When fangs erupt in children: timing, symptoms, and first aid
Teething in children is accompanied by symptoms that will make all households worried. The child refuses to eat and is naughty due to severe jaw pain, giving into the eyes and ears. Excessive anxiety of the baby scares parents, making you wonder if the process is normal, how to alleviate the condition of the baby during this period, whether a doctor is needed. These and other points are described in the article.
Content
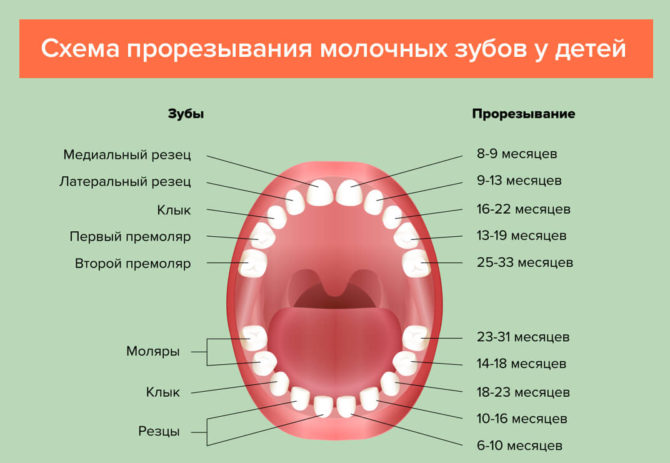
At what age do fangs climb in a child
Nature endowed man with four fangs, located in pairs in the lower and upper dentition. In dentistry, this type of teeth is called a triple, since the place of their localization is the area between the lateral incisors (second from the center of the row) and the first molars (fourth in a row).
Teething begins in children aged 16–18 months. By this time, the baby’s mouth already has 12 milk teeth: 4 central and lateral incisors and 2 molars in the lower and upper row.
Fangs are cut unevenly: the upper ones appear earlier - from 16 to 22 months, the lower ones a little later - from 17 to 23 months. However, the norms in dentistry are a conditional concept. It often happens that the “schedule” is shifted to one side, in rare cases, the sequence of eruption of different types of teeth may go astray. The timing and sequence of teething depends on the individual characteristics of the body: heredity, the nature of mineral metabolism, the degree of absorption of calcium.
What affects the timing of the appearance of teeth
Often, fangs in children climb at a different age than normal, a great influence on the term of their teething has an intrauterine developmental period:
- how was the bookmark and the process of formation of dental primordia;
- how full was the nutrition of the mother;
- woman's age;
- how was the pregnancy.
The formation of teeth continues after the birth of the baby, therefore:
- it is desirable that breastfeeding of newborns lasts at least 6 months, ideally up to 9 months;
- a sufficient amount of milk and dairy products, fish and seafood rich in minerals of vegetables should be included in the diet of a nursing woman;
- with the approval of the doctor, you can take vitamin-mineral complexes.
Also, the period when the child grows a complete dental kit is affected by the climate and geographical zone of residence.
Why teeth are “late”
If hereditary reasons are excluded, then the problem of late teething can be a lack of nutrients and metabolic disorders. Most likely, the children's body lacks minerals, vitamin D, which affects the absorption of calcium.
Adentia can cause tooth problems. A rather rare disease is the result of a violation of intrauterine development, in which tooth rudiments do not form. There is only one way to solve this problem - with the help of implantation.
What symptoms appear when a child has fangs
The most striking symptom of teething teething in a child is excessive salivation, but this manifestation does not immediately join. 3-4 weeks before the moment when the tooth will have to cut from the gums, the preparation of its roots begins.The process is invisible externally, but the baby already feels discomfort, so the initial signs of early teething are manifested by a change in behavior:
- there is no mood, causeless vagaries appear;
- sleep becomes restless, its rhythms are broken;
- there is a need to pull in the mouth and gnaw toys.
External symptoms of eruption of fangs will appear when a small white spot forms on the lower gum - this is a milk tooth, ready to erupt on the surface.
External signs
2-3 days after the baby’s mood worsens, parents can notice the first visible signs of teething:
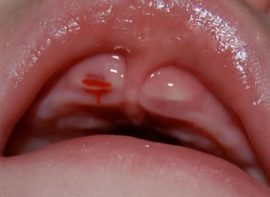 in places where teeth grow, swelling and redness are observed, gums become embossed, as in the photo;
in places where teeth grow, swelling and redness are observed, gums become embossed, as in the photo;- the soreness of the gum section on which a new tooth will come out increases;
- salivation increases;
- the temperature rises to low-grade indicators - 37–37.3 ° C;
- the child’s appetite noticeably worsens, sometimes he completely refuses food.
