Types of modern methods of anesthesia in dentistry, drugs for pain relief
Fears associated with pain in the treatment and extraction of teeth are due to the fact that before there were no high-quality anesthetics. But today, almost all dentistry clinics use local anesthetics of a new generation. Modern drugs can completely eliminate pain, not only during the main operation, but even at the time of their administration.
Content
Dentistry anesthesiology
Anesthesia is an absolute disappearance or a partial decrease in sensitivity in the whole body or its individual parts. This effect is achieved by introducing special preparations into the patient’s body that block the transmission of pain impulses from the area of intervention in the brain.
Types of anesthesia in dentistry
According to the principle of impact on the psyche, two main types of anesthesia are distinguished:
- Local anesthesia, in which the patient is awake and loss of sensation occurs exclusively in the area of future medical procedures.
- General anesthesia (anesthesia). The patient is unconscious during the operation, anesthesia of the whole body and relaxation of skeletal muscles occur.
Depending on the method of supplying the anesthetic to the body in dentistry, injection and non-injection anesthesia are isolated. With the injection method, the anesthetic is administered by injection. It can be administered intravenously, in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, in the bone or periosteum. With non-injection pain relief, the anesthetic is given by inhalation or applied to the surface of the mucosa.
General anesthesia in dentistry
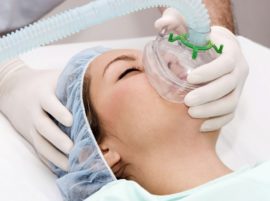
General anesthesia is the complete loss of sensitivity of nerve fibers, accompanied by impaired consciousness. In dentistry, anesthesia for dental treatment is used less often than local anesthesia. This is due not only to the small area of the surgical field, but also to a large number of contraindications and possible complications.
General anesthesia can only be used in those dental clinics that have an anesthetist and resuscitation equipment, which may be required in case of emergency resuscitation.
General anesthesia in dentistry is necessary only for long-term complex maxillofacial operations - correction of the cleft palate, multiple implantation, surgery after injury. Other indications for the use of general anesthesia:
- allergic reactions to local anesthetics;
- mental illness;
- panic fear of manipulation in the oral cavity.
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system;
- intolerance to anesthetics.
An anesthetic may be administered by injection or via inhalation. The most popular medication for general inhalation anesthesia among dentists is nitrous oxide, known as laughing gas.Using an intravenous injection, the patient is immersed in a sleep medication, for this, drugs that have sleeping pills, analgesic, muscle-relaxing and sedative effects are used. The most common are:
- Ketamine
- Propanidide.
- Hexenal.
- Sodium hydroxybutyrate.
Local anesthesia in dentistry
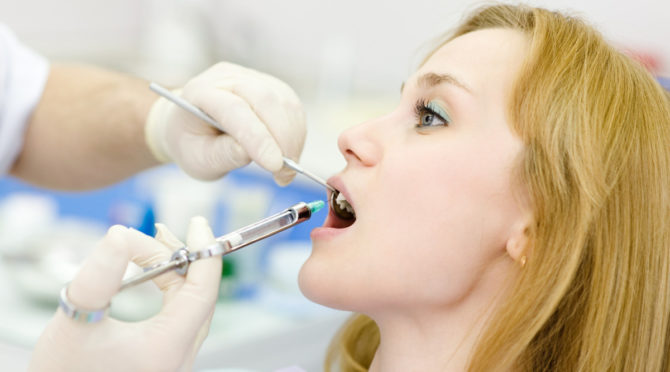
When treating teeth, local anesthesia is most in demand, aimed at blocking nerve impulses from the area of the surgical field. Local anesthetics have an analgesic effect, due to which the patient does not experience pain, but remains sensitive to touch and temperature.
The duration of anesthesia depends on how and what exactly the dentists anesthetize the surgical field. The maximum effect lasts for two hours.
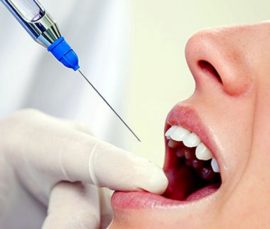 Local anesthesia is used for the following manipulations:
Local anesthesia is used for the following manipulations:
- removal of cystic formations;
- turning under a bridge or crown;
- pin extension of teeth;
- implant implantation;
- canal cleaning;
- surgical treatment of gums;
- removal of carious tissues;
- tooth extraction;
- excision of a hood over a wisdom tooth.
Types and methods of local anesthesia in dentistry
Depending on what area and for how long you need to deprive sensitivity, the dentist selects the optimal technology, medicine and its concentration. The main methods of administering anesthetic are:
- infiltration;
- intraligamentary;
- stem;
- intraosseous;
- applique.
Infiltration method
It is used in dental practice and maxillofacial surgery. The advantage of the method is its quick action, long analgesic effect, the possibility of repeated administration with a prolonged operation, the rapid removal of the anesthetic from the body, deep analgesia of a large area of tissue. About eighty percent of dental interventions are performed under infiltration anesthesia.
