Methods and stages of installation of tooth implants, indications, contraindications, duration of operation and terms of engraftment
All stages of the installation of a tooth implant are as safe and painless for the patient as possible if the operation is carried out in a good dental clinic using high-quality equipment and modern materials. This type of prosthetics is to restore not only the crown, but also the root of the tooth, which helps the entire jaw system to function normally. Having resorted to implantation, you can save the jaw bone from atrophic changes without injuring the remaining healthy teeth.
Content
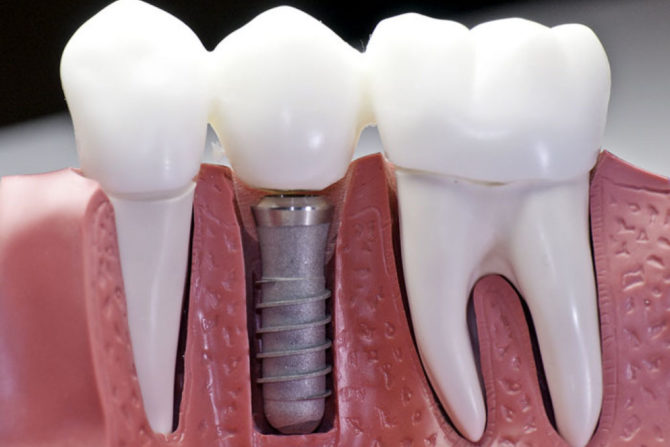
How do implants, their structure
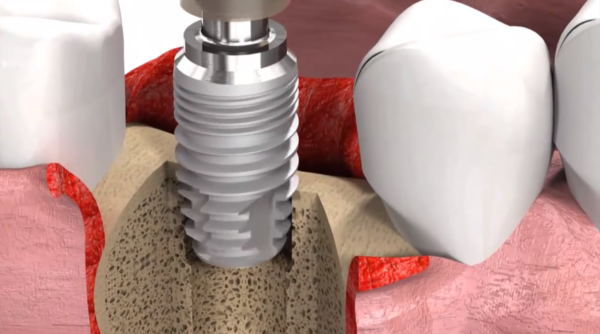
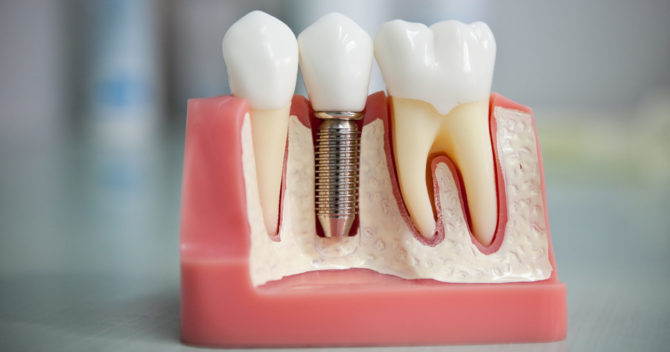
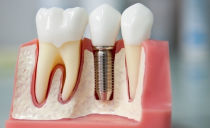
Implant or implant (in English - implant) Is a tooth root shaped pin. It is made of a medical metal alloy and is placed in the jawbone. Then the abutment is installed on the prosthesis, and on it is the crown, which can be changed without removing the implant.
Before prosthetics, the dentist evaluates the feasibility of installing the implant, taking into account the physiological characteristics of the patient’s body, his health status.
You can learn more about how implants are made from the video:
Indications and contraindications
The classic indications for implantation are:
- end defects of the dentition;
- complete and incomplete absence of teeth;
- intolerance to removable prostheses due to allergies or gag reflexes;
- defect in functional occlusion (jaw closure) after tooth extraction or improper dental treatment.
Absolute contraindications include:
- tumors (if you insert implants, they will begin to grow);
- increased tone of the masticatory muscles;
- bleeding disorder;
- pathologies of the nervous system and mental disorders;
- childhood;
- immunodeficiencies;
- diabetes mellitus (especially uncompensated type);
- tuberculosis;
- osteoporosis;
- some forms of stomatitis;
- allergy to anesthesia;
- chronic forms of diseases of various internal organs;
- rheumatism.
Relative contraindications for dental implant surgery:
- pregnancy at all times;
- period of breastfeeding;
- pathological bite;
- bruxism;
- poor oral hygiene;
- carious cavities (the prosthesis is inserted only after the complete treatment of caries);
- mucosal inflammation;
- cachexia;
- pathology of the temporomandibular joint;
- smoking.
The patient should warn the doctor about all existing chronic diseases in order to exclude the likelihood of complications.
