Splinting of mobile teeth in dentistry: what is it, methods for periodontal disease and periodontitis
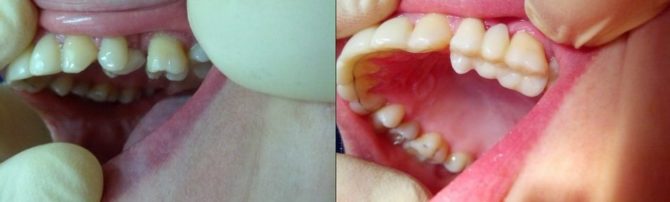
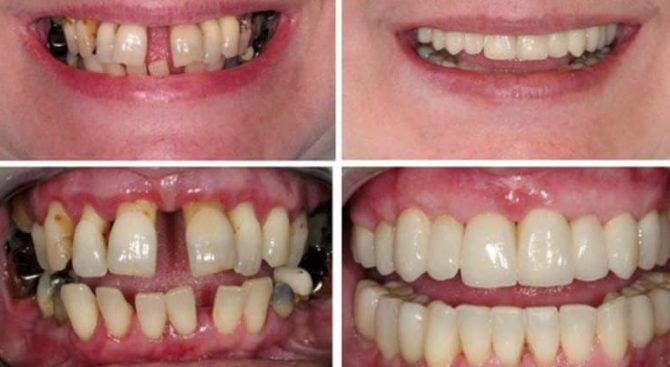
In some diseases, the teeth become loose and deviate from their normal position. Subsequently, this can lead to the loss of individual dental units, since the load on the chewing surface becomes uneven. To preserve the chewing function and esthetics of the dentition, movable teeth strengthen with splinting. The procedure is performed in different ways, the choice of the optimal depends on which teeth are affected - incisors, fangs or molars - and how high demands are placed on the appearance of the dentition.
Content
What is splinting of moving teeth and when is it used
Splinting or shunting is a procedure that allows you to fix loose teeth and prevent their loss. It is prescribed to those patients whose teeth are not firmly held in the cells of the jaw. The loosening of incisors, fangs and molars occurs for the following reasons:
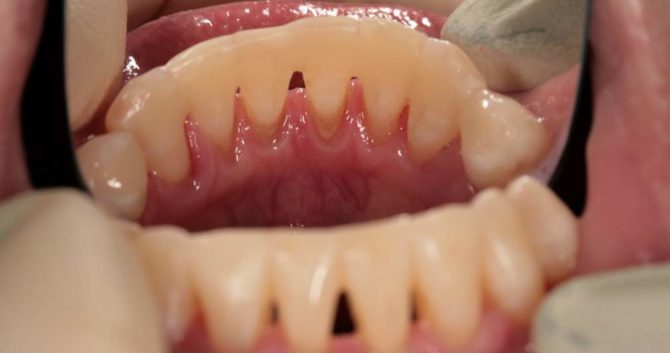
- Periodontal disease, accompanied by damage to the apparatus that holds the root of the tooth. A noticeable loosening of the dental crowns is observed in the middle and severe stages of periodontitis development, as well as in periodontal disease. With these diseases, the bone tissue of the jaw processes atrophies, the gums become inflamed and move down from the necks of the teeth, forming pockets in which the infection develops, and pus accumulates. After exposing a quarter of the tooth root, there is an increased mobility of the crown and its deviation from the normal position - the risk of tooth loss increases.
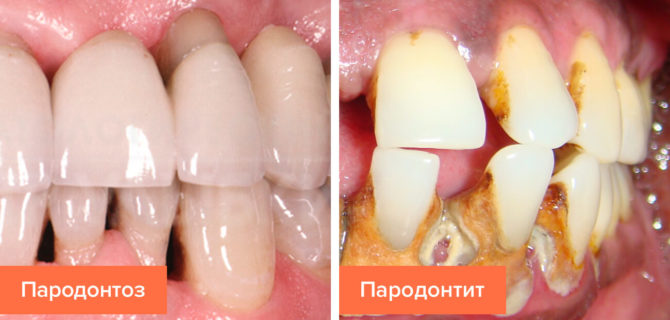
- Congenital defects in the structure of the dentition, in which the malocclusion or fan-shaped discrepancy develops. Uneven chewing load with such pathologies also leads to loosening of dental units over time.
