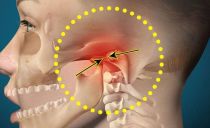
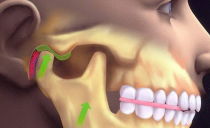
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth
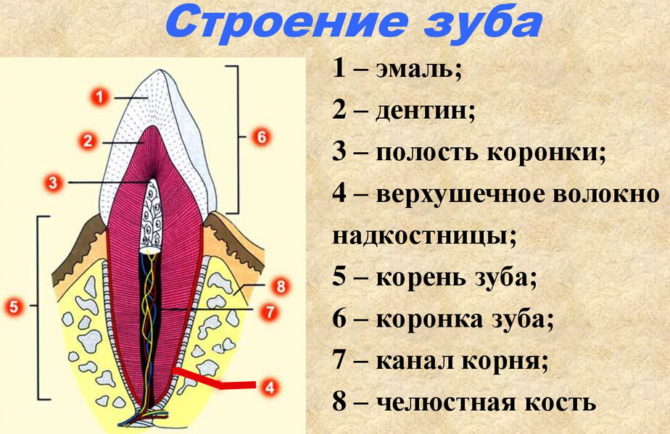
The periosteum or periosteum is the connective tissue that envelops the jaw bone. It consists of an inner and outer layer, contains connective fibers, blood vessels, nerve endings. Near the periosteum are the roots of the teeth, from which the infection can spread. therefore dental diseases are the main cause of periosteum inflammation, which is accompanied by very vivid symptoms and requires immediate treatment.
Content
What is the periosteum of a tooth, photo
The periosteum or periosteum is a dense membrane of connective tissue that covers the surface of the jaw bone. In young children, the periosteum provides bone growth, in adults it serves as a connecting link between bone and soft tissues.
Symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth
In medicine inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw is called periostitis. Symptoms of periostitis are classified into local (in the oral cavity) and general (deterioration of well-being). The jaw hurts in a person, there are signs of general intoxication, changes in the blood test are observed, which indicate the presence of inflammation in the body: leukocytosis, increased ESR. An X-ray examination reveals signs of a chronic or acute inflammatory process.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth include:
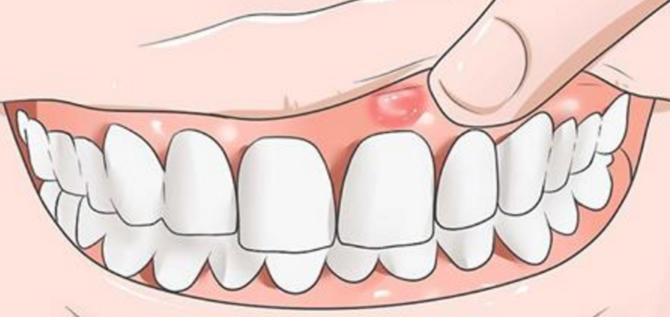
- Pain, swelling, redness of the gums in a certain area of the jaw.
- Swelling and thickening of the alveolar ridge on both sides.
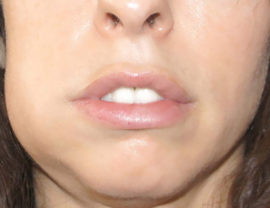
- Swelling and asymmetry of the face.
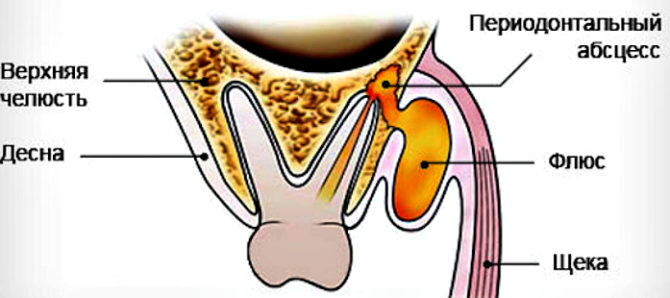
- The formation of an abscess on the gum.
- Soreness and mobility of the causative tooth.
- The formation of fistula or bleeding of the affected area.
- Inability to fully eat and carry out hygiene procedures.
- Increased salivation.
- The formation of plaque on the oral mucosa.
- The spread of pain to various parts of the face: temples, neck, eyes.
- Enlarged and sore regional lymph nodes.
- Increased body temperature, intoxication, weakness, headache, malaise.
Causes of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth
Reasons for inflammation and pain of the periosteum of the tooth, There are three types:
- Odontogenic. The infection spreads from the teeth to the soft tissues, periosteum and jaw bone. Odontogenic causes of periostitis include various dental pathologies: advanced forms of caries, periodontal disease, cysts, improper tooth extraction, infection during dental procedures, insufficient cleansing or incorrect filling of root canals, pathological eruption of the eighth tooth.
- Traumatic. They occur with mechanical damage, fractures, bruises of the jaw, after a complex tooth extraction, when pathogenic microflora gets into the wound.
- Hematogenous. The spread of infection to the periosteum occurs during acute infectious processes in nearby areas. Most often, the cause of periostitis is ENT diseases (rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis), SARS, influenza, furunculosis, acute stomatitis.
Forms of inflammation of the periosteum
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth depend on the form of the disease. Like all inflammatory diseases, periostitis is acute and chronic. In acute inflammation of the patient, acute pain and pronounced external symptoms — swelling of the cheek, the formation of an abscess from which the exudate is released, are disturbed. The chronic form of the disease proceeds secretly and manifests itself during an exacerbation.
Such forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Acute serous form. The first stage of the development of the inflammatory process, during which transparent serous exudate is released from the gums. Symptoms are mild, the patient has a certain area of the jaw that hurts. Serous periostitis is characterized by the occurrence of edema, swelling, pain in a certain area of the jaw. With a sufficient level of immunity, the disease goes away within 5-7 days.
