Molar teeth in children: terms and order of teething, symptoms, how to help
When children turn 5-6 years old, their baby teeth begin to give way to molars, and the order of teething of permanent teeth and the symptoms that arise during this period coincide in almost all babies. However, there are still some differences, so you can and should prepare for such a difficult period.
Content
How permanent teeth differ from milk teeth
After changing the bite, the rules for caring for the oral cavity also change, since permanent and temporary teeth are very different from each other:
- Indigenous more dense, they have a high degree of mineralization.
- Milk teeth are much whiter than permanent ones. Enamel of root incisors, fangs or molars is naturally light yellow in color.
- Pulp (a bundle of nerve endings) in permanent teeth is more developed, because of this, the walls of hard tissue are much thinner.
- In a young child, the dentition has a less developed root system, after a change in bite it becomes more durable.
- Even outwardly baby teeth are smaller. The kids have not fully developed the jaw, so the standard row on it simply would not fit.
- There are more permanent teeth. In adolescence, sixes begin to form, which young children do not have.
At what age do molars begin to climb in children
Usually the first molars appear in children aged 5-6 years, but sometimes milk lower incisors fall out in four-year-old babies or even in children younger. In pediatric dentistry, the exact dates for changing the dentition are usually not indicated, since each child is individual. In some, milk incisors begin to fall out immediately after the formation of a temporary bite, while others, even in grades 2–3, still do not have a single permanent tooth.
The last temporary molars are replaced at the age of 12-13 years. The period when six teeth erupt in children does not begin until after 14 years. These premolars no longer have dairy predecessors.
There is another group of teeth that comes out later than the rest. They are popularly known as wisdom teeth, dentists prefer to call them eights. They grow up in 18 years and later. There are cases when third molars begin to appear only after 30 years. This phenomenon cannot be called a pathology, as are the cases when the eights do not cut through at all.
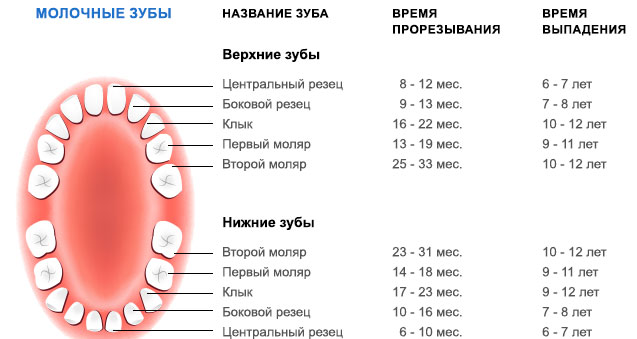
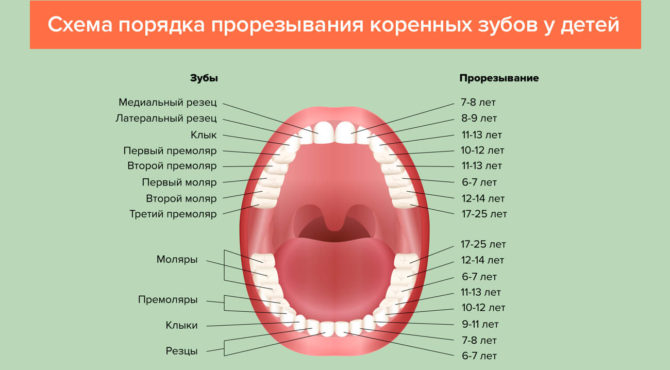
The order and timing of eruption of molars: table and diagram
First, the child’s teeth change in the same way that they are cut in newborns. Only in 14-15 years will additional molars grow, which were not present with a temporary bite.
