periodontal fibers perform several functions at once:
- regulate mechanical pressure;
- hold the tooth in the alveolus;
- provide periodontal nutrition through the vasculature;
- provide reparative capabilities of the tooth, nearby areas;
- support homeostasis of surrounding tissues, serve as a barrier to infection.
Such multifunctionality has a “side” effect: periodontium often becomes a target of inflammation.
Pathogenesis
Inflammatory diseases of the dental tissue are secondary. Blessed the soil for the development of periodontitis is chronic caries or pulpitis. The course is complicated by infection. Here's how the “average” tooth collapses:
- Bacteria or spores of fungi penetrate to the root through natural anatomical cracks or minor injuries, carious openings.
- Pathology first affects the pulp, and then goes along the periodontal tissue.
- At the apex of the root, general inflammation develops, passing into foci of a purulent abscess.
- With the generalization of dental periodontitis, cysts with serous and then purulent exudate are formed in the upper basal part. In advanced cases, the gum bone is destroyed, and the person is left without teeth.
Periodontal / periodontal lesions are far from harmless. With a blood stream, infectious agents and products of the inflammatory process spread throughout the body. As a result, lesions of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs are possible. Endocarditis, diseases of the ENT organs develop.
Localization of periodontitis
Depending on the focus of inflammation, there are:
- Marginal variant of the development of the disease (regional). Here, the primary lesion is located on the border of the gums with subsequent spread to adjacent tissues.
- Apical type of course (apical), when the pathology is localized at the apex of the roots of the tooth.
When the bone decays in the basal region, the cavity is filled with purulent granules. Usually the papule erupts on its own, and pus spills out. As a result, a fistula or granule appears with the formation of periodontal cysts.
Causes
- Traumatic destruction. Biting off hard objects, cracking nuts, and strong blows to the jaw sometimes result in driving teeth deep and chipping. This is indicated by a sharp pain.
- Violation of the protocol of medical manipulations.For example, filling channels with particles of potent drugs in the root region. Problems arise from arsenic, formalin, phenolic drugs.
- Bacterial inflammation of the periodontium, which occurs when the infection spreads from old carious or pulpitis foci, badly treated teeth.
How to recognize a periodontal lesion
Symptoms of periodontitis of teeth depend on the course of the disease. The following forms are distinguished:
- sharp process;
- chronic;
- relapses of an old pathology.
Acute periodontitis
The most painful option. A person from pain is not able to sit, lie and think normally. Much depends on the individual characteristics and nature of the process, but the general symptoms of primary periodontitis are as follows:
- sharp or aching pain;
- with chewing load, the discomfort increases;
- taking analgesics is not very effective: gradually the pain intensifies and changes in character to a sharp pulsation with a short calm;
- a specific sign of periodontitis is the illusion of a tooth moving up;
- general malaise, mild fever, sometimes chills.
With an increase in inflammation, the amount of purulent exudate increases. Pain with active periodontitis always gives to neighboring areas: infraorbital region, ear, temple, jaw. Swelling and hyperemia of the soft tissues surrounding the affected tooth appear.
If pus does not leak out, the condition worsens. Swelling increases, temperature rises, life-threatening complications develop - osteomyelitis, phlegmon, sepsis.
Chronic periodontitis
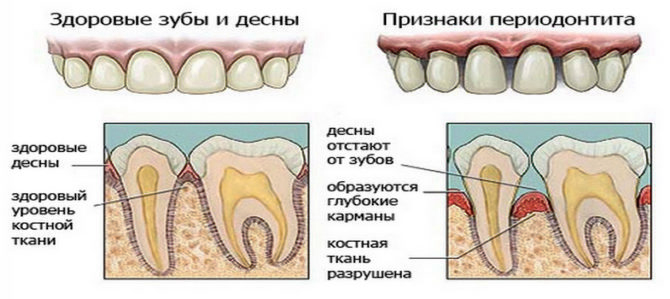
There are no pronounced clinical manifestations of the chronic form of inflammation. From time to time, the lingering symptoms of periodontitis are supplemented by light aching sensations that subside on their own or after an analgesic pill. And only a dentist on examination diagnoses a protracted disease according to the following manifestations:
- Grayish tooth shade.
- Fistula on the affected gum. Visually, the formation is presented in the form of a bubble with milky gray contents. For the doctor, this is a signal about the accumulation of exudate in the bone tissue.
- A dull sound when tapping the crown of a tooth.
- The smell of rot from the mouth.
Chronic periodontitis is in most situations the patient’s "merit". Afraid of visiting a doctor, people prefer to swallow painkillers in batches and wait for improvement. When the loading dose stops the pain, the person believes that the tooth “passed by itself”. Alas, this is a fallacy. Sooner or later, “dormant” inflammation will remind itself of a relapse.
Often hidden periodontitis is the result of unsuccessful endodontic treatment. Here are just some of the medical disorders:
- with poor-quality treatment of the root canals, toxic exudate enters the tissues;
- partially absorbable pastes are used in the canal.
