Wrong bite: causes, correction, prevention
Deviations in the closure of the dentition of the lower and upper jaw - malocclusion - to varying degrees observed in half the inhabitants of the globe. Without adequate therapy, such anomalies lead to a deterioration in overall health, cause speech defects, and change appearance. Timely detection of pathology and correction of atypical occlusion will help to avoid these complications.
Content
What is a malocclusion?
The mutual arrangement of the lower and upper row of human teeth in a tight connection, with the maximum number of contacts between them, is called a bite. Orthodontists distinguish between physiological and pathological types of closure of the dentition.
The correct bite provides a functional and aesthetic optimum: distributing chewing pressure evenly, it relieves the jaw of overload. The physiological types of bites include: opistognathia, direct and orthognathic bite, physiological bipognathia.
Improper tooth position - deviation from the norm, expressed:
- in violation of forms and functions,
- in defects of closure during eating, during conversation, at rest;
- in increased loads on the jaw when chewing.
Anomalies are formed under the influence of a number of factors and must be corrected in order to avoid severe consequences for the body.
Reasons for the development of a pathological bite
Acquired and congenital etiological factors of the occurrence of abnormal closure of the teeth are distinguished.
Congenital causes of malocclusion are heredity (genetic defects transmitted from parents) and intrauterine pathologies of the fetus (infections, metabolic disorders, low levels of hemoglobin in the mother). Malocclusion resulting from these factors is most difficult to correct.
Acquired causes of malocclusion provoke the development of deviations in the location of the jaws immediately after birth or at a later age. In children, the wrong bite is formed under the influence of:
- birth injuries;
- rickets;
- chronic ailments (pathologies of the respiratory system, endocrine diseases);
- increase the duration of artificial feeding;
- bad habits (sucking a finger, biting lips);
- untimely excommunication of the child from the dummy (nipples);
- early tooth extraction;
- lack of good nutrition (lack of fluoride, calcium, trace elements);
- lack of food products with coarse fibers (fruits, vegetables) - the result of a small load on the jaw becomes the incorrect formation of their closure;
- multiple lesions of milk teeth by the carious process;
In adult patients, normal bites change pathologically with periodontal disease, after the loss of some of the permanent teeth or injuries of the facial bones. Anomalies often develop due to improper prosthetics (inconsistencies of implants with the anatomical features of the patient's chewing apparatus).
How to identify the wrong bite
In order to independently evaluate the type of tooth closure and decide whether to contact a specialist for help, you need to know how to determine the correct bite and identify developmental abnormalities. The initial assessment of occlusion at home is carried out visually. Its principles are given in the table below.
| Signs of proper closure | Symptoms of malocclusion |
|---|---|
| Harmonious face contour | Asymmetry |
| No visible defects in the lower part of the face | Lower jaw protrudes forward |
| Undeveloped chin | |
| Upper lip does not cover teeth, protruded | |
| The midline is between the first lower and upper incisors of the dentition | Crooked teeth not completely touching |
Only an orthodontist is able to accurately determine the presence of pathologies.
If only the deformation of the teeth is present in the oral cavity, then there are no external differences indicating orthodontic problems.
Determination of malocclusion in a medical clinic is carried out using methods such as:
- symmetroscopy (studying the location of teeth in the sagittal, transverse directions);
- MRI of the temporomandibular joints;
- electromyotonometry (determination of muscle tone).
To identify anomalies, a number of specialists are additionally involved fluoroscopy.
If a malocclusion is detected, the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s disease, will advise the most suitable type of correction for closure of the dentition.
Types of malocclusion
Clinical orthodontics classifies abnormalities in the development of occlusion of teeth into 6 types: deep, cross, distal, mesial, understated and open.
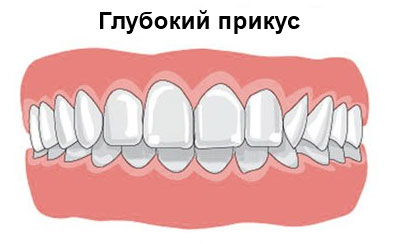
Deep bite
Deep incisal dysocclusion is characterized by a significant overlap by the front teeth of the upper jaw of the lower incisors, i.e., dentoalveolar elongation. Visually, the signs of such an anomaly look like a thickened lower lip and a reduced facial area. There are 2 types of development of deviations from the correct bite:
- deep bite (lower incisors slide to the gingival margin);
- the formation of a deep frontal overlap (this means that the cutting edges of the lower teeth articulate with the dental tubercles of the upper).
