Causes of the appearance and treatment of mouth ulcers in a child
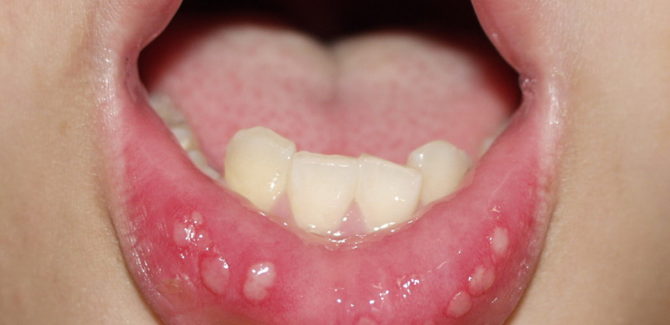
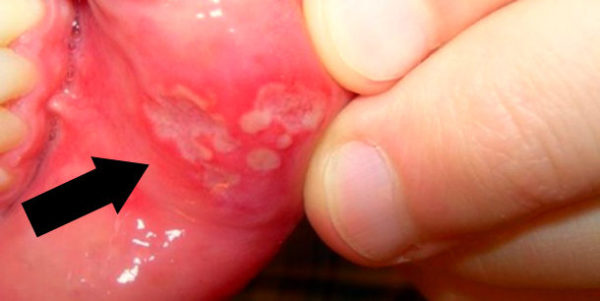
Mouth ulcers most often indicate stomatitis. It can manifest itself in the form of a single afta or multiple formations that cause pain. Children are most susceptible to pathology due to an incompletely formed immune system. But if you know how to effectively treat white mouth sores in a child, you can quickly eliminate the disease and protect the baby from discomfort.
Content
Causes of a single mouth ulcer in a child
In most cases, the appearance of pustules in the mouth in children is associated with mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In the first months of life, the cause of aphthae can be prematurely erupted teeth, foreign objects adhering to the hard palate, or a defective bottle nipple.
Common causes of ulcers in the mouth in children are:
- biting your cheeks or tongue while eating;
- careless brushing with a stiff brush;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the palate with hard or hot food;
- wearing orthodontic constructions.
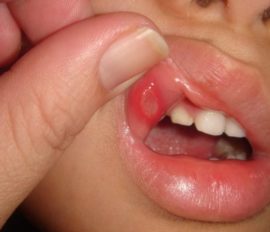
The appearance of mouth ulcers in children on artificial feeding is promoted by the pressure of the long nipple of the bottle. The lesions are located on the midline of the sky and have a rounded shape, the surface of such aphthae is covered with loose coating. This disease was called Bednar aphtha.
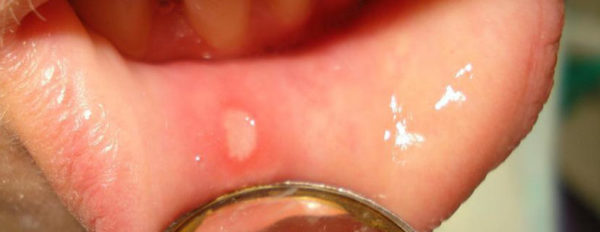
Single mouth sores in children, caused by the above reasons, do not require treatment. They independently heal within 7-14 days, provided that the irritant is eliminated. If pain occurs, it is permissible to use children's painkillers or folk remedies.
Multiple aphthae as a symptom of a disease
The presence of numerous ulcers in the baby's oral cavity signals the development of a serious disease:
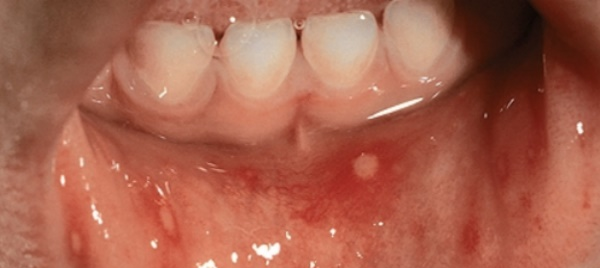
- Chronic aphthous stomatitis. The disease is characterized by the recurrent nature of the course. Most often, single or multiple aphthae are localized on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips, back of the tongue and are covered with a coating of fibrin.
- Vesicular stomatitis. It differs in the formation of aft filled with a clear liquid. Rashes cause pain, accompanied by chills, loss of strength.
- Allergic stomatitis. It occurs as a reaction of the body to an allergen. Most of all the disease affects children with atopic eczema.
- Herpetic stomatitis. It manifests itself as an increase in temperature, swelling of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, pain. The disease provokes the herpes virus, transmitted by household and airborne droplets.
- Bacterial stomatitis. The disease is caused by streptococci and staphylococci, its second name is pyoderma. The disease is often observed in infants with weakened immunity.
Abscesses accompany other pathologies that are characterized by an acute course. These include ulcerative gingivitis, necrotic aphthous stomatitis, tuberculosis, syphilis. Each disease requires an individual approach to treatment.
