Doped and retined teeth: the essence of pathology, removal
Turning to the dentist with complaints of discomfort and toothache, many patients receive a referral for the removal of a retarded or dystopic tooth. A person who is ignorant of dentistry, such a recommendation can be confused and cause to panic. However, it is often a radical solution to the problem may be the only right one.
Content
Concept, types of dystopia
Dystopic are teeth whose teething and growth develop with abnormalities. Usually, such a pathology entails an incorrect location of all other teeth, discomfort in the patient, and the need for dental treatment.
There are many types of dystopia. For example, the tooth itself can be of the correct shape, but grow not where it should be, or take the right place relative to neighboring teeth, but have a pathological shape, an irregular growth angle, be located on the wrong side.
In medicine, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- Vestibular dystopia. Means tooth growth at an angle in one direction or another.
- Torposition. The tooth is deployed in the opposite direction.
- Medial dystopia. The tooth extends beyond the dentition.
- Distal. Tooth as if pressed through the inside of the jaw.
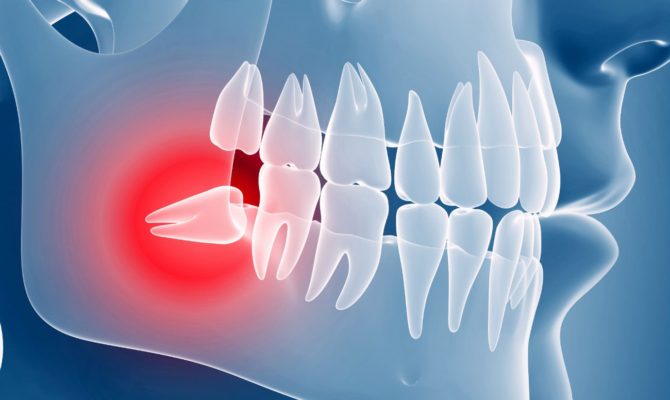
The essence and varieties of retention
Retention also means pathological development of teeth, but differs somewhat with dystopia. A tooth is defined as a tooth that is fully formed in the tissue of the gums and periosteum, but not cut out, or only partially cut. Sometimes this pathology is asymptomatic, but more often the development of infection, discomfort in the form of pain, phlegmon, abscesses are observed.
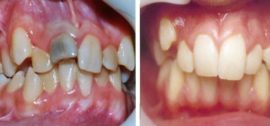
What is a refined tooth can be seen in this photo:
Science knows 2 varieties of retention:
- full;
- partial.
With full retention, the tooth hides under the gum and bone tissue, it can not be seen when examining the jaw. And with a partial degree of development of pathology, you can see the crown when examining the oral cavity, but its main part is still hidden under the gum.
Reasons for the appearance
The main factor in the appearance of refined and distoped teeth is detrimental heredity. All people have a genetic program for the formation of the dentition, and some teeth may not have enough space for growth.
Specialists in the field of dentistry note several more reasons for the development of such a pathology:
- If a single tooth grows before all the following, which could play the role of landmarks.
- Sometimes one extra tooth appears in a row, and everyone else does not have enough space for proper development.
- Excessively dense tissue in the tooth socket.
- The loose structure of the periodontium.
- Dense arrangement of crowns.
- Traumatic injuries also often lead to malocclusion.
- The superearly loss of milk teeth often entails the incorrect formation of the entire series.
Types of teeth susceptible to pathology
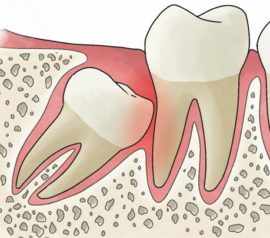 The most commonly observed dystopia or retention of the following types of teeth:
The most commonly observed dystopia or retention of the following types of teeth:
- A doped tooth of wisdom is a common pathology. The cause of this phenomenon may be heredity or trauma to the jaw. In addition, molars of the third row are considered a sign of atavism, which may gradually disappear during evolutionary development.
- Fangs.This pathology occurs in 10-12 years due to improper development of molar type teeth. A distant or retarded canine usually indicates not only a violation of the aesthetics of the oral cavity, but also constant problems when chewing solid food. Besides canine with medial dystopia can permanently injure the soft tissues of the cheeks and tonguecausing the patient discomfort, provoking the danger of an inflammatory process.
