White plaque in the child's tongue: causes and treatment methods
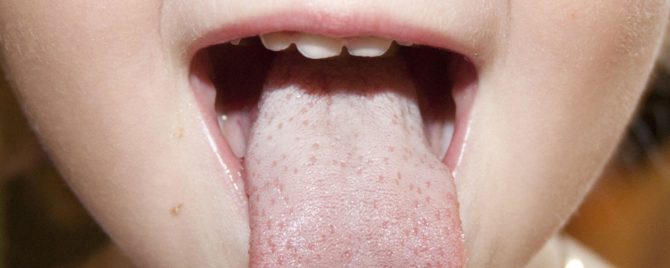
White plaque can appear in the child’s tongue, both for natural physiological reasons and against the background of dental or some common diseases. The back and sides of the tongue are covered with keratinizing epithelium. Its desquamation leads to the formation of a thin whitish film in the tongue, which is the norm. But if the plaque covers the tongue with a thick layer or spots, has an unusual color, is accompanied by other symptoms, you should take the baby to the pediatrician.
Content
- Why does a plaque appear in the mouth of infants
- Causes of plaque in the mouth in children of all ages
- Causes of a morning plaque in the mouth
- White plaque on the child’s tongue and bad breath
- A gray coating on the child’s tongue
- Indications for urgent examination by a doctor
- Treatment of white plaque in the tongue of a child
Why does a plaque appear in the mouth of infants
If a white coating appears on the tongue of an infant, it is necessary to assess the general state of its health. If the baby is active, eats well and puts on weight, there is nothing to worry about. The non-standard color of the tongue of the newborn may be due to breastfeeding. To wash off the remaining milk from the mucous membrane of the baby’s oral cavity, you need to give him to drink 2-3 tablespoons of chilled boiled water.
White lumps in the mouth of a healthy baby can appear due to regurgitation after feeding. In addition, the tongue may whiten before teething.
In no case should you scrape off the plaque from the tongue, since there is a high probability of injury to its mucous membrane.
Overheating in Komarovsky
According to the famous pediatrician Komarovsky, a plaque in the baby’s mouth can appear up to a year due to overheating of the body. To eliminate the symptom, you need to undress the baby and wipe his body with gauze soaked in cool water.
To prevent overheating of the body, the baby should ventilate the living room. Do not use heaters, store carpets and other dust collectors in the apartment. You can purchase a standard humidifier, but even with it you need to carry out wet cleaning in the nursery at least once a day.
Inflammatory process
Plaque in the tongue in children aged from a month to 1 year can be caused by many inflammatory diseases that require medical treatment. In the presence of auxiliary symptoms indicating inflammation, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician. Only he will be able to conduct an otolaryngological examination of the baby, appropriate laboratory diagnosis and identify the causative agent of the disease.
Causes of plaque in the mouth in children of all ages
White plaque in the tongue in children and adolescents can indicate such diseases:
- gastrointestinal disorders: dysbiosis, constipation, colitis, enteritis, gastric acidity, gastritis, peptic ulcer, biliary dyskinesia, reaction of the stomach to an unexpected change in diet or early feeding;
- CNS pathology;
- thrush;
- diabetes;
- helminth infections;
- asthma;
- viral stomatitis, which manifests itself if the child is sick with chickenpox, scarlet fever, measles, herpes and other viral diseases;
- decrease in hemoglobin in the blood;
- acute respiratory infections;
- allergy to medications taken, most often antibiotics;
- immunodeficiency, decreased immunity;
- hypovitaminosis;
- cold;
- anemia;
- glossitis;
- infectious diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
- insufficient oral hygiene.
With the listed diseases, a white coating on the tongue is an auxiliary symptom, therefore, it requires the use of complex therapy. It will disappear after eliminating the root cause of the pathology, and only a pediatrician can establish it based on the results of laboratory tests and a visual examination.