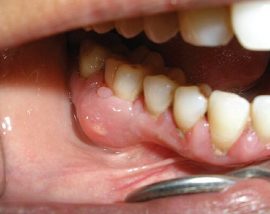 Acute purulent form (pictured). It occurs with an unfavorable course of serous inflammation, and can develop 2–5 days after the onset of the disease. It is distinguished by the occurrence of acute pulsating pains, severe swelling of the cheek, facial asymmetry, redness of the painful area, and the manifestation of general symptoms of intoxication. Purulent contents can burst into the oral cavity through soft tissue or spread to other areas, which can lead to serious complications. Pathology requires urgent professional treatment.
Acute purulent form (pictured). It occurs with an unfavorable course of serous inflammation, and can develop 2–5 days after the onset of the disease. It is distinguished by the occurrence of acute pulsating pains, severe swelling of the cheek, facial asymmetry, redness of the painful area, and the manifestation of general symptoms of intoxication. Purulent contents can burst into the oral cavity through soft tissue or spread to other areas, which can lead to serious complications. Pathology requires urgent professional treatment.- Chronic form. It develops with a sluggish inflammatory process, may be the result of an inferior treatment of acute types of periostitis. It is characterized by the formation of a seal on the gums, the occurrence of periodic aching pains, discomfort, discomfort. Under the sick jaw, enlarged lymph nodes are observed, which can become even more inflamed during an exacerbation.
Chronic periostitis usually affects the lower jaw, can last for years and appears only during periodic exacerbations. Diagnosis of pathology can be done using radiography.
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth
Treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth cannot be carried out independently, at home it is impossible to fully cure the lesion, which threatens with unpleasant complications. The disease is treated by a dentist, therapist or surgeon.
Therapy of periostitis should be comprehensive and complete. Treatment includes surgery, medication, physiotherapy, the use of folk remedies, the implementation of the doctor's recommendations at home.
Dental treatment
If the first symptoms of the disease occur, you should immediately visit the dentist and undergo the necessary procedures. Most often, specialists perform periostomy - an incision of the focus of inflammation with further drainage of tissues.
If you suspect inflammation of the periosteum, the doctor performs the following manipulations:
- Inspection of the oral cavity, painful area.
- Collection of information about the patient’s health status.
- Appointment of examinations (radiography and others at the discretion).
- Determining the cause of the pathology.
- Anesthesia with highly effective anesthetics.
- Periostomy - a section of the gum in the area of the abscess. Intervention is carried out in order to extract purulent contents, to alleviate the general condition of the patient.
- Antiseptic treatment of wounds.
- Latex or polyethylene drainage installation.
- Treatment of a causative tooth. If it is impossible to conduct conservative therapy, the tooth will be removed.
- If the causative tooth has not been removed, the root canals are filled.
- The patient is prescribed medication and given recommendations for treatment at home.
Treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth with antibiotics
With all forms of periostitis, patients are prescribed medications that help eliminate inflammation, reduce edema, anesthetize the causative area and contribute to recovery.Medications are taken orally (for a general effect on the body) and applied topically (for a quick effect on the lesion in the oral cavity).
With inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth, antibiotic treatment is performed. The doctor should select and prescribe an antimicrobial agent, given the sensitivity of the microflora of the patient's oral cavity to the drug. On average, treatment of the disease with antibiotics is necessary within 5-7 days.
Drug therapy includes:
- Antibiotics in the form of tablets or injections. Ciprofloxacin, Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Clindamycin, Macropen, Amoxicillin are effective.
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs: Nimesil, Afida, Diclofenac, Tsifran, Tsiprolet.
- Antihistamines that enhance the action of anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs and exclude an allergic reaction. The most popular are Lorano, Loratadin, Cetirizine.
- Gels and ointments used in the form of applications: Metrogil-dent, Levomekol, Holisal.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions: Chlorhexidine, Bigluconate.
- Reception of vitamin complexes and immunomodulating agents: Alphabet, Duovit, Vitrum.
Physiotherapy
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures that affect the inflamed area of the periosteum. Physiotherapy relieves inflammation, anesthetizes tissues, promotes resorption of exudate and edema. Under the action of the procedures, the wound remaining after surgery is cleared. In addition, improves blood circulation, tissue trophism, accelerates healing of the gums and recovery. It is recommended to go to the procedure for 3–7 days.
The following physiotherapy procedures are effective:
- Electrophoresis of drugs.
- Ultraphonophoresis.
- UHF
- Darsonvalization.
- Laser Therapy
- Electromagnetic therapy
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth at home
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth at home, the doctor will tell after surgery. Eliminate the disease at home is impossible. To make an incision on the gum and to remove pus at home is unacceptable, such actions threaten with serious complications.
After visiting a specialist, it is necessary to undergo medical procedures and adhere to all medical prescriptions. At home, you can rinse, oral baths, make applications, take medications and thorough hygienic care of the oral cavity.
For a speedy recovery from periostitis, traditional medicine recipes can be used. But such drugs should be used as adjunctive therapy, and not the main one.
The treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth is recommended using such folk remedies:
- Make a solution of salt and soda (1: 1) in a glass of warm water.
- Brew calamus root and rinse the mouth with the resulting broth in the morning and evening.
- To rinse the mouth or use inside decoctions of medicinal herbs: sage, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, oak bark.
- Brew 5 tbsp. l lemon balm in 2 glasses of water, insist 2 hours. The finished product can be used for rinsing and applications.
To eliminate inflammation, you can apply cold compresses to the affected area. And in order to disinfect the oral cavity, chew and hold a piece of propolis in your mouth for 5-10 minutes.