How to put dental implants, methods
How many implants are needed depends on the number of dental units that need to be restored. If one tooth is lost, one implant is placed. If two or three molars are missing, then two or three prostheses are placed respectively. It is not advisable to be limited to one implant, since it may not withstand the increased load during chewing. In the case of complete adentia, the number of prostheses is determined by the doctor depending on the estimated interdental distance.
Types of implantation:
- Intraosseous placement of dental implants is characterized by the introduction of a prosthesis into the bone tissue.This technology is the most popular and sought-after in the world, because it has the least number of possible complications. A tooth implant is inserted directly into the bone bed.
- Basal implantation is indicated for bone deficiency and the absence of several consecutive teeth. Using this technique, implants are installed if it is not possible to build bone tissue. But it is dangerous with possible side effects and complications. In addition, the designs made according to the basal type are not very reliable, so the basal installation of dentures occupies a modest place in modern implantology.
- Intra mucosal technology is most often used with removable prosthetics for convenient and reliable fixation of the false jaw. In this case, the implant is inserted directly into the gum.
Dental implantation can be divided into three types:
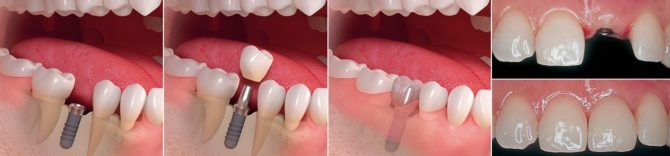
- One-stage implantation allows you to put an artificial root and crown in one visit to the dentist.
- Two-stage installation is done 2 times:
- At the first stage, a metal pin is implanted in the jaw.
- At the second visit, a crown is installed.
- Mini implantation is used to simulate premolars or in narrow parts of the jaw and is characterized by the installation of small prostheses.
Tooth implant installation: stages and terms
The standard procedure for installing a tooth implant is carried out in several stages. Their duration depends on many factors, including the patient’s health status and the level of methods used.
Preparatory stage
The installation of a tooth implant is a serious surgical procedure for implanting a foreign body into the jaw, so the doctor who performs the operation must be sure that the patient is ready for the procedure.
Prosthetics is stress for the body that activates diseases that were previously in a vegetative state. Before the operation, the dentist must make sure not only that the implant has taken root, but also that the patient's body will withstand this load, so the process of dental implantation begins with a basic diagnosis. To do this, the following procedures are carried out in a planned manner:
- visual inspection of the mouth;
- examination by a cardiologist, allergist, neurologist and endocrinologist (the need and sequence of visits to doctors is determined by the therapist);
- passing tests;
- ENT examination (if you need to install the implant in the upper dentition);
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- hardware research;
- bone tissue extension.
Testing
In the framework of dental implants, a number of important studies are done, they include a general blood test with additional parameters:
- Coagulogram or blood coagulation test - determination of the level of fibrinogen, prothrombin and thrombin time.
- Determination of the level of glucose in the blood.
- Biochemistry or blood composition test for:
- amylase;
- common and direct bilirubin;
- cholesterol;
- transaminases;
- electrolytes;
- total protein;
- alkaline phosphatase;
- urea
- creatinine;
- Testing for HIV and hepatitis.
- Atikardiolipin test for syphilis.
You will also need to pass a general analysis of urine, and in the presence of gastrointestinal pathologies, an analysis of feces. In the absence of chronic diseases, taking tests will take little time.
Hardware Research
The following types of examinations are necessary to determine the anatomical structure of the jaw, the quality of bone tissue and its pathologies:
- Roentgenography. Allows you to make a detailed high-quality picture of the studied part of the jaw, due to which the state of bone tissue and existing roots is traced.
- Orthopantomogram. Gives a detailed idea of bone quality and possible pathologies due to volumetric panoramic image.
- CT scan. Helps to get a three-dimensional image of the bone, which allows you to determine the structure and density of the jaw bone.
Without these examinations, not a single tooth implantation takes place, since when an implant is implanted in a bone, there is a high risk of hurt nerves and important blood vessels, and panoramic images can avoid such problems. This rule applies to all forms of prosthetics.
Bone growth
Dental implants are placed only with a sufficient volume of bone tissue. If as a result of hardware studies it is established that the volume of the jawbone is not enough for high-quality prosthetics, then in the absence of contraindications, bone tissue is plastic. For this, various techniques are used:
- Directed regeneration. It is characterized by an increase in bone volume due to the implantation of natural or artificial material.
- Bone block grafting. It is carried out when the bone is resorbed, within its framework tissue is taken on another part of the body and transplanted into the jaw.
- Sinus lifting. Raising the mucous membrane of the lower part of the maxillary sinuses, due to which the volume of the upper jaw increases.
Dental implantation does not occur immediately after bone growth, but several months after the completion of a dental operation.