All this leads to infection of the periodontium with anaerobic bacteria.
Symptoms of exacerbation
The manifestations of the activation of inflammation are almost no different from the acute course of periodontitis. Sometimes an exacerbation of the chronic process can be confused with the primary pathology. However, secondary tooth periodontitis has special symptoms:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- sharp darkening of the crown, its destruction;
- tooth loose.
To clarify the stage of tooth periodontitis and treatment tactics, an examination of the affected area is performed. Depending on the nature of the process, complex diagnostics are used or limited to one method.
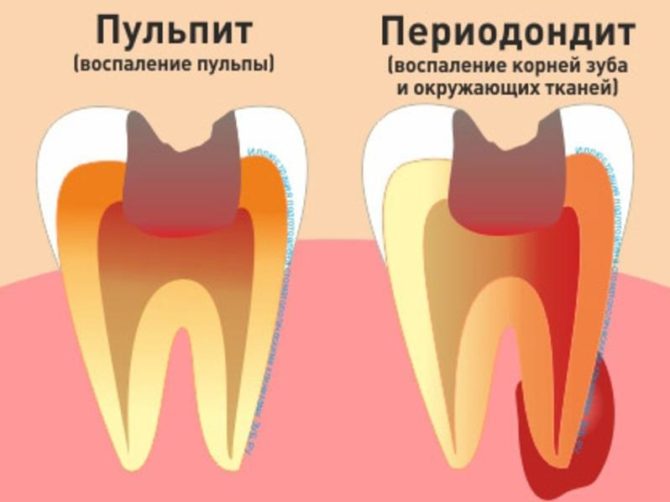
What is the difference between pulpitis and periodontitis
Similar symptoms of pulpitis and periodontitis stem from the inflammatory nature of these diseases. In both cases, dental tissue is affected. The differences lie in the localization of the process and the visible manifestations of pulpitis:
- Regardless of the stage, the focus of inflammation is concentrated in the pulp - soft tissue inside the crown. Changes in the surrounding areas are not observed, the crown is firmly held in the alveolus.
- Specific pulpitis differs from periodontitis in the acute reaction of a diseased tooth to a temperature stimuluslack of discomfort when tapping.
- There is no pronounced difference in the color of the crown from the general tone of the dentition.
- Opening the pulp in the chronic form of the disease is extremely painful, the area bleeds slightly.
Since periodontitis is often a complication of pulpitis, an accurate diagnosis is made after a differentiated examination.
Diagnostic procedures for periodontitis
Modern dentistry has the following methods of diagnosis:
- electroodontometry (EDI);
- radiography.
EDI
Instrumentally measures the sensitivity threshold of the pulp. A low threshold for tissue response to an irritant indicates the likelihood of inflammation and tissue necrosis. Electrodontometry allows you to:
- Distinguish running pulpitis from periodontitis. An indicator of 25–95 μA confirms pulpitis.
- Determine the periodontitis stage. Thus, 100–160 μA indicate a chronic periodontal lesion, data of 180–200 μA are observed in acute form or in exacerbation.
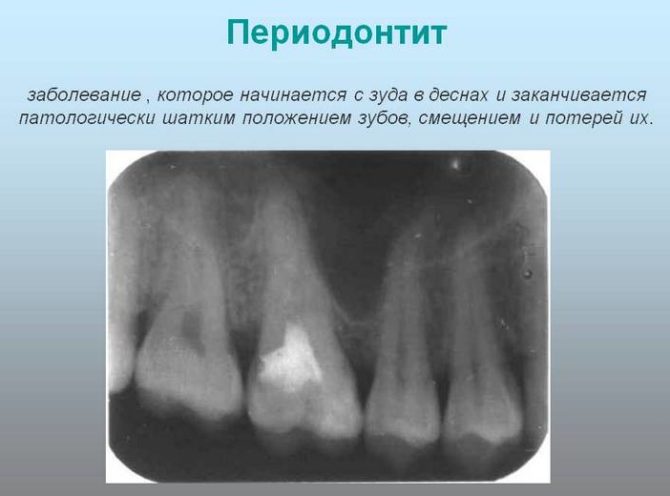
X-ray
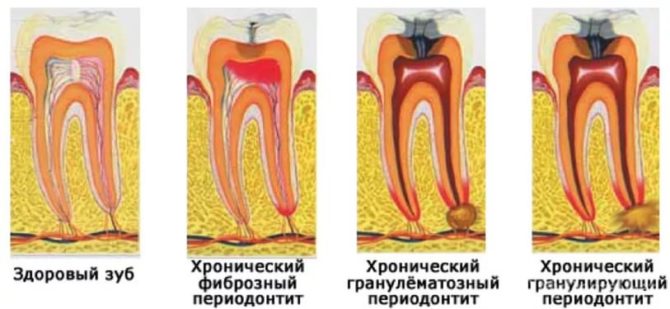
Provides accurate information about the course of chronic periodontitis, clarifies its form. Depending on the type of lesion, the following picture is visible on the x-ray:
- With the fibrous process, the periodontal gap is changed, the root cement is unevenly thickened. If the tooth has been treated before, you can notice the remains of the fillings of the channels.