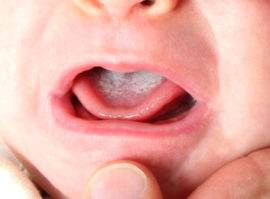
Thrush (candidiasis)
Oral candidiasis is characterized by the presence of small dark white granules in the oral cavity, which eventually acquire a curdled structure and are transformed into flakes. Localization of plaque is the central part of the tongue and the inside of the cheeks.
The disease is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (Candida). The auxiliary factors contributing to the development of pathology include:
- weakened immunity;
- prematurity (applies to newborns);
- long-term use of antibiotics and glucocorticosteroids;
- insufficient oral hygiene by the child or mother during breastfeeding.
Flu and ARI
White plaque in the tongue can occur with SARS, flu and colds. These diseases lead to a decrease in immunity, dehydration and intoxication, which causes a discoloration of the tongue. However, usually acute respiratory viral infections and colds are identified by other, more pronounced symptoms: fever, sore throat, runny nose, weakness.
A whitish coating may appear in the mouth at the initial stage of any viral disease due to an increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood and the multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity often develops against the background of intestinal dysbiosis. In addition, a violation of the microflora in the mouth can occur due to prolonged antibiotic therapy.
At first, with dysbiosis, there are no signs of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, although they are already actively propagating. If you do not treat the disease at this stage, the following symptoms may appear:
- bad taste;
- burning in the oral cavity;
- smell from the mouth;
- the appearance of ulcers, wounds, pimples on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
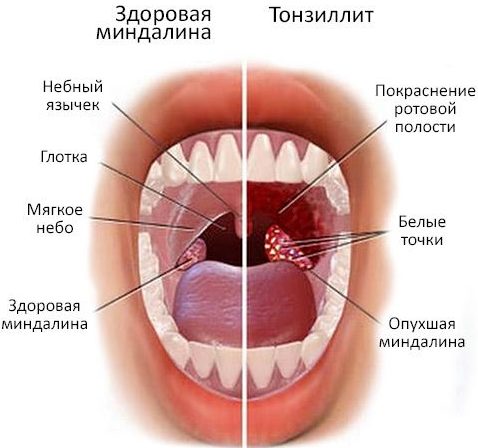
Angina (tonsillitis)
Tonsillitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the tonsils. Bacteria that accumulate on the glands can spread to the root of the tongue, leading to a partial change in its color. The disease is often accompanied by fever and swollen lymph nodes.
Appearance of white color in the tongue may mean that angina has passed from an acute form to a chronic one. Also, such a symptom may indicate an incorrectly selected method of treating tonsillitis, uncontrolled intake of antibacterial drugs and their repeated use several months after the previous therapy.
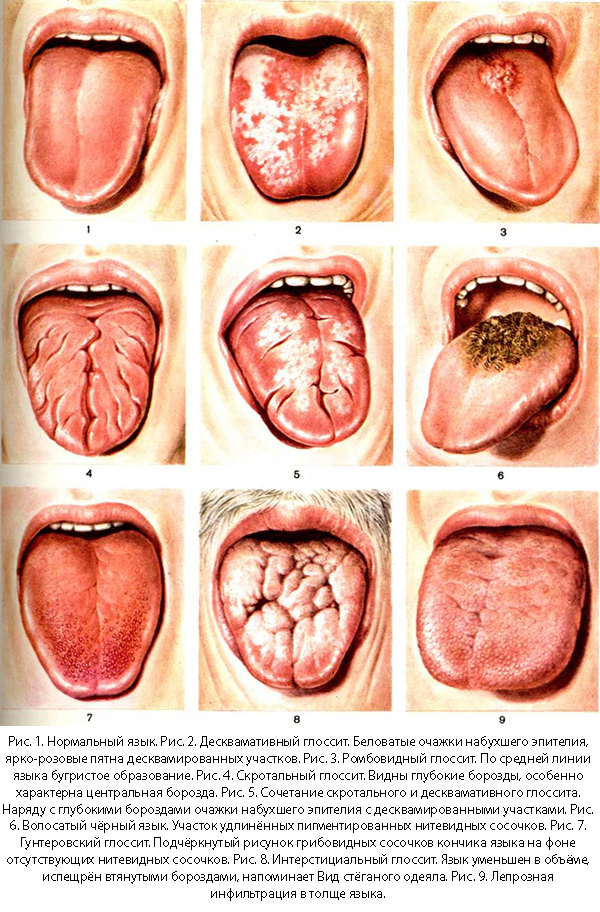
Glossitis
The reason why a white coating appeared on the child’s tongue could be glossitis - a type of stomatitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue, most often manifested in babies from three to five years. The disease can have a different nature:
- allergic - develops under the influence of an allergen;
- bacterial - manifests itself in lesions of the tongue with staphylococci and streptococci;
- fungal - develops with the active reproduction of Candida fungi;
- herpetic - manifests itself with activation of the herpes virus of the first or second type.
