Gum inflamed and swollen near the wisdom tooth: causes, symptoms, treatment at the clinic and at home
Only the dentist knows what to do if the gum near the wisdom tooth becomes inflamed. therefore when the first signs of inflammation and swelling of the gingival tissue in the region of the third molar appear, you need to go to the doctorrather than trying to fix the situation at home. Gum edema is a serious pathology that requires medical intervention.
Content
Causes of the inflammatory process
Gum disease next to a wisdom tooth is most often accompanied by soreness and discomfort, so it can be quickly noticed and cured. Before prescribing a course of treatment, the dentist finds out the cause of the pathology in order to eliminate not only its symptoms, but also the focus of infection.
To find out why the wisdom tooth hurts and the gum swollen, you will have to take an X-ray. Only after collecting an anamnesis and radiography of the painful area, the dentist proceeds to excise the gum tissue, remove the tooth or medical treatment.
In some serious diseases, for example, with a cancerous tumor in the jaw, AIDS, removing a tooth without thorough preliminary preparation for surgery is dangerous for human life.
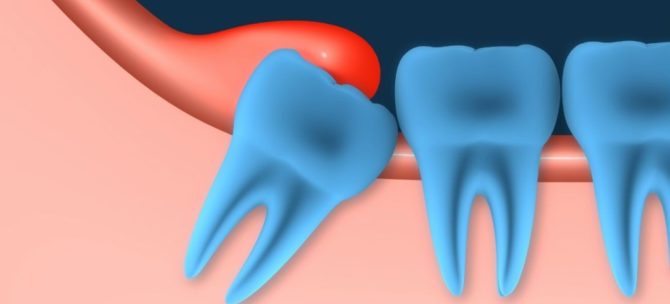
Difficult teething wisdom
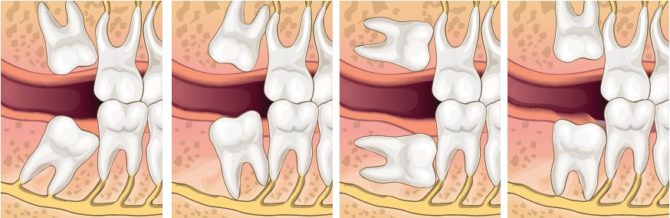
Most often, the gum near the wisdom tooth hurts due to pathologically incorrect eruption of the figure eight. The last molar in the dentition can erupt for years due to:
- bone thickening;
- too large, due to which the tooth does not have enough space for full growth;
- the dystopic position at which the tooth does not grow correctly: horizontally or at an angle.
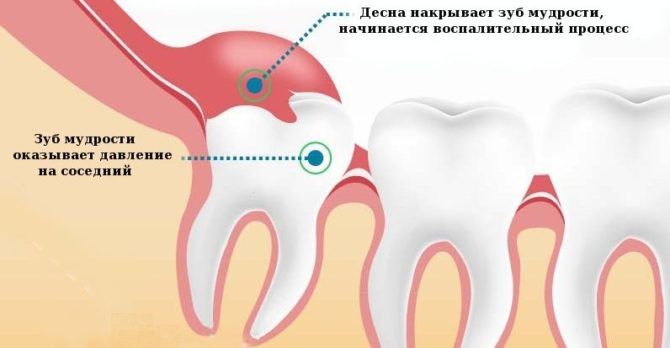
Pericoronitis
With a slow eruption of the latter, a gum hood may form in the tooth row. It interferes with the further growth of the eight and is a convenient place for the accumulation of various food residues and saliva. As a result, harmful microorganisms begin to multiply in this hood.
If you notice pericoronaritis at the initial stage of development, you can neutralize the inflammation with antibacterial drugs. If the pathology has grown into a purulent form, and the patient has all the signs of general intoxication, doctors have to do a small operation: excise the gum, removing pus and helping the wisdom tooth to cut through.
Caries
Eight has the same structure as the other teeth, so it is prone to caries. In the presence of carious cavities, the tooth itself and the gum around it can become inflamed and begin to hurt. In addition to caries, the formation of periodontitis and pulpitis is characteristic of the wisdom tooth.
Dental diseases of the eights are detected during a visual or radiographic examination. The principle of their treatment depends on the number and size of carious cavities, the presence of antagonist teeth (paired third molars in the opposite jaw) and the general prognosis.
Typically, decayed wisdom teeth are removed. But in some cases, they try to save them in order to use them as a support when installing removable prostheses.
Other reasons
Gum disease near the eighth tooth can occur for the following reasons:
- mechanical injury or burn of gum tissue