- Granulomatous development is characterized by a destructive lesion of a round or oval shape with pronounced boundaries.
- In the case of a granulating course of periodontitis in the root apex, foci of bone discharge are noticeable with a violation of the pattern. Irregular changes without a clear edging.
The roentgenogram of acute periodontitis is not very informative: pathological changes are not visible. In rare situations, an expansion of the periodontal gap in the area of the bone of the hole is observed.
Using X-rays, you can evaluate the quality of dental care once provided, find out the causes of dental problems and think out a treatment plan.
Methods and stages of treatment of periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis depends on the symptoms and form of the disease. Conservative and / or surgical methods are selected.
Conservative assistance
- drug and manipulation effects;
- physiotherapy.
The stages of treatment of periodontitis will require at least a 3-fold visit to the clinic. The exact duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
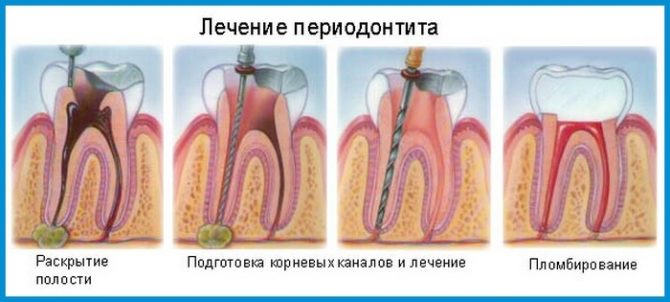
Drug and manipulation treatment
Therapy regimen on the first day:
- radiography and other diagnostic procedures;
- pain anesthesia;
- providing access to channels by drilling areas affected by periodontitis;
- removal of a nerve (if the tooth has not been treated before), removal of old fillings;
- elucidation of the anatomical features of the canals;
- their expansion, leaching of pus and treatment of the cavity with antiseptics;
- placement in the channel of medical paste, filling the crown of the tooth with temporary material.
Dental lesions always lead to periodontal infections, so antibiotics are indispensable. The doctor will prescribe the necessary drugs additionally.
After 2-3 days you will need:
- unseal the canals and remove the paste;
- rinse the root cavity with antiseptic solutions;
- carry out temporary filling of the canals.
In the third visit, control pictures of the tooth are taken, then temporary material is removed and the cavity is again washed with antiseptics. If it was possible to cure the canals and eliminate periodontal inflammation, put a permanent filling to the top of the tooth.
Physiotherapy
In the case of a calm course of chronic periodontitis effective:
- basal electrophoresis;
- laser beams;
- UHF
Periodontitis in the acute phase is an absolute contraindication for hardware exposure.
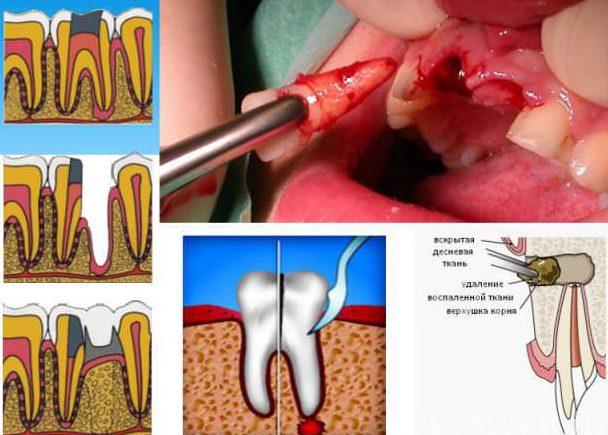
Surgery
It is used when therapeutic methods have not brought the expected result. The main methods of intervention:
- incision of the gums with periodontitis;
- resection of the root or part thereof;
- radical tooth extraction.
An emergency incision (gigivotomy, dissection) is necessary if the infection has reached the basal tip with a purulent flux. When root pathological formations (phlegmon or cysts) are treated, a planned gum dissection is performed.
If the inflammation has partially affected the tooth, a gentle surgery is considered. In this case, only destroyed tissue is resected. The root and part of the crown are retained for subsequent prosthetics.
Tooth periodontitis is serious
A diseased tooth is a powerful source of bloodstream infection. If you drag out the time, the consequences can be most dire. Until blood poisoning. Then it will be necessary to save not the tooth, but its owner.
But it’s better not to bring the matter to periodontitis at all, but to visit the clinic on time. Today, intelligent specialists and modern equipment are not only in Moscow, but also in regional centers. With timely help, even a severe defeat can be eliminated without extreme measures.