Causes of a morning plaque in the mouth
White plaque in the child’s tongue that occurs in the morning does not require treatment, since the reason for its formation is natural physiological processes. The salivary glands at night work in a gentle mode, which means they produce less saliva, which performs a protective function. As a result, various microorganisms are activated in the oral cavity. And the raid is just a product of their life.It is easily removed during standard hygiene procedures and does not appear in the afternoon.
A morning raid on the tongue may mean that the teenager is smoking. In this case, a comprehensive treatment is indicated, including giving up a bad habit, detoxification therapy and restoring the body's water balance.
White plaque on the child’s tongue and bad breath
White plaque on the child’s tongue may be accompanied by bad breath. Its appearance is associated with an excess of the concentration of hydrogen sulfide, which is released as a result of reproduction and other activities of anaerobic bacteria. The following factors lead to increased odor:
- caries and periodontal disease;
- violation of the activity of the digestive tract;
- tonsillitis;
- kidney and gall bladder diseases;
- insufficient amount of protein food in the diet;
- mental stress.
A gray coating on the child’s tongue
A thick gray coating on the root of the child’s tongue may indicate a stomach ulcer. In addition, this plaque color may be due to diabetes. The development of this disease is indicated by acetone breath.
Indications for urgent examination by a doctor
If white plaque in the mouth is not associated with breastfeeding and overheating, the doctor should be shown to the child. You can not wait for a scheduled appointment and call an ambulance, but only if you have the following symptoms:
- hyperemia and swelling of the tongue on one or two sides;
- fingerprints appear on the surface of the tongue;
- differentiated color of the tongue: in the center it is white, brown or yellowish gray, and on the sides it is bright red;
- violation of taste perception;
- a strong increase and redness of the papillae;
- the appearance of pain and burning;
- it is difficult for the child to speak;
- sharp darkening of the tongue to green, brown or black;
- temperature increase;
- the occurrence of an unpleasant putrefactive breath.
Treatment of white plaque in the tongue of a child
It is categorically impossible to independently treat white plaque in the child’s tongue. Improper therapy, especially limited to the use of folk remedies, is fraught with serious complications. If the color of the tongue changes, you need to contact a pediatrician, only he can correctly identify and cure the causative disease.
Hygiene
Parents should ensure that the child follows the basic rules of oral hygiene, which include:
- brushing your teeth at least twice a day;
- regular mouthwash with plain water;
- timely treatment of gingivitis and caries.
It is necessary to choose the right hygiene products, as some of them may develop an allergy in the child. Proper oral hygiene is the basis for the prevention of white plaque in the mouth in a healthy person.
Candidiasis Treatment
Thrush of the oral cavity is treated with the following medications:
- Amphotericin.
- Diflucan.
- Beefiform.
- Clotrimazole.
The form of release of the drug and the plan for its administration depend on the severity of the disease. Medications are prescribed by the pediatrician.
Treatment of bacterial and viral glossitis
Bacterial glossitis is treated with antibacterial drugs, viral - with antiviral drugs. In addition, parents should treat the tongue, gums and the inside of the child's cheeks with antiseptics (Chlorhexidine), rosehip oil with vitamin A, give him anti-inflammatory (Romazulan, Korsadil) and antihistamines.
Most often, a white plaque in the tongue in children indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the mouth. To get rid of this symptom, you need to strengthen the immune system and cure the underlying disease that led to the development of inflammation.