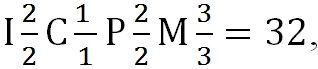Names and layout of teeth in adults and children
All teeth in a person have their own names and are located according to a certain pattern. The formulas of milk (temporary) and permanent dental units are somewhat different, but have a common construction logic.
Content
What is a dental formula?
A dental formula or scheme is a brief description of the dental structure of a person’s dentofacial apparatus using numbers and Latin letters. Letters are abbreviations of the Latin names for teeth accepted in medicine:
- I are dentes incisivi or incisors.
- C is dentes canini or fangs.
- P is dentes premolars or premolars.
- M are dentes molars or molars.
An alphanumeric dental formula is common in many countries, including America, which is why it is sometimes called American. After the letters in the formula, there is always a digital fraction, where the numerator indicates the number of teeth on the upper jaw, and the denominator on the lower.
The dental formula of a healthy adult with a normal bite and the number of teeth in the amount of 32 pieces looks like this:
This formula indicates that on each jaw of a person is located:
- 2 pairs of incisors;
- 1 pair of fangs;
- 2 pairs of premolars;
- 3 pairs of molars.
Dental formula in the absence of certain teeth
It is not difficult to correctly number the dental units with a healthy dentition; it is much more difficult to indicate the location of the teeth if the person does not have any molars, incisors, fangs or premolars. In this case, the dentist indicates the number 0 opposite to a certain group of teeth, and does not shift the number series.
If the patient has any abnormalities in the development of the dentition, for example, teething in the wrong place (hyperdontia, polydontia), the dentist prescribes an individual formula. In addition to numerical designations, the doctor generates a detailed report on the structure of the dentition of a person.
Description, structure, functions, name and location of teeth in humans
The teeth of a person for a reason have a different shape, structure and size. Each tooth performs certain functions, and its purpose, one way or another, is reflected in the name:
- Incisors are the front teeth that fall into the smile zone. They are quite sharp, as their function is to tear or cut food, hence the name. Normally, each person has lateral and central (larger) incisors.
- Fangs are cone-shaped teeth with which you can tear and hold food. They are located immediately behind the incisors.
- Premolars are the posterior small molars located behind the fangs.
- Molar teeth are the posterior teeth necessary for the mechanical processing of food. The wisdom tooth refers specifically to molars.
The listed types of teeth are in animals. But in the process of their evolution, some dental units were somewhat modified:
- the upper incisors of the elephants became tusks;
- poisonous snakes have fangs in their fangs.
Many animals have human-like front teeth, but as they are called differently, they cannot always be identified with familiar incisors and fangs.
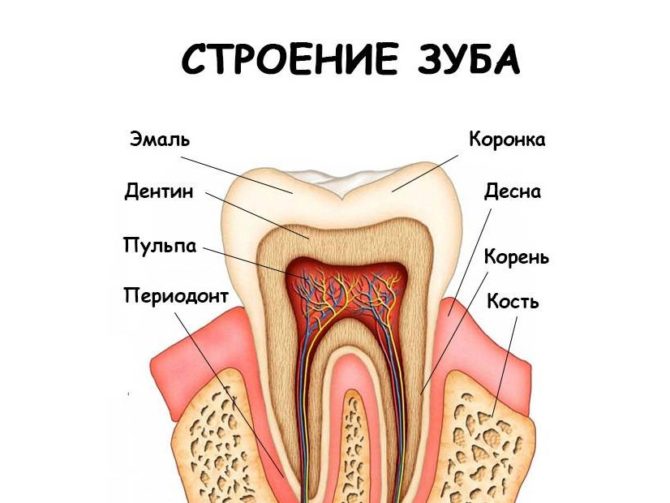
The structure of teeth in humans
Human teeth are made up of coronal and root parts. The first is above the level of the gums, the second is inside it.From above, the crown is covered with enamel - the most durable tissue in the body. It protects from the external influence the inner layer of the tooth - dentin. Under the dentin is a hollow chamber with nerves and blood vessels - the pulp.