The most difficult time for parents is when the child's fangs climb with an increase in unpleasant and painful symptoms:
- Salivation causes irritation around the mouth and rash on the chin;
- loose stools are possible, which, according to pediatricians, is the result of swallowing a large amount of saliva;
- salivation may cause vomiting;
- when the fangs climb to the surface, the child’s body temperature can reach critical values - up to 38–38.5 ° C;
- intensifying itching covers nearby tissues.
A child whose teeth erupt constantly bites toys to somehow suppress the itching and pain in the gums.
Temperature
If the body temperature does not go beyond the norm, such hyperthermia is considered a normal physiological manifestation of the body's internal defense. When a child has lower or upper fangs, his gums become inflamed, so the body mobilizes internal reserves to fight inflammation, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature.
What parents should consider:
- How many degrees can the thermometer increase. According to pediatricians, indicators exceeding 39 ° C are critical for a child.
- How long can the temperature last? It is unacceptable that the high temperature lasted longer than 3-4 days. Slightly elevated temperatures usually subside after 5–7 days.
If hyperthermia lasts for a long time, or the thermometer has risen too high, you should seek medical help. Weakened due to teething, the body of the child is susceptible to viruses and infections, so the baby could become seriously ill.
Why kids can’t tolerate the growth of fangs
The most painful symptoms occur when a child has fangs, which is due to the special anatomy of the "troika" and the location:
- the roots of the third teeth are long and powerful, located deep in the gums;
- fangs of the upper row grow in the immediate vicinity of the facial nerve, therefore they are also called ocular teeth.
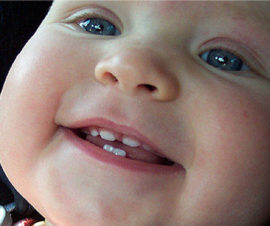 The fangs on the upper jaw cut through for a long time and are especially painful. Due to irritation of the facial nerve, signs of inflammation of the conjunctiva are added to the usual symptoms: in the photo on the right, the swelling of the eyelids of the child is clearly visible.
The fangs on the upper jaw cut through for a long time and are especially painful. Due to irritation of the facial nerve, signs of inflammation of the conjunctiva are added to the usual symptoms: in the photo on the right, the swelling of the eyelids of the child is clearly visible.
Lower fangs erupt less painfully, but not asymptomatically. Parents should prepare for a fever that can last up to 3 days, and short-term upset stool in the baby.
How to help baby during teething
Many of the symptoms that occur when fangs are cut in children can be alleviated. Home and medical methods will come to the rescue:
 Gel teething toys, as in the photo, will remove the itching of the gums, but the baby should not gnaw them without a break - periodically, such items are washed, cooled in the refrigerator and again given to the child.
Gel teething toys, as in the photo, will remove the itching of the gums, but the baby should not gnaw them without a break - periodically, such items are washed, cooled in the refrigerator and again given to the child.- Pharmacy anti-inflammatory and analgesic gels for local applications will help relieve inflammation and pain.In pediatric dentistry, Dentinox, Kalgel, Baby Doctor, Kamistad are used.
- If the fangs are cut in a child against a background of high temperature, antipyretic medicines can be used. Paracetamol-based drugs effectively relieve fever and inflammation. Drugs containing ibuprofen are equally well tolerated by infants.
Children's antipyretic drugs are available in several dosage forms. For children of the first year of life, syrups or candles are relevant. Potions quickly reduce temperature, but their effect is short-lived. Candles do not work immediately, but they last a long time. Before using any remedy, a consultation with a doctor is necessary.
How to care for baby teeth, how old are the permanent
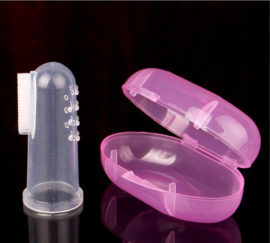 Hygiene of milk teeth must be observed during their growth, enamel is cleaned by parents using a gauze swab or silicone fingertip, as in the photo. After the teeth have grown, the baby is taught to take care of their own teeth. Toothbrush and toothpaste should be appropriate for the age of the child.
Hygiene of milk teeth must be observed during their growth, enamel is cleaned by parents using a gauze swab or silicone fingertip, as in the photo. After the teeth have grown, the baby is taught to take care of their own teeth. Toothbrush and toothpaste should be appropriate for the age of the child.
Early loss of teeth will lead to improper formation of the maxillofacial apparatus, therefore it is so important to preserve milk teeth until the age of their physiological replacement. Normally, the time series changes to a constant of 10-12 years:
- the first "losses" begin at the age of 7: first the front incisors fall out, then the lateral ones;
- permanent fangs grow from 9–10 years, a dental arch forms up to 11–12 years, and finally, adult teeth form at 25 years old.
The health of the child’s permanent teeth depends on the condition of the milk line, so it is so important that the dentist controls the process of teething and tooth change. It is necessary at least 2 times a year to take the baby to dentistry in order to correct the bite in time if it is improperly formed or to heal developing caries.