The table below shows the timing of teething of permanent teeth in children. Do not exactly rely on the specified age, the period of a replacement bite can go much faster or drag out.
| Dental kit | Age |
|---|---|
| Lower central incisors | 5-6 years |
| Upper central incisors | 5-6 years |
| Lower side incisors | 8–9 years old |
| Upper side incisors | 8–9 years old |
| Upper first molars (premolars) | 9-12 years old |
| Lower first molars (premolars) | 9-12 years old |
| Fangs | 12-13 years old |
| Second molars of the lower jaw | 14-15 years old |
| The second molars of the upper jaw | 14-15 years old |
The age at which teeth begin to grow in children may be different, but the order of teething of permanent teeth is almost always the same as in the table. Only in rare cases does everything happen in a different sequence.
Teething scheme for permanent teeth in children:
Symptoms of Teething
If you have the following symptoms, you should prepare to change the bite:
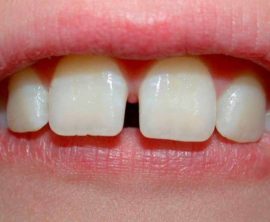 Between the teeth, gaps appear and increase, as in the photo. This suggests that the jaw bone is growing and soon there will be enough space on it for permanent molars and incisors.
Between the teeth, gaps appear and increase, as in the photo. This suggests that the jaw bone is growing and soon there will be enough space on it for permanent molars and incisors.- Milk teeth become less stable, gradually loosening. This is due to the fact that under the temporary teeth of the child the process of growth of the indigenous ones has already begun.
- Of course, the loss of a baby tooth is a sure sign that a permanent one will soon begin to grow. Exceptions are a violation in the order of growth and trauma to children's teeth.
- Even if the tooth has not yet fallen out and is not staggering, a swelling and redness may form around it. If during the bite change you do not care about hygiene, it may result in the formation of a fistula or cyst.
- The child has a runny nose, and the discharge from the nose is fluid and transparent.
- Salivation increases sharply, you have to constantly use a scarf.
- Bad sleep, tearfulness and general malaise are also common symptoms.
- When teeth erupt, there are also various digestive problems. Due to toothache, nutrition is disturbed, which leads to such symptoms.
Teething temperature in molars
Often the appearance of molars in children is accompanied by a temperature, but it should not rise above 38 °C and stay longer than four days. If the fever lasts longer than several days, accompanied by a runny nose (profuse and opaque), dry and frequent cough, you need to show the baby to the pediatrician. Such symptoms indicate an infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract, which often develops during teething due to the increasing vulnerability of the body.
How to relieve unpleasant symptoms during teething
Toothache is an extremely unpleasant symptom even for an adult, not to mention babies. Teething is accompanied not only by discomfort, but also by general malaise, therefore it is better to know in advance at what age molars are climbed in children, and prepare for this period.
How can the symptoms be relieved:
- If the milk tooth has already fallen out and the gum is very itchy, gently massage it with your finger. Only wash and disinfect your hands thoroughly first. You can use special brushes for massage.
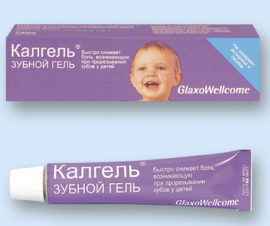 Cold compresses will also help, but do not resort to them too often and for a long time. A few procedures per day will be enough.
Cold compresses will also help, but do not resort to them too often and for a long time. A few procedures per day will be enough.- Anesthetic gels, such as Holisal, Metrogil Dent, Kamistad, Kalgel, will also help. You need to use them carefully - no more than 4 times a day.
- To remove the temperature, use standard tools that you usually use. Just keep track of how many drugs have been given to the child over the entire period, and do not exceed the norm.
- If the temperature does not drop already for 2-3 days, consult a doctor.
What problems can occur during a tooth change
There are many problems when molars climb in children. The most common complications include:
- Lack of permanent teeth.
- The growth of a permanent tooth before a temporary loss.
- Pain in the molar.
- The loss of molar.
In each case, dentists have a solution, you only need to find the problem in time and seek help. The last two phenomena arise due to the low mineralization of hard tissue, and such anomalies appear regardless of how old molars climb.
A new dentition is always very vulnerable in the first few weeks after formation.If you pay little attention to caring for the oral cavity, caries will quickly form on permanent incisors, fangs and premolars. Physical effects on hard tissues during this period also lead to a host of consequences.