Despite its durability, enamel is vulnerable to bacteria. If untreated, caries can affect dentin and pulp. With damage to the pulp chamber, in which the nerve fibers are located, pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute throbbing pain. If the infection spreads to the root of the tooth, it is highly likely that it will have to be removed.
The base of the lower part of the tooth is the root canals, which also contain arteries, veins and nerve fibers. Through the apical opening, all of these structures are connected to the main neurovascular bundle.
The lower part of the tooth is covered with dentin and cement, which is attached to the periodontium using collagen fibers. Dental roots hide in the alveoli - depressions in the jawbone.
By what principle are teeth numbered according to different classification systems
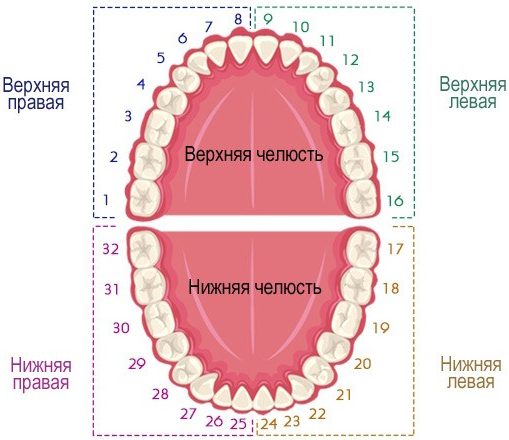
In addition to the Latin names of teeth, in dentistry use digital notation. Numbering of teeth is based on the order of their teething. It starts from the front incisors (from the middle of the jaw) and runs in the direction to the left and to the right of them.
There are several generally accepted systems for numbering teeth in humans.
Universal system
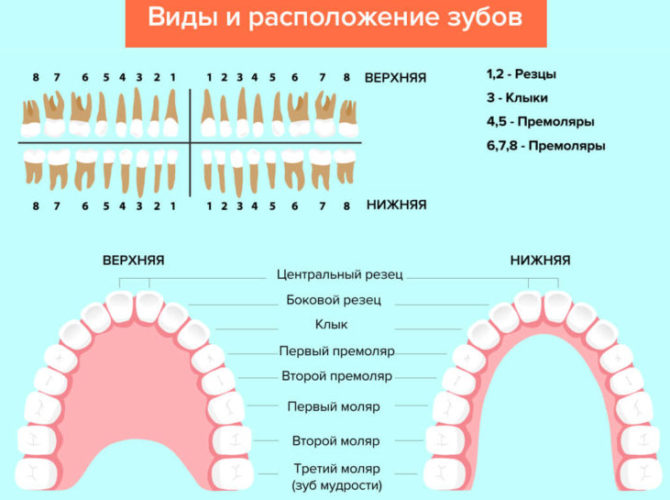
Most often, dentists call teeth not in Latin letters, but in accordance with their location in the oral cavity (serial number). And using not Roman, but familiar Arabic numerals.
Names of teeth according to the universal classification system:
- two central incisors are located at number 1 and are called unity;
- the second incisors are numbered 2;
- fangs are called triples;
- chewing teeth or premolars are called fours and fives;
- molars are called sixes, sevens and eights.
According to the universal classification system of dental units, the jaw is divided into 4 segments:
- upper left;
- upper right;
- lower right:
- bottom left.
The further name indicates not only the serial number, but also the location of the dental unit in the human oral cavity.
The universal dental numbering system is the most popular and often used. It is used by dentists and surgeons in various countries.