Surgical stage
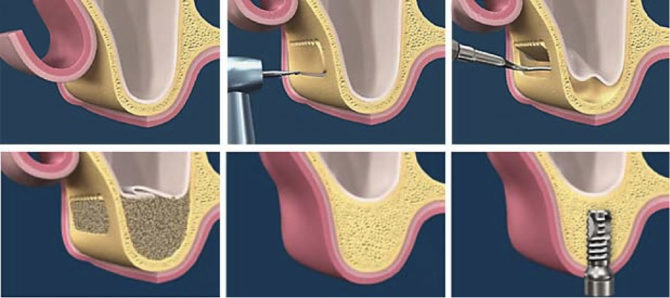
After complete preparation of the oral cavity, the operation itself occurs. The tooth implant installation process does not last long. The time period depends on the quality of the diagnostic work performed, the complexity of the technique used and the physiological characteristics of the structure of the patient's jaw apparatus. A standard dental implant is placed in about 90 minutes. - as much as a regular dental appointment lasts.
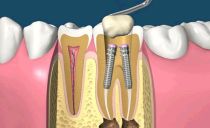
Surgical intervention begins with a flap incision and exfoliation of the gingival and periosteal tissue, resulting in exposing a portion of the bone. A milling mark is mounted on it to form an artificial root bed. Then in this place the doctor drills a thin channel along the length of the implant. After reaching the desired depth, the channel is expanded using special drills.
After obtaining the necessary width in the channel, a thread is made that matches the thread of the prosthesis. Due to it, dental implants are installed. That is, they are simply screwed into the resulting hole, and then closed with a screw cap. Then the mucous and periosteal tissue is placed on the implant and sutured with simple sutures accepted in surgery.
Postoperative period
Dental root implants are placed quickly, but their engraftment lasts a long time. During the first 5 days, swelling and soreness can be observed, then unpleasant symptoms should go away. In the postoperative period, stressful situations, physical exertion, visiting the sauna and bath, as well as chewing on the side of the wound surface should be avoided. It is necessary to treat the oral cavity with antiseptic drugs and do everything possible to make the implant take root. Otherwise, material will be rejected.
Signs of rejection
Signs that the implant has not taken root:
- redness of the gums;
- a tumor at the place of installation of the prosthesis;
- severe pain in the jaw (does not go away even after taking strong painkillers);
- mobility of adjacent teeth;
- rise in temperature.
If you experience any unpleasant symptoms, you should immediately contact your dentist.
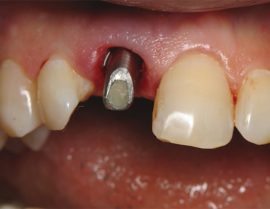
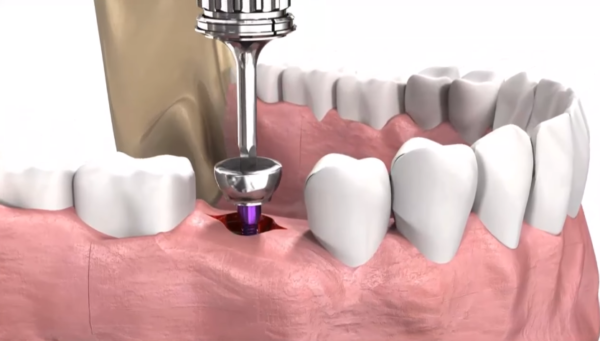
Gingival Stage
To form the natural contour of the gum tissue, a special screw titanium cylinder, called a gum former, is installed instead of the existing screw plug. Its installation occurs 3-6 months after the introduction of the pin.
Within 15 days after the installation of the shaper, a natural gum roller will form around the implant, which plays a key role in retaining the artificial root.
Abutment Installation Step
An abutment is an intermediate part of the implant connecting the root to the crown.It is inserted instead of the gingiva former after the formation of the mucous roller around the future artificial tooth. The procedure lasts not a few hours, but only 15-20 minutes.
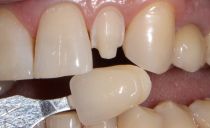
Prosthetics Stage
After engraftment of the tooth implant, an artificial crown is installed. First, casts will be taken from the jaws so that the manufactured dentures have the desired shape, do not interfere with the patient’s bite and help restore chewing function. Then, the resulting crown with adhesive material is placed on the abutment.
Rehabilitation stage
After all stages of tooth implantation, the rehabilitation period begins. Its duration depends on the method of the dental procedure and the physiological characteristics of the body. During this period, you must:
- carefully and thoroughly clean the oral cavity;
- use aseptic rinses;
- visit the dentist regularly (at least once a month);
- reduce the amount of solid food consumed.
The joint work of the dentist and the patient at all stages of the installation of a dental implant guarantees a good engraftment of the dental prosthesis and a complete restoration of the masticatory function.