Flux in a child: causes, symptoms, treatment, what can be done at home
Diseases of the oral cavity equally often occur in both adults and children. But childhood illnesses make people worry more than their own, as many parents do not know what to do if a flux has popped up on the gum of a child, as many medications are contraindicated. However, the task of adults is simple - to timely identify the disease and take the baby to the dentist.
Content
Etiology of flux in children
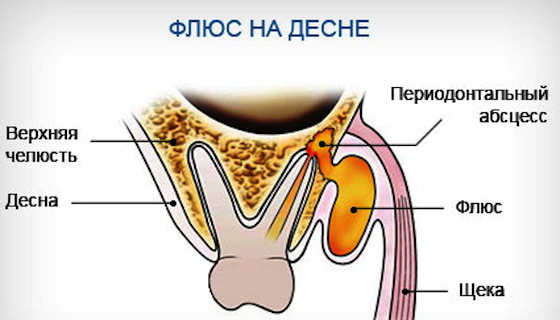
Flux or purulent periostitis is an infectious disease that affects tissues at the apex of the tooth root and in the subgingival and periosteal zones of the jaw. Pathology is quite dangerous. Due to poorly developed immunity in children, flux develops more rapidly than in adults, and it is much more difficult to treat.
The most common cause of the development of the disease is the penetration of infection from the oral cavity or a diseased tooth to the tissues of the periosteum. As a result, the inflammatory process begins, accompanied by swelling of the gums.
Periostitis often proceeds in a severe form, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature and a rapid increase in an abscess on the gum. In this case, immediate intervention by a specialist is necessary.
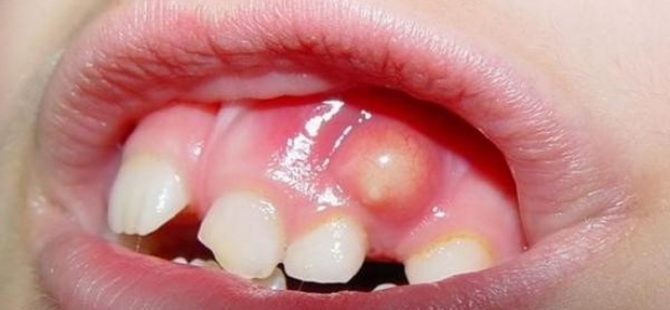
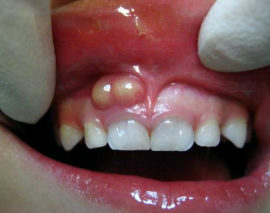
In the early stages of periostitis, a kind of pimple forms on the gum. Gradually, its size increases, the gum and cheek swell, pain appears when touching a diseased tooth. A purulent process is of particular danger to health, since pus enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Causes of flux in children
Flux can develop in a child under the influence of the following factors:
- Poor adherence to oral hygiene. Teeth are cleaned either improperly or irregularly.
- The development of caries.
- Injury to the tooth or jaw.
- Genetically acquired pathology, which is transmitted from the mother and occurs during intrauterine development.
- Permanent mechanical damage to the gingival mucosa.
- Dentist mistakes during dental treatment.
The risk of developing periostitis is increased due to child mobility and activity. Kids often hit, pull dirty toys in their mouths, and brush their teeth poorly. All of these factors create ideal conditions for the development of infection in the mouth.
Flux does not always occur immediately after infection penetrates the periosteum. The inflammatory process may begin after some time during a period of weakening of the immune system.
The danger of flux for preschool children
Some believe that milk teeth should not be treated. After all, over time, they will fall out anyway, and with them the problems will disappear. Because of this negligence, dentists often encounter a neglected form of flux in children 6-7 years old. During this period, milk teeth begin to be replaced by permanent ones, and often the latter grow already affected by caries.
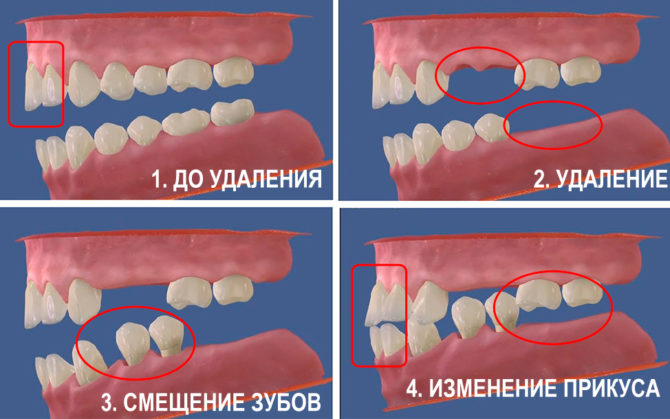
Failure to treat tooth decay and filling a temporary tooth can lead to more serious complications: the infection will spread to the rudiment of a permanent tooth or even to the baby’s internal organs.
It is important to keep the first teeth healthy until the age of six. If earlier sick milk teeth were removed, today they are treated.Since long-term studies have confirmed that the removal of temporary dental units adversely affects the formation of a permanent dentition. The remaining teeth begin to move, trying to fill the resulting void and inhibiting the growth of the molar, which leads to malocclusion.