The picture shows the designation of teeth in the oral cavity of an adult according to the universal numbering system:
European system
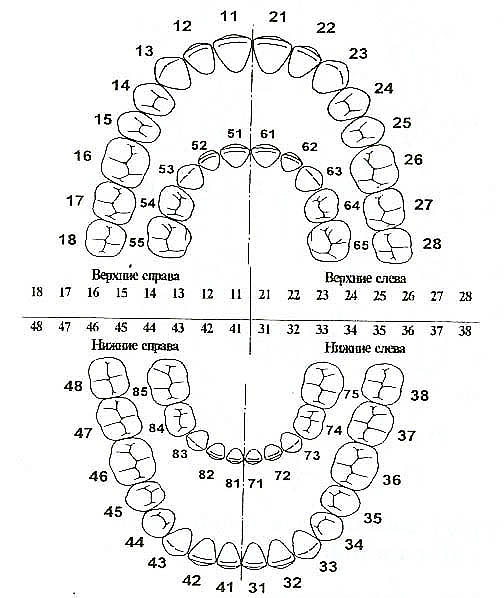
The European Viola system is one of the newest and most advanced methods for naming human teeth. It is characterized by the separation of the jaw into segments (two from the bottom and from the top). Each segment is numbered (from 1 to 4).
Based on these numbers, each tooth receives a two-digit number. The first digit represents the segment, and the second the actual serial number.
The Viola system is recognized internationally and is therefore popular throughout the world. It is used in radiography, the production of panoramic images and allows the exchange of patient information for dentists from different countries, overcoming the language barrier.
Haderup system
Arabic numerals are used to designate dental units according to the Haderup system and segmentation into the lower and upper jaws is used:
- the “+” sign indicates belonging to the upper jaw;
- the “-” sign indicates the lower jaw.
The disadvantages of this numbering can only be attributed to the fact that you have to additionally indicate that the dental unit belongs to the left or right side of the jaw.
Sigmond-Palmer System
The Sigmond-Palmer system is recognized as the most imperfect, since only tooth numbers without their location are indicated on it. Standard Arabic numerals are used for numbering.
This tooth numbering system is practically not used for medical and diagnostic measures. Only orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons use it.
Alternative names for teeth in humans
In addition to official names, there are alternative names for teeth in humans. They are not written in dental charts, but have long been used in informal communication, as these teeth are located or grow in people in certain places or at certain times.
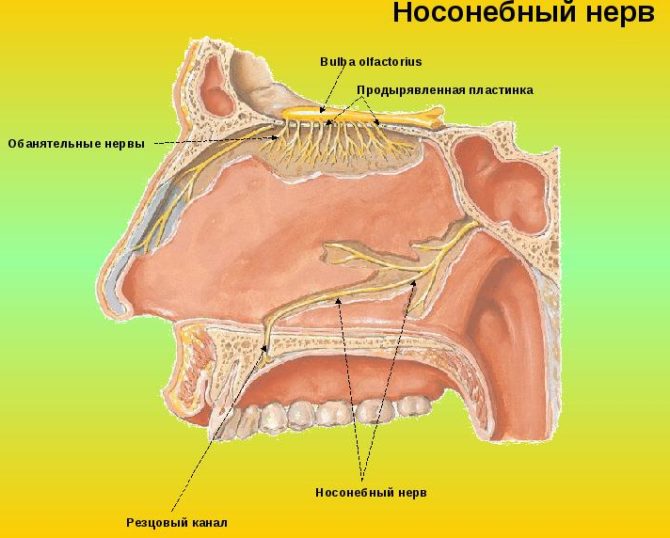
Eye teeth
Ocular fangs are referred to as upper canines due to their close proximity to the branches of the facial nerve. When they become inflamed, the pain radiates to the eye and upper face. How closely the incisal canals and the dental nerve are located are shown in the figure:
Wisdom tooth
The tooth of wisdom is the posterior third molar. He was called "wise" because he grows up in adulthood - when a person has already managed to gain wisdom (by about 20 years).
Correct names for primary teeth
In Latin, baby teeth are called the same as permanent teeth in an adult. But the kids do not have all the dental units that are characteristic of older people. Milk teeth are divided into:
- central incisors;
- side incisors;
- fangs
- first and second molars.
There are different names for teeth, but it is better to focus on Latin terms and serial numbers. In this way, teeth can be identified even without serious knowledge in dentistry.