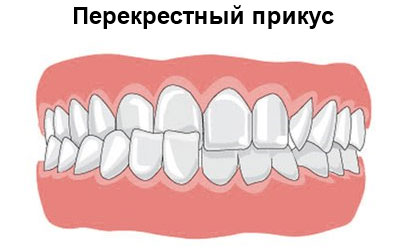
Vestibular occlusion
The cross type of malocclusion is manifested by the apparent asymmetry of the face. In the oral cavity, unilateral underdevelopment of the jaw is noted. This causes the intersection of the teeth in the upper and lower row. The lack of contact of molars during the chewing process is both unilateral and bilateral.
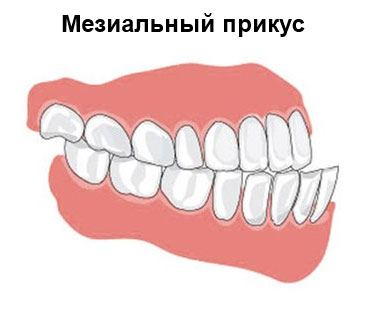
Mesial bite, progenia
Subdivided into:
- partial (displacement in the region of the anterior teeth) and general;
- maxillary and dental.
It is possible to determine the presence (absence) of a mesial bite by the position of the lower teeth. When progeny they are significantly advanced.
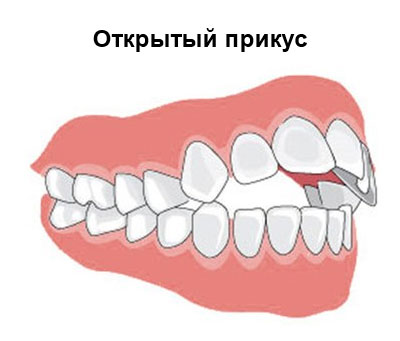
Open bite
It is characterized by the presence of a gap between the teeth. With this type of malocclusion, do not contact:
- only incisors;
- fangs and incisors;
- only the last molars come together.
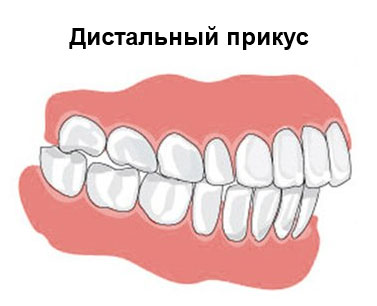
Distal bite
The diagnosis of “Prognathy” implies the presence of abnormal closure of the teeth, a crooked bite, which reveals a mismatch in the ratio of the dentition due to the standing of the teeth of the upper jaw or the distal position of the teeth of the lower jaw. To determine this type of bite by external symptoms is quite simple (there is an upper lip extended forward, a small chin, a reduced lower third of the face).
Low bite
The type of malocclusion, in which the result of abrasion of the teeth (lowering their height) becomes an underestimated closure.
Malocclusion: developmental implications
The crooked type of closing of teeth is the cause of a large number of pathologies.Among the most common - dental diseases (caries, soft tissue injuries, stomatitis, periodontal disease), caused by the lack of the possibility of high-quality and proper hygiene procedures.
An incorrect bite provokes the erasure and chipping of dental crowns, malfunctions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract resulting from a violation of chewing function. Digestive system diseases lead to weakened immunity; this is the cause of the development of diabetes, hypertension.
The consequences of malocclusion include speech therapy pathologies (incorrect pronunciation of individual sounds), facial expressions defects.
The result of a malocclusion is frequent ENT diseases (sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media), respiratory dysfunction, cervical spine deformities, and headaches.
The presence of crooked teeth often leads to psychological complexes that reduce the level of socialization of a person in society.
After detecting the first signs of atypical occlusion, you should immediately contact a medical clinic. Timely and correctly performed correction will reduce the likelihood of the described ailments.
Treatment
It is impossible to correct the wrong bite on your own.
Bite correction takes a long period. Often, therapy lasts more than a year. The age of the patient who went to the doctor also means a lot: the earlier treatment is started, the faster the expected effect will be achieved.