The method is used for the following manipulations:
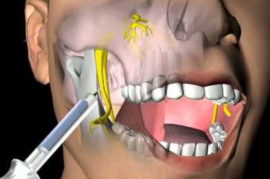 extraction and treatment of teeth (mainly the upper jaw row);
extraction and treatment of teeth (mainly the upper jaw row);- opening and removal of purulent formations under the skin;
- foreign body extraction from the gums;
- treatment of complicated caries;
- suturing;
- tumor extraction;
- hernia repair.
Anesthetic medicine is administered in layers, first under the mucous membrane at the top of the tooth root, and then into the deeper layers. The patient feels discomfort only at the first injection, the rest are carried out absolutely painlessly.
There are two types of infiltration of dental anesthesia - direct and diffuse. In the first case, the anesthetic injection site is anesthetized directly, in the second, the analgesic effect extends to the nearest tissue sites.
For local infiltration anesthesia in dentistry, the following drugs are used:
- Procaine.
- Lidocaine.
- Mepivacaine.
- Ultracain
- Trimecaine.
Intraligamentary (intracircular) method
It is a modern form of infiltration anesthesia. The dose of injected anesthetic is minimal (does not exceed 0.06 ml), which makes it possible to treat and remove teeth in pregnant and lactating women.
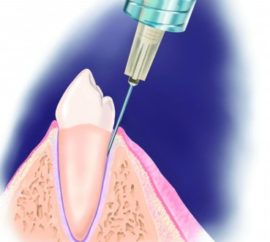 Anesthetic is injected into the periodontal space using a special syringe and under high pressure. The number of injections depends on the number of roots in the tooth. Sensitivity to pain disappears instantly, without causing a feeling of numbness, so the patient is free to speak and does not feel discomfort after surgery.
Anesthetic is injected into the periodontal space using a special syringe and under high pressure. The number of injections depends on the number of roots in the tooth. Sensitivity to pain disappears instantly, without causing a feeling of numbness, so the patient is free to speak and does not feel discomfort after surgery.
Limitations to the use of the method are:
- The duration of the manipulation is more than 30 minutes.
- Fang manipulations. Due to the anatomical features, it is not always possible to anesthetize them intramuscularly.
- Inflammatory processes in the periodontium, periodontal pocket, flux.
- Basal cyst of the tooth.
The intraligamentous method of pain relief is the most painless and safe in dentistry, which is why it is often used in pediatric practice. Simplicity of execution, painlessness, safety and high efficiency makes the method popular among dentists. The cost of this procedure is higher than the infiltration, due to the high prices of injectors.
The following medications are used for intraligament anesthesia in dental treatment:
- Ultracaine.
- Trimecaine.
- Lidocaine.
Stem (conductor) method
Distinctive features of the stem method of anesthesia are the power and high duration of the effect. It is used during prolonged surgical operations and in situations where it is necessary to block sensitivity in the tissue area of the entire lower or upper jaw.
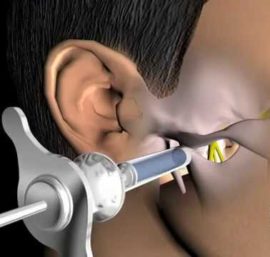 Indications for conduction anesthesia are:
Indications for conduction anesthesia are:
- high intensity pain syndrome;
- neuralgia;
- removal of cystic formations;
- endodontic treatment;
- severe injuries of the jaw and zygomatic bone;
- curettage;
- complex tooth extraction.
An injection is injected into the region of the base of the skull, so that you can block two jaw nerves at once - both the upper and lower. An injection is performed by an anesthesiologist and exclusively in a hospital.
Unlike all other methods of local anesthesia, the stem does not affect the nerve endings, but completely on the nerve or group of nerves. The time of anesthetic action is one and a half to two hours. The basic drugs are Novocain and Lidocaine; in modern anesthesiology, more effective drugs are used.
Application method (surface, terminal)
It is used mainly in pediatric dental practice to deprive the sensitivity of the place where the anesthetic will be made, which ensures an absolute absence of pain. As an independent method, it is used in cases where it is necessary:
 reduce the sensitivity of hard tooth tissues;
reduce the sensitivity of hard tooth tissues;- remove milk or pathologically movable molar;
- open a submucosal abscess of a small area;
- treat the mucous membrane with stomatitis and gingivitis;
- prepare the tooth for prosthetics;
- remove mineralized deposits in the cervical region.
For application anesthesia in dentistry, painkillers in the form of a spray, ointment, paste and gel are used. Most often, dentists use ten percent lidocaine in an aerosol as an analgesic. The drug penetrates deep into the tissues by 1-3 mm and blocks the nerve endings. The effect lasts from several minutes to half an hour.