Why doesn’t the root grow for a long time after a tooth decay
As soon as the baby has a milk incisor, canine or molar, the root can usually be felt on the gum. Even if this is not so, then he should appear within a week. If there is no seal, then the milk tooth fell out too early. Many children loosen their teeth, sometimes parents themselves take part in pulling them out.
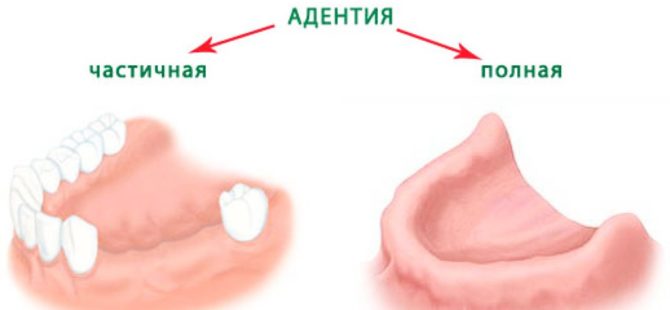
In the worst case, a similar symptom may indicate adentia. Such a pathology is extremely rare, it is caused by a serious violation of mineralization even in fetal age. Sometimes the disease appears during life due to infectious diseases. The problem is easily solved by prosthetics.
Another reason for the violation can serve as a physiological delay in tissue growth. The eruption of all permanent teeth with such a pathology ends much later than usual. If the dentist finds such a defect, he will advise you to make a removable denture. If you do not take the advice, permanent incisors and fangs will grow curved.
What is the danger of molar growth before milk loss
Usually, molar growth leads to loosening of the milk tooth, but there are exceptions. It is possible to understand that the bite is replaced incorrectly if you have all the signs of teething, which were mentioned earlier, not accompanied by loosening of milk incisors or fangs.
Such a problem with the growth of a permanent tooth can lead to a number of problems:
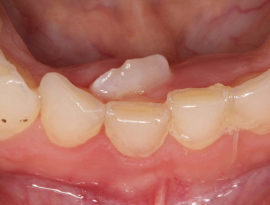 The incisor or canine begins to look for another way to erupt. In this case, molars in children grow as in the photo on the right. Molars and premolars usually nevertheless creep out of the gums, bending the entire dentition.
The incisor or canine begins to look for another way to erupt. In this case, molars in children grow as in the photo on the right. Molars and premolars usually nevertheless creep out of the gums, bending the entire dentition.- The incisor or canine itself can become very distorted. It begins to bend in different directions, and even before full germination.
- Redness, itching and pain become more noticeable. Because of this, bacteria very often enter the damaged area. An infection may begin that will develop into a cyst or fistula.
- If a child develops molars when milk is still in place, consult your dentist. He will be able to immediately detect the problem and remove the permanent tooth "milkman" that impedes the growth.
How to care for an oral cavity during a bite change
It is necessary to teach a child to care for the oral cavity from a very early age. By the period of the change of bite, he should already be able to use a brush and paste. During germination of molars, other recommendations must be observed:
- It is better to use pastes with a high amount of calcium and fluoride.
- Make sure your baby regularly uses antiseptic mouthwashes.
- It is worth limiting the amount of sugar a child consumes, as it leads to the development of caries. When molars in children are only cut and have not yet had time to get stronger, the disease can form in just a few weeks.
- Include more fruits, vegetables, and dairy products in your diet. All of them have a positive effect on oral health.
- Do not limit your child to hard foods, it massages the gums and improves the growth of hard tissue.
- Consult with a pediatrician and with him choose a complex with a high content of vitamin D, which improves the absorption of calcium.
- Try to show the baby for the first time to the dentist no later than 3-4 years. When the first molars begin to erupt, the child should no longer be afraid of the dental office, as he will have to go to the specialist very often.
You should not let the health of your baby’s baby teeth go by the gravity and even more so you should not ignore it when a permanent bite begins to form.