- Fixing the result after using braces to correct the bite, since after removing them there is a possibility of repeated curvature or displacement of the teeth.
- Restoring the jaw after injuries, fixing fragments for their proper fusion.
The choice of a suitable bypass method depends on the available indications, the equipment of the clinic, and the financial capabilities of the patient. In modern dentistry, the following splinting methods are used:
- Splinting teeth with fiberglass tape or silk or aramid floss (cable-stayed).
- Clasp splinting.
- Installation of fixing prostheses on several teeth.
- Fixation of teeth using structures used for fractures of the jaw.
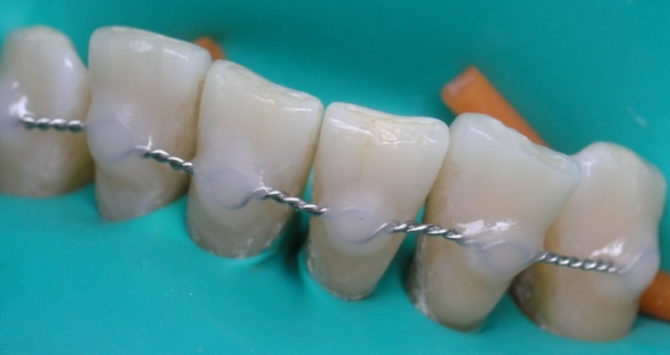
Splinting teeth with fiberglass (fiberglass tape)
The use of fiberglass floss is an effective and widespread way of fixing the dentition. Fiber splinting of teeth is carried out according to a scheme common to all patients, the features of the procedure depend only on which teeth are planned to be fixed:
| Fixed teeth | Front lower incisors | Front upper incisors | Back molars |
|---|---|---|---|
| Features of fixing thread installation | A furrow with a width and depth of 2 mm is drilled on the inner surface of the crowns, into which a fiberglass tape is laid. | The groove is drilled on the front surface of the crown.Splinting the front movable teeth eliminates large interdental fissures. | The groove is drilled on the top of the crown. |
| The number of teeth used in fixation | In addition to incisors, fangs are also splinted for greater strength and better load distribution. | Incisors and fangs are fixed with a tape. | The number of fixed molars depends on the degree of their mobility. |
Fiberglass floss is fixed by applying light-curing filling material, which is used to build up the side surfaces in the gaps between the teeth. During the procedure, anesthesia is required. Such tires look hardly noticeable, since the composite material has a shade similar to the natural color of the patient's enamel.
Method Advantages
The main indications for splinting teeth using fiberglass floss are periodontal disease and periodontitis. The method has many advantages:
- The installed design is removable, so the dentist will be able to remove the thread when the need for fixation disappears. The remaining furrow is closed with filling material.
- Dental tissues suffer less than with prosthetics, since with fiberglass splinting there is no need for preliminary grinding of enamel and trauma to the gums.
- The teeth remain open for other dental procedures and full oral care.
- The fiberglass is strong enough to secure the movement of the teeth. This bypass method allows you to evenly distribute the chewing load. If immobility of the dentition is achieved, the pathological processes that occur during periodontal disease and other diseases are suspended, and further atrophy of bone tissue is prevented.
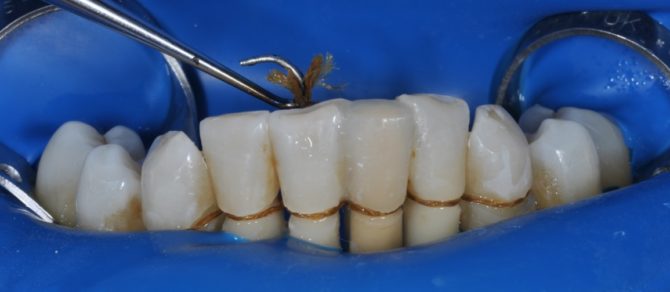
Cable-stayed splinting of teeth (fixation with aramid floss)
Fixation of teeth with aramid floss is called cable-stayed splinting. The technology for its implementation is similar to that used when using fiberglass. But in this case, a splint made of braided aramid thread is installed on the teeth, which has some advantages over the type of material described above:
- Great durability.
- Maximum compatibility with living tissues in the oral cavity, which reduces the risk of intolerance reaction.
- Inertness of the material: it does not react with either the components of saliva or the components of food.
Otherwise, the method has the same advantages as with fiberglass splinting of teeth.