Only the orthodontist is able to determine the method for correcting the closing curve of teeth. Clinics in Moscow offer the most modern methods of therapy, including the use of various devices (braces, orthodontic mouthguards, palatine plates, veneers, Angle, Coffin, Hausser, Planas devices) and surgical intervention.
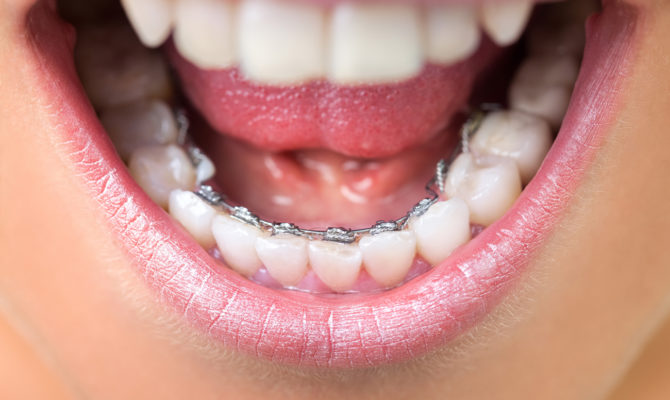
Braces Installation
Bracket systems are non-removable orthodontic constructions that contribute to the elimination of certain pathologies of malocclusion using constant pressure. They will give the opportunity to correct alveolar prognathism.
The process is ensured by the power arc structures fixed in the grooves. Made of ceramics, plastic, metal. It is allowed to install braces on the front surface of the dentition (vestibular type of apparatus) and their inner side (lingual systems). Correction lasts from a year to 36 months; the duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
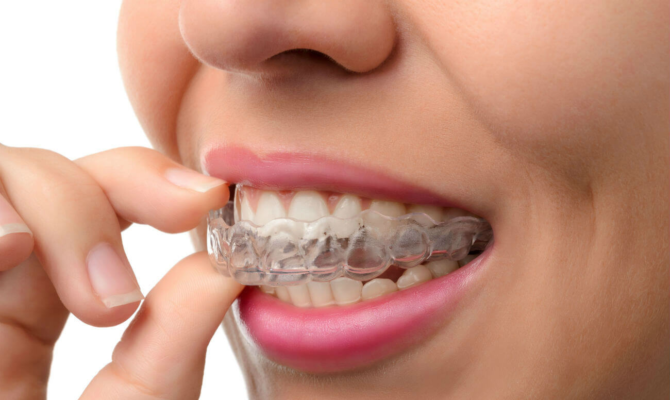
Involving orthodontic caps
Special overlays for teeth change the wrong bite and align the dentition. The principle of action is a tight "fit" of the teeth, pressure in the right direction. The use of orthodontic cap is ineffective in mesial, deep or distal types of malocclusion.
Using veneers and palatine records
Composite, ceramic veneers help hide minor occlusion defects.
The use of bite palatal plates is used to correct a deep bite. The design is divided into removable and non-removable types. The plate is mounted on the teeth using a special (clasp) fastening. It acts by pressure on the dentition in a given direction. The clinic specialist will help you choose the right device.
Surgical intervention
It is carried out with pronounced deviations in the anatomy of the dentition and jaw bones. It is possible to remove part of the bone or build it to the required size.
Qualified orthodontists will help determine the choice of correction method.
Malocclusion: Prevention
Preventive measures of abnormal occlusion are conditionally divided into 3 periods.
- Gestation period. During pregnancy, a woman should carefully monitor her health and nutrition. Enough level calcium and phosphorus in food intake means the maximum reduction in the risk of fetal tooth pathologies.
- Age from 0 to 14 years. Until the child reaches one year old, parents are required to monitor the correct feeding of the baby.
Particular attention should be paid to the diameter of the hole in the nipple during artificial feeding. It is important to timely eliminate breathing problems (if the child breathes through the mouth, then the growth of the upper jaw changes, an open bite forms). Starting from the age of two, you should control the bad habits of the baby, timely accustom him to oral hygiene.
- Age from 14 years. The time of the final formation of a permanent bite; any loss of teeth means a violation of the correct course of the process. If symptoms of abnormalities are found, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Timely resolution of bite problems will minimize the development of complications and the term for correction of pathology. Correction of abnormalities on molars is a lengthy and expensive process. The main rule for preventing the occurrence of a problem is prevention and regular visits to the clinic.