Most often, infants from three to five years suffer from periostitis. If a child of 5 years old has a flux, you don’t need to do anything on your own - you need to consult a dentist for help. The treatment of fluxes for both permanent teeth in adults and milk teeth in children should include drug therapy and medical intervention. If measures are not taken to eliminate inflammation, the infection will enter the bloodstream, which can lead to blood poisoning and death.
Flux in children over 7 years old
For the appearance of healthy teeth, you need to prepare a favorable "soil". This means that molars must grow in a healthy oral cavity. Otherwise, the risk of their infection from dairy "brothers" increases.
By the age of 7, the immune system of children becomes stronger, so flux occurs less frequently. And if it does, it is less painful. However, if the flux has developed in a child older than 7 years old, there is also nothing worth doing on your own - you need to take him to the doctor.
At this age, children can more accurately indicate what is bothering them, show a neoplasm in their mouth, or talk about pain. This factor speeds up the process of diagnosing a disease and facilitates its treatment.
If it is difficult for a three-year-old baby to explain how to rinse his mouth and why it is necessary to drink pills, then a seven-year-old child can easily cope with rinsing and taking medication. Therefore, in adolescents, periostitis is treated much easier and faster.
Flux symptoms
It is impossible to ignore or not notice the flux. Toddlers begin to worry about pain in the oral cavity. Signs of the disease are also visible to the naked eye. In the process of periostitis, the following symptoms appear:
-
the formation of an abscess on the gum;
- aching pain in the area of a diseased tooth;
- swelling of the face (enlarged cheeks);
- enlarged and sore lymph nodes;
- redness of the gingival mucosa;
- very pronounced bad breath;
- lethargy amid weakened body;
- fever.
In the process of developing the disease, the severity of symptoms increases. Edema can spread to the entire cheek, right down to the eyes. The inflammatory process causes an increase in temperature.
Treatment of flux in primary teeth in children
The flux in a child should be treated in a dentistry clinic, and not at home. Only a dentist can make an accurate diagnosis and choose the most suitable and safe way to treat this disease.
If the process of suppuration has already begun, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. The pus formed is disposed of by outflow through the drainage, which is inserted into the gum. The procedure is performed under the influence of general anesthesia. Badly damaged, untreatable teeth break out. It is contraindicated to open the abscess at home, this should be done by a specialist.
Of the medicines used to fight the disease, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used. The course of treatment lasts about a week, improvements are usually observed on the third day.
Drug therapy should not be interrupted, even if the visible symptoms of the disease have disappeared, and the child has recovered. If the flux is not treated, an infection will remain in the tooth, and the inflammatory process may begin anew.
Features of the treatment of flux in children from 3 to 8 years
Milk and permanent teeth with periostitis are treated differently. Therefore, the tactics of therapy depends on the age of the patient:
- Treatment of flux in babies up to three years old is aimed at preserving the tooth, since its absence can affect the formation of the bite. To relieve inflammation, safe infusions and decoctions of herbs are used, diluted to a safe concentration and used to rinse the mouth or topically treat the affected area.
- When treating periostitis in babies four years old, you can cauterize the foci of infection with a solution of Lugol or iodine.
- A baby tooth with a running flux in a child of five years old can be removed, since a permanent one will soon grow in its place. If there is a high risk that tooth extraction will affect the process of bite formation, the baby is given a temporary removable denture.
- In almost 100% of cases, the teeth with flux in children older than 6 years are removed, since at this age they already begin to be replaced by permanent ones. Prosthetics are not performed. Therapy may include the use of painkillers and antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action.
- In children seven and eight years old, the teeth affected by periostitis are treated in the same way as in adults. The differences are only in the use of children's medications.
The child has a flux: what to do at home
Flux in children can not be treated exclusively with folk remedies. But they can be used together with medications prescribed by a doctor and only after his approval. With the use of complex therapy, the healing process will come much faster.
The main folk remedies used in the treatment of periostitis are soda-salt solution and decoctions of herbs. To make a soda-salt solution, you need to dissolve in a glass of warm water for half a teaspoon of soda and salt. To prepare the broth, chamomile and sage are usually used. These herbs have excellent antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. Both solutions and decoctions should be at room temperature.
If a young child who does not know how to rinse his mouth has a flux on his milk tooth, you can make oral baths: persuade the baby to hold a solution or broth in his mouth for several minutes. The procedure should be carried out 5-6 times a day.
Do not test on the baby the effectiveness of dubious recipes of traditional medicine. And it should be remembered that the flux must never be heated.
Flux Prevention
In order to avoid the formation of flux, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. Parents should monitor how the baby observes oral hygiene. In addition, it is necessary:
- Take him to the dentist every six months.
- Choose a toothbrush and toothpaste for the child according to his age.
- Accustom him to rinse his mouth with water after each meal.
- Give crumbs to eat carrots and apples. They help strengthen the gums, and the process of chewing acts like a massage.
- Constantly carry out activities to strengthen immunity.
You need to regularly inspect the baby's mouth. The sooner a disease is detected, the faster and easier it is treated. On average, flux symptoms disappear within a few days after the start of treatment. Therefore, be attentive to your children and try to help them on time.