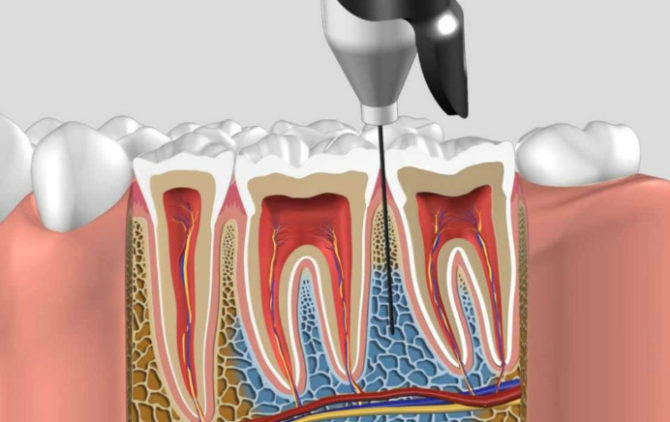
Intraosseous (spongy) method
It is used to anesthetize the lower molars, during the extirpation of which infiltration and conduction anesthesia are ineffective. Instantly removes the sensitivity of one tooth and adjacent gingiva. The advantage of the method in the field of dentistry is strong anesthesia with small doses of the drug.
Classical intraosseous anesthesia has not been widely used in anesthesiology, due to the complexity of the implementation and the morbidity.
The essence of the method is the introduction of anesthetic into the spongy layer of the jawbone between the roots of the teeth. Pre-performed infiltration analgesia. After numbness of the gums, the mucosa is dissected and the cortical bone plate is trepanded with the help of a drill. Boron is buried into the spongy tissue of the interdental septum by 2 mm, after which a needle with an anesthetic is inserted into the formed channel.
Contraindications to local anesthesia
Before prescribing the patient local anesthesia, the dentist must determine whether there are any contraindications to it. The doctor should take special precautions when prescribing anesthesia for children and expectant mothers.
Contraindications to local anesthesia are:
- a history of allergic reactions to drugs;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- suffered a stroke or heart attack less than six months ago;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders and pathologies of the endocrine system.
Modern anesthetics (painkillers) in dentistry
With the advent of local new-generation anesthetics and technologies, they almost never use the usual Novocaine in the field of dentistry, especially in Moscow and other large cities. Despite possible complications and a high percentage of allergic reactions, lidocaine remains the main local anesthetic in regional clinics.
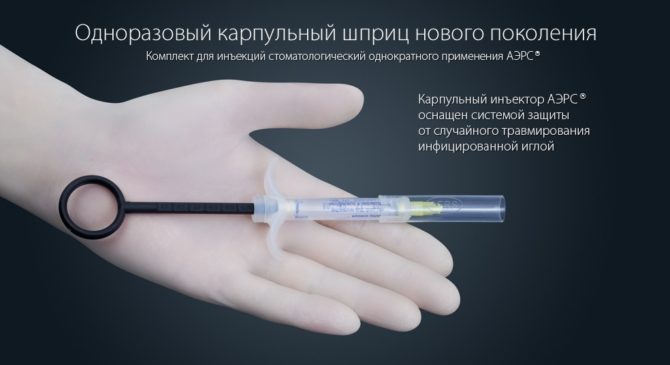
When visiting the clinic, you need to provide the attending physician with a complete and reliable history so that he can eliminate all the risks and choose the right drug. Most dental clinics use carpul technology for the administration of anesthetics, which consists in the fact that the active substance is contained in a special disposable carpule, which, without opening manually, is inserted into the syringe. The dose of the drug in karpul is designed for one administration.
The basis of modern means for local anesthesia are drugs Artikain and Mepivacaine. In the form of capsule capsules, Artikain is produced under the names Ultracain, Septanest and Ubistesin. The effectiveness of drugs based on it exceeds the effectiveness of lidocaine by 2, and novocaine by 5-6 times.
In addition to Artikain himself, the karpul contains adrenaline (epinephrine) and an auxiliary substance that helps to narrow the vessels. Due to the narrowing of the vessels, the period of action of the anesthetic is prolonged, and the rate of its spread into the general bloodstream decreases.
Patients with endocrine disorders, bronchial asthma and a tendency to allergic reactions in dentistry are usually prescribed anesthetics without adrenaline. If powerful anesthesia is required, the use of Ultracain D with a minimum concentration of epinephrine is acceptable.
Adrenaline-free anesthesia in dentistry
To treat patients with contraindications to epinephrine in dentistry, mepivacaine is used. A drug with this active substance, produced under the name Scandonest, is less effective than articain. But it does not include epinephrine, so Scandonest is suitable for administration to children, women in position, people with heart diseases, and individual intolerance to adrenaline.
With diseases of the endocrine system, Scandonest and drugs without adrenaline are more often used. It is unacceptable to use drugs with vasoconstrictor components for hypertension.
From what kind of anesthesia dentists use, not only the degree of painlessness of the medical intervention depends, but also the list of consequences that will have to be encountered after the operation. Modern drugs minimize the risks associated with incorrect administration of the drug, the wrong dosage and the occurrence of allergic reactions to the anesthetic.