Aramid yarn used in cable-stayed splinting is made quickly - on the day the patient goes to the clinic. Only in rare cases does it require a longer revision in the office of a dental technician.
Denture splinting
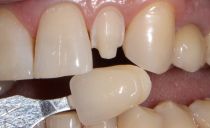
Splinting of mobile teeth with crowns requires preliminary grinding of enamel to maximize the convergence of the tooth and prosthesis. Before correcting the form, it is necessary to carry out depulpation.
For the manufacture of the prosthesis, different materials are used:
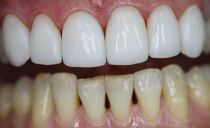
- Cermets. Extremely strong and durable material that provides greater reliability than fiberglass or aramid splint teeth. Ceramic-metal crowns are more often used to fix incisors and fangs when the esthetics of the dentition are important, since their shade is indistinguishable from the color of the patient’s natural teeth. The product is very expensive, especially the all-ceramic crown.
- Metals These prostheses are durable, although over time they can become thinner in those places where the greatest chewing load is created. They are very different from the natural dentition and are striking, but they can be used to fix molars that are invisible in the process of communication.
To install the tire in the form of a prosthesis, you will have to visit dentistry several times to prepare the dentition and take an impression on which the structure will be made.
When fixing several mobile teeth with prostheses, dentists must use healthy fixed teeth to increase the strength of the structure.
Clasp prostheses
With periodontitis and periodontal disease, splinting of teeth can be carried out using arch prostheses. This is one of the most reliable methods of eliminating tooth mobility in periodontics. It provides for the installation of a metal structure, which is fixed with hooks (clasps), micro locks or telescopic crowns. To make an individual prosthesis, a cast of teeth is required.
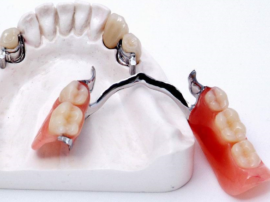 In addition to eliminating tooth mobility, using the clasp prosthesis, you can make up the gaps in the dentition with the loss of incisors, fangs or molars. The design is very durable, it takes up most of the chewing burden on itself, relieving teeth from periodontitis or periodontal disease from destructive effects.
In addition to eliminating tooth mobility, using the clasp prosthesis, you can make up the gaps in the dentition with the loss of incisors, fangs or molars. The design is very durable, it takes up most of the chewing burden on itself, relieving teeth from periodontitis or periodontal disease from destructive effects.
Aesthetics of the dentition is achieved if the prosthesis is fixed on micro-locks. They are mounted on a pre-installed cermet crown and on the arch of the prosthesis itself.
The most difficult type of shunting is fixing on telescopic crowns, which consist of the lower and upper parts, worn on top of each other. But this type of fixation is less commonly used in dentistry.
The least aesthetic way to secure the clasp prosthesis is to use clasps, as metal hooks are visible during the conversation.
Fracture splinting
When injuring the jaw, the patient is given structures consisting of metal or quick-hardening transparent plastic. There are such varieties:
| Type of construction | Appointment |
|---|---|
| Double jaw | It is used for complex fracture of one jaw or simultaneous fracture of both jaws. |
| Single jaw | It is established with a fracture of the lower jaw without a shift. |
| Splinted splinting | It is installed in the place where the fracture occurred, and some teeth are missing. |
| Lashing with hook hooks | It is used for complex fractures with or without displacement. |
| Smooth | A simple option for fixing the jawbone. |
| Combined | Installation of several types of structures at the same time when combining different jaw injuries in a patient. |
Who is contraindicated for splinting
Despite the variety of modern approaches to bypass surgery, it is not always possible to perform this dental procedure. There are certain contraindications, due to which the procedure may be delayed or prohibited:
- Pregnancy.
- The presence of cancer or radiation therapy for the previous 6 months.
- Mental disorder.
- Acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and in the internal organs.
- Severe diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- Bone disease.
- Hypersensitivity to the materials used.
- The lack of strong teeth that can serve as a support for loosened.
- Irresponsible neglect of oral hygiene.
Splinting of moving teeth involves some unpleasant stages: the need for anesthesia, drilling and grinding of enamel. But the result of such manipulations will allow a person to avoid even more deplorable consequences of periodontal disease, periodontitis, injuries or congenital problems with periodontal and occlusion.