Other causes of abscesses in the child's mouth
The appearance of white sores in the mouth in children is promoted by many factors, including vitamin deficiency.Deficiency of vitamins B2 and B6 manifests itself in the form of cracks on the lips and pustules of white color on the mucous membrane of the palate, tongue, gums or cheeks. And the lack of ascorbic acid leads to blueing and bleeding of the gums, the formation of aphthae. To normalize the condition of the oral cavity, it is necessary to give the baby vitamin complexes or products containing elements that are missing from the body.
Factors leading to the formation of pustules on the oral mucosa are stressful conditions, excessive consumption of acidic or flour products, malocclusion, and breathing through the mouth.
Before treating mouth ulcers in a child, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of their appearance and eliminate the provoking factor. The source of the disease is identified by a specialist after examining the child’s oral cavity and analyzing severe symptoms. Self-treatment of sores in the child's mouth can cause the progression of the disease and the spread of infection to the internal organs.
Diagnosing the cause of sores in a child’s mouth
The reason for the formation of ulcerative abscesses on the gums, tongue, lips and palate of a small patient is established on the basis of a medical history and a set of related symptoms:
- Chronic aphthous stomatitis is characterized by an upset digestion. A more severe degree of the disease is characterized by swelling of the soft tissues in the affected area, inflammation of the lymph nodes, and apathy. The disease is recurrent in nature.
- With herpetic stomatitis, a few rashes in the oral cavity, a sudden slight increase in temperature, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses are observed. Further development of the disease is expressed in the deterioration of health, weakness, bleeding gums. Rarely, nosebleeds, halitosis, muscle-skin sensitivity, or bradytachycardia occur.
- The clinical picture of enteroviral vesicular stomatitis is characterized by the formation of pustules on the gums, tongue, cheek or palate, as well as on the palms and feet. Formations cause severe itching, excessive salivation, sore throat. High temperature, pain in the eye area are noted.
- A bacterial lesion is characterized by an increase in temperature, the formation of erosion, the development of lymphadenitis. Pustules are covered with a gray-yellow crust, upon removal of which bleeding is observed.
In the diagnosis of the disease, the quantity, color, localization and prevalence of pustules in the oral cavity are of great importance.
Treatment of stomatitis in a child, drug names
The formation of a single mouth ulcer in a child usually does not require treatment by a specialist, however, if there are other symptoms or an increase in the number of aphthae, home therapy without medical supervision can lead to a complication of the disease.
Treatment of sores in the mouth is the task of the dentist. It is he who diagnoses the pathology and prescribes medications. The tactics of therapy depends on the cause of the disease and is aimed at its elimination:
- With herpetic and vesicular stomatitis, antiviral drugs are recommended - ointment or tablets Acyclovir; anti-inflammatory drugs - a decoction of chamomile or St. John's wort; healing medicines - sea buckthorn or rose hip oil; vitamin complexes.
- Allergic stomatitis is treated with antihistamines - drops of Fenistil or Suprastin solution (for infants up to one year old), Diphenhydramine, Tavegil (for older children).
- Bacterial diseases are treated with antibiotics - Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Sumamed. When choosing a medicine, the age of the patient should be considered.
- Ulcers resulting from malocclusion or exposure to dental units can be cured after restoration of the tooth surface or structure.
- Vitamin deficiency is treated with vitamin complexes.
Taking medications is a small part of the complex of mandatory therapeutic measures for stomatitis. In addition, therapy includes a strict diet (it is not recommended to eat hard, hot and sour foods), plentiful drinking and thorough brushing of teeth and tongue. Hygienic procedures are recommended with a gauze swab, since using a toothbrush until the pustules heal completely causes discomfort.
Regardless of the cause of the formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa, they often cause pain that can be alleviated with painkillers: Kamistad, Instillagel. However, their use is desirable only for acute painful sensations. In other cases, home remedies help to reduce pain: applying ice to a sore spot, rinsing the mouth with salt water.
Treatment of sores and mouth ulcers in a child at home
Traditional medicine can be used as an additional method of treatment. However, parents need to remember about a possible allergic reaction in the baby to the collection of herbs and other folk remedies for treating the oral mucosa.
To speed up the regenerative process, decoctions or tinctures are made from herbs that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects: chamomile, calendula, sage. The child should rinse their mouth 3-4 times a day.
Healing ulcers contribute to the oil based on sea buckthorn, chamomile or rose hips. The medicine must be applied to the wounds 2 times a day. Many parents make healing paste from aloe leaves. The plant is used as an antimicrobial, painkiller. To disinfect the affected soft tissues of the oral cavity, honey, paste from curry leaves are applied to the pustules.
Extremely it is contraindicated to do iodine mesh on the mucous membrane of the baby's oral cavity, apply to the pustules brilliant green, open bubbles. Such manipulations will lead to increased pain and complication of the disease.
Stomatitis Prevention
To avoid the development of pustules in the child's mouth, parents should protect him from stressful situations, maintain the daily regimen, and conduct hardening procedures. It is necessary to monitor the baby’s diet and food temperature, remove small items in an inaccessible place, teach the baby to brush their teeth and tongue from infancy.