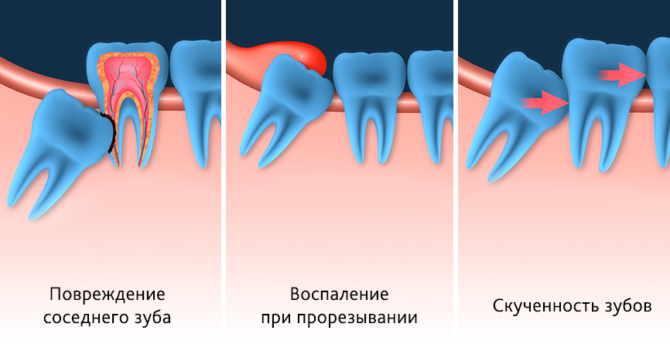
Possible consequences of pathology
Often patients get used to the wrong bite without going to the dentists. This is especially often the case when the patient does not experience pain and other discomfort. However, in the absence of timely treatment, the presence of a retarded or doped tooth can lead to other disorders of the body.
Possible complications:
- An incorrect bite does not allow you to completely chew food, which is fraught with incomplete digestion, and subsequently with diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- With the wrong location or the presence of extra distant teeth, cases of loss of an absolutely healthy neighbor are not uncommon.
- If the dentition is not formed correctly, diction disturbances, problems with the pronunciation of those or other sounds are possible.
- Traumatic injuries to the inside of the cheek and tongue are common.
Removal of retined and distoped teeth
Indications for the removal of the retined tooth are:
- pathological location, lack of space in the dentition;
- delay in retrograde tooth loss;
- destruction of the tooth neck;
- if the retined tooth is redundant and interferes with the normal growth of the rest;
- dentists advise removing such teeth in the presence of complications.
Removing a retined and dystoped tooth implies a high invasiveness of the intervention, since it is necessary to exfoliate the mucosa and periosteum, extract the tooth from the bone using boron, remove it from the bone using forceps, and also suture. If the roots of adjacent teeth are exposed, the doctor resects them, and then does the retrograde filling procedure.
When there are no indications for the removal of a retarded or dystopic tooth, doctors perform an intervention to excise the gums or periosteum. The next stage of therapy will be orthodontic treatment in the form of braces or special buttons.
With regular injuries to the cheeks and tongue due to dystopia or retention, dentists can perform a procedure for polishing dental tubercles. However, most often with such pathologies, a radical solution to the problem is recommended. Sometimes after such a procedure, dental prosthetics may be required.
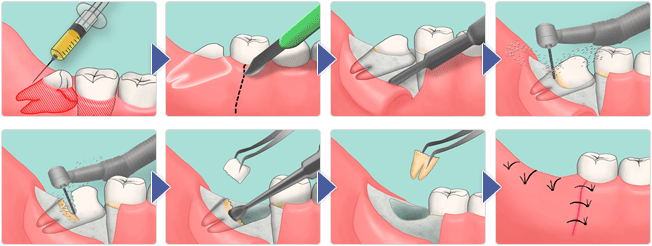
Procedure for the removal of a retarded wisdom tooth:
- Gum surface anesthesia with a special gel or spray.
- The introduction of an injection of anesthetic drug.
- Incision of the gums with a scalpel, exposure of the wall of the bed.
- Drilling holes for access to a wisdom tooth.
- Dental crown slice and extraction.
- Separation and extraction of dental roots.
- Cleaning and disinfection of the wound, sometimes - the imposition of turunda with iodine.
- If turunda has not been established, a seam is applied after antiseptic treatment.
The removal of a dystopic wisdom tooth occurs according to a similar pattern.
Postoperative period
After surgery, the patient’s teeth need enhanced care and medical supervision.
- If turunda was applied, during the first three days from the time of the intervention, you need to visit the dentist to monitor the condition of the wound, perform disinfection procedures. After this time, the dentist will remove the swab and suture.
- Every day brushing your teeth should be carried out sparingly, avoiding injury to the operated area.
- For 3 days after surgery, the use of mouth rinses is prohibited.
- All food must be mashed, chewing on the operated side is prohibited.
- In the first few hours after the intervention, it is not recommended to drink, eat, use tobacco products.
- If the patient is worried about severe pain, then it is not forbidden to take an analgesic pill.
- For 2-3 days after the operation, you should not get involved in physical exercises.