Teething temperature in children
The appearance of the first incisors and molars is a difficult time for the child. The baby whimpers, requires the utmost attention, since teething in children is accompanied by malaise and fever, which usually lasts up to 3 days. To facilitate the well-being of the baby and not to confuse the syndrome of cutting teeth with another ailment, you should know the main symptoms, why and how high the temperature can rise, when and how to bring it down.
Content
Teething Symptoms
At the age of 4 to 8 months, most babies have teething teeth. It happens that a baby is born already with teeth. And sometimes this process begins after a year.
Famous pediatrician Komarovsky says that his small patients can experience completely different sensations during teething, among which common signs are determined:
- Actively, saliva is released in large quantities, which flows onto the chin, neck. Thanks to its bactericidal and anti-inflammatory qualities, the risk of virus infection is reduced. If you constantly wipe the baby, skin irritation will occur, so saliva is only occasionally blotted with napkins.
 Decreased appetite. It happens that small patients flatly refuse to eat. In this case, breastfeeding helps, which pacifies and anesthetizes.
Decreased appetite. It happens that small patients flatly refuse to eat. In this case, breastfeeding helps, which pacifies and anesthetizes.- Nervousness. Without good reason, the baby suddenly begins to whimper and also, by itself, calms down. The eruption period can be accompanied by round-the-clock painful sensations, the sleep and wakefulness is upset.
- Loose stool. A large discharge of saliva leads to a relaxation of the stool. Diarrhea is possible, caused by changes in the intestinal microflora and the activity of pathogenic bacteria due to a decrease in the body's defense.
- Inflammation. Gum swelling is the norm. A white streak that shines through the gums indicates that the tooth will come out soon.
- Runny nose. Swelling in the mouth can go to the nasal mucosa, which provokes a runny nose.
- Itchy gums. The child seeks to test objects "by the tooth." In this simple way, he scratches the gum. Teethers, which are sold in abundance in stores, solve this problem.
- Temperature. When teething can be a high temperature - up to 39 °C. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the child in order to bring down the fever if necessary.
The following video shows the procedure for teething:
Causes of fever
When teeth are cut, changes occur in the organisms of infants that provoke temperature:
- In the place where the teeth climb, active substances are produced that are necessary to soften the gums and jaw bones.
- All the forces of the body are focused on solving the “dental problem”. Immunity is weakened, and infections, which appeared at this time in the body, provoke fever.
- Full body protection has not yet been formed. Due to poor appetite and lack of sleep, it loses strength, immune function decreases, and a favorable environment for the development of harmful bacteria occurs. To prevent the growth of their population, the temperature rises.
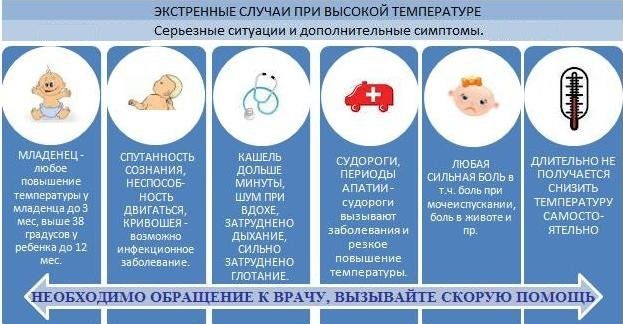
Dangerous signs
The temperature during teething in babies is one of the mechanisms of body protection, a manifestation of the wisdom of our body.However, it is important not to overlook the symptoms that signal the ailments hiding behind the teething syndrome:
- Stuffy nose. Natural recognize odorless, colorless discharge. Snot greenish-purulent color and strongly stuffy nose suggest the development of rhinitis.
- I have a stomachache. If diarrhea is accompanied by cutting abdominal pain, an intestinal infection is predicted. Gnawing everything, the baby could put it in her mouth.
- Painful cough. So much saliva is released that the child does not have time to swallow it. Choking on saliva, the baby coughs, this is normal. But sputum discharge and coughing rales may be associated with respiratory problems.
- Redness of the throat. In the process of teething, swelling of the gums is not able to go to the throat. If the sky reddened, pharynx, the baby may develop pharyngitis.
- Vomiting In children, the gag reflex can be triggered by fever. Vomiting also accompanies damage to the nervous system and poisoning. Therefore, a doctor’s call is required to exclude these ailments.
If the described symptoms are present in the baby at the moment when his teeth are being cut, medical care is required at any temperature.
