Gingivitis in children and infants: causes, symptoms, treatment
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. If the child has developed gingivitis, it is necessary not only to eliminate the symptoms, but also to treat the causative disease. If the disease is only a consequence of any other pathology, then you should focus on systemic therapy, and not just on the elimination of gingivitis as a sign.
Content
Causes of gingivitis in children
Gingivitis often occurs precisely in childhood and can be associated with poor oral hygiene, poorly polished fillings, periodontitis, and eruption of molars and milk teeth. If a small patient is used to chewing food on only one side of the jaw, this can also cause the development of the disease. In adolescents, gum disease can be caused by hormonal changes.
In addition to these reasons, gingivitis may occur due to:
- hypovitaminosis, especially with a lack of vitamins of group B and C;
- ARVI;
- chronic tonsillitis (the infection is always nearby - in the throat);
- cholecystitis;
- tuberculosis
- diabetes mellitus;
- anemia and other blood diseases.
These diseases weaken the general and local immunity, which leads to inflammation of the gum tissue or the development of other pathologies of the oral cavity. Also, the disease may occur due to the use of certain anti-epilepsy drugs, cardiac drugs, calcium channel blockers or cephalosporins. But anyway the main cause of sore red gums is advanced caries.
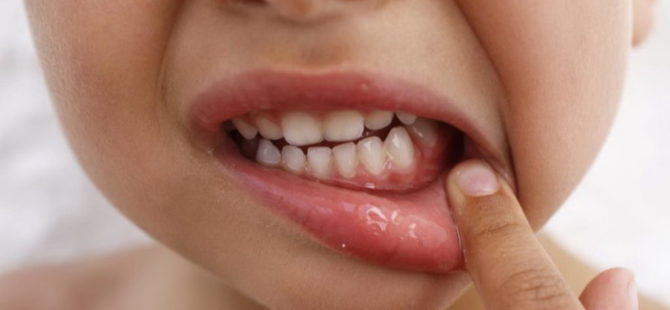
Gums in a baby are inflamed
In children under 1 year of age, gingivitis can develop against the background of teething. The well-known pediatrician Komarovsky recommends that, with such a development of events, regular sanitation of the baby's oral cavity with antiseptics and smear the gums near the incisive tooth with Kalgel. Usually, signs of inflammation disappear after the first treatment of the gingival mucosa.
If a newborn or an older baby is breastfed, the mother should take care of her own hygiene and carefully treat her breasts before and after feeding.
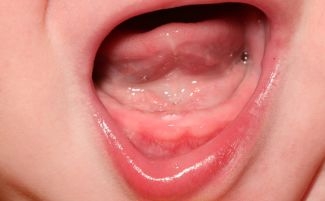
Inflammation in babies over two years old
At 2 years old, the child already has teeth that begin to deteriorate when hygiene is insufficient. The presence of carious cavities often leads to various gum diseases: first, children are diagnosed with gingivitis or stomatitis, and later diseases can develop into periodontitis.
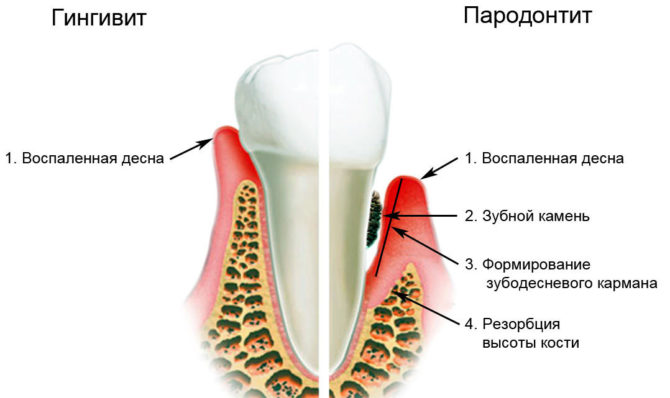
Classification and types of gingivitis
The intensity of gum disease and some additional signs distinguish several varieties of gingivitis in children:
- mild catarrhal;
- ulcerative with severe symptoms;
- atrophic, which is expressed in a decrease in gum tissue and exposure of the neck of the tooth;
- ulcerative necrotic, which is characterized by general intoxication of the body.
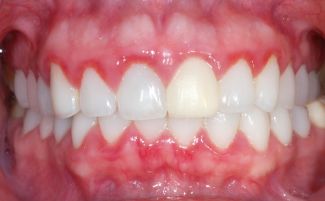
Symptoms and signs of gingivitis in children
The classic symptoms of gingivitis include:
- soreness, swelling and bleeding of the gums (the symptoms are worse when chewing on the side of the reddened gum tissue);
- tooth mobility;
- bad breath;
- enhanced salivation;
- redness and blueness of the mucous membrane of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes.
The typical signs of intoxication indicate the development of gingivitis: headache, fever and general lethargy. Breasts who cannot express their feelings in words begin to behave strenuously, cry and refuse to eat. Teenagers may complain of malaise.
Many consider this disease not serious, but it should not be allowed to drift. Inflammation of the gums of a child can cause infection of its other organs and tissues and lead to serious consequences, up to the development of a tumor near the inflamed area. Therefore, after the appearance of the first symptoms (gums are red and sore), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Gingivitis in children: photo
Diagnostics in Dentistry
If the child has inflamed and swollen gums, but there are no more complaints, then an additional examination may not be necessary. The doctor will only conduct a visual instrumental examination of the oral cavity, fix the swelling and make a diagnosis. Laboratory diagnostics will be needed only if a secondary infection is attached.