Standard and allowable temperature
Temperature standards in infants and adults are very different:
| Age and place of measurement | In the armpit | In the ear and rectum | In the mouth |
|---|---|---|---|
| up to 1 year | 37.2–37.5 ° C | 38.2–38.5 ° C | 37.7–38 ° C |
| over 2 years | morning up to 37.2 ° C evening up to 37.5 ° C |
morning up to 37 ° C evening up to 37.9 ° C |
morning up to 35.5 ° C evening up to 37.7 ° C |
Teething temperature
On average, the temperature in the armpit rises to 37.5–37.7 ° C. The child almost does not notice such an increase. For teething, a temperature of 38 ° C is acceptable. If the temperature rises to 38–39 degrees, measurements are taken every hour, but do not intervene, because hyperthermia contributes to increased production of antibodies.
Allowed Dates
It is normal if the body temperature, when the teeth come out, is elevated and lasts up to three days. Doctor's help is needed if the fever has not subsided on the fourth day and reaches a maximum of 40 ° C.
It happens that with severe inflammation of the gums and the eruption of several teeth at one time, the temperature lasts 5 days. The maximum temperature is also possible with the eruption of molars and upper canines.
When second molars are cut, the malaise can last up to several weeks. At about six years old, when permanent teeth grow, the process goes much easier.
Symptoms requiring a decrease in temperature
Immediately bring down the fever with the following symptoms:
- teething temperatures above 39 ° C;
- cramps occur;
- breathing quickens;
- the baby sleeps too long;
- the baby is constantly crying, can not calm down;
- with other signs of deterioration: the cheeks are red, the lips are dry, the eyes shine unhealthily.
If the infant has already experienced cramps, then the fever is knocked down at indications above 38 degrees or at the first signs of convulsive readiness: with muscle tension and twitching.
Heat Risks
As a result of hyperthermia, the natural course of many processes in the body changes, which leads to the following consequences:
- disturbed water-salt balance;
- increased load on the heart;
- cramps occur that can cause respiratory arrest;
- blood in blood vessels may clot.
When the fever, despite the measures taken, continues to hold on or quickly returns to its previous value, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Ways to bring down the heat
An increase in temperature is a natural process in teething in children. It is not worth adjusting it for no particular reason. But in an emergency, quick action is needed.
There are two ways to normalize the temperature in young children:
- drug;
- folk.
Drug method
 In pediatrics to normalize the temperature two substances are allowed: ibuprofen and paracetamol. Ibuprofen is effective against heat and pain.It is suitable for babies older than 3 months. From the first days of life, they are allowed to take paracetamol. The drug is suitable for pain relief, but is not effective at 39 ° C and above. These drugs are given to infants strictly for their intended purpose and in the exact dosage.
In pediatrics to normalize the temperature two substances are allowed: ibuprofen and paracetamol. Ibuprofen is effective against heat and pain.It is suitable for babies older than 3 months. From the first days of life, they are allowed to take paracetamol. The drug is suitable for pain relief, but is not effective at 39 ° C and above. These drugs are given to infants strictly for their intended purpose and in the exact dosage.
Syrup preparations quickly relieve heat, but produce a short-term effect. Candles affect the body more slowly, but the effect of their use lasts longer.
As a result of the actions taken, the temperature cannot always be brought down to normal. It is enough if it drops by at least one division of the thermometer.
Folk remedies
 Simple folk methods make it possible to bring down the heat by 1-2 degrees. These include:
Simple folk methods make it possible to bring down the heat by 1-2 degrees. These include:
- Wrapping the baby in a wet diaper.
- Rubbing the baby with warm water. Wet feet and hands of the baby, inguinal and axillary cavities, elbow bends and under the knees are wiped with a wet sponge.
- Linden blossom. Children from one year old can make tea from linden flowers. Thanks to it, sweat secretion increases, which leads to cooling the body.
- The leaves of cabbage, which are previously kept in boiling water, help, beat off, cool and apply to the body.
One folk remedy is not enough. You can use it, as an auxiliary, between doses of drugs.
Inappropriate Methods
When teething in a child:
- Do not let him bite crackers or a crust of bread. He may choke or scratch his gums.
- It is forbidden to massage the gum, cut and do other manipulations in the oral cavity of the infant, because there are great chances to infect it. If something confuses parents, you need to see a dentist.
- Do not use alcohol and vinegar to wipe. Evaporating, they cool the skin, and the increased temperature inside persists. Alcohol and vinegar can cause intoxication.
Activities that alleviate the condition of the baby
The love and patience of parents will help the baby survive the painful process. Facilitate well-being:
- frequent touch “skin-skin”;
- frequent breastfeeding;
- distracting games;
- walks, if the general condition allows;
- a lot of drinking;
- Lightweight clothing;
- rest from the diaper;
- cool in the room (17-18 ° C).
High temperature in teething is a natural response of the body to the release of biologically active substances and swelling of the gums. The child can react to teeth with temperatures up to 39 ° C. But since it is poorly protected at that time before respiratory, intestinal infections, serious ailments can be hidden behind “dental” ailments, so you need to carefully monitor the child. A clear plan will help confidently take care of the baby: a doctor’s consultation, an antipyretic drug and plenty of water.