If other dental diseases (periodontitis, periostitis, periodontal disease) are suspected by the dentist or pediatrician, an additional x-ray examination will be prescribed. If the patient has only gingivitis, the image will not reveal any changes in bone tissue, and therefore it will only be necessary to treat gum disease.
Treatment of gingivitis in children
The algorithm for treating gingivitis in a child depends on the etiology of the disease, but therapy should always be started with sanitation of the oral cavity, removal of plaque and stone. If there are teeth with cavities in the mouth, they must be cured or removed. If a child has stomatitis, then this disease also needs treatment.
Regardless of how old the child is, 14 or 2 years old, it is up to the doctor to decide how to treat the gingivitis manifested in him. Self-medication, even on the advice of an experienced pediatrician Komarovsky, is dangerous, especially if it is administered to minors.
Ultrasonic tartar removal
If the child has tartar (which rarely happens), then it is best to remove it with ultrasound. Features of the procedure include:
- ultrasound removal of tartar lasts about half an hour;
- Before the start of the session, professional toothbrushing is carried out with the complete removal of food particles;
- first of all, the supragingival stone is removed;
- the subgingival stone is removed second, but first the neck of the tooth should be carefully released;
- then the teeth are treated with a special paste with the smell of menthol.
This procedure is carried out only on molars and under local anesthesia. After it, the gum sometimes hurts a little, so Dr. Komarovsky recommends that parents stock up on children's pain reliever gel.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
To quickly remove the symptoms of gingivitis, you need to treat the baby’s inflamed gums with the following solutions and ointments:
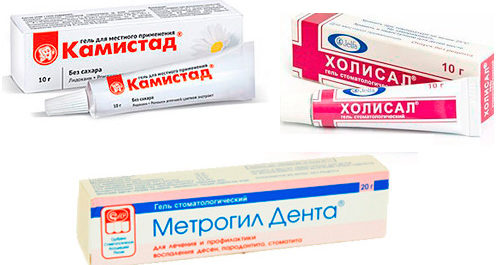
- Chlorhexidine.
- Kamistad.
- Holisal analgesic gel.
- Miramistin (from 3 years).
- Ointment Metrogil Denta (from 6 years old).
The use of these funds is permissible only after removal of dental plaque. Otherwise, there will be a reappearance of signs of inflammation, and the acute form of the pathology will become chronic. A chronic inflammation of the gums in children can lead to periodontitis.
If the baby does not know how to rinse his mouth independently, it is necessary to treat the mucous membrane of his gums with antiseptic solutions 2-3 times a day. Children of all ages are recommended to make applications of aloe gruel around the inflamed gum.
How to treat complex forms of gingivitis in children
In the case of diagnosing a ulcerative, ulcerative, necrotic or atrophic form of pathology, additional treatment methods are used that reduce the signs of intoxication and relieve inflammation of the gums of the child. These include:
- gingivectomy - surgical excision of the gum tissue around a diseased tooth, which is performed under general anesthesia;
- freezing by introducing a solution of calcium chloride into the gum;
- chemical moxibustion;
- current therapy (for patients older than 5 years);
- trypsin enzyme-based gum necrolysis.
But usually gum disease in children does not require the use of such techniques. Most often, gingivitis is determined at an early stage and is calmly treated with antiseptics.
Antibiotic therapy
Antibiotics for gingivitis are prescribed only if there is no positive effect after the use of antiseptic agents, and ulcers and pus begin to form on the gums. With a complicated course of gingivitis, the child’s gum hurts, pus from his mouth smells, fever is observed, and other signs of intoxication are present.
In the inflammatory process, the following antibiotics can be prescribed for the child:
- Cephalexin.
- Erythromycin.
- Clindamycin (not recommended for patients under 6 years of age).
- Amoxicillin.
- Metronidazole.
- Tarid
- Ciprofloxacin.
- Ampicillin.
For the final relief of gum disease, the child must take medication for at least a week, even if the signs of gingivitis disappear after one dose. The exact dosage is determined by the doctor based on the severity of the pathology.
Traditional medicine
If the child has a gum inflammation, he needs complex therapy, so it is not advisable to neglect traditional medicine. They can be used at home after a doctor’s permission. Lubricate the gums around the painful area:
- sesame or coconut oil (up to three times a day);
- essential oils;
- regular cosmetic clay (the method is suitable only for those children who already know how to rinse their mouths);
- a solution of myrrh extract;
- tincture of the upright cinquefoil;
- pasty suspension from baking soda;
- gruel of garlic.
In the treatment of gingivitis in infants, folk remedies must be used with extreme caution. Some products, for example, essential oils, can cause allergies, so appropriate tests should be performed before using them.
Do not leave gingivitis unattended or try to treat it exclusively with folk remedies. Carious milk teeth and red gums, even if the symptoms appeared in a child younger than 2 years old, require hardware and drug treatment, as they can cause serious pathologies.
What to do so that the child does not suffer from gingivitis
Gingivitis is a fairly common pathology among children. To avoid its development, it is necessary to carry out prophylaxis: sanitize the mouth, carry out antiseptic rinses and monitor the diet. If gingivitis develops due to teething, gums near the top of the tooth that has appeared should be treated with cooling and antiseptic drugs. Otherwise, they will begin to become more inflamed, and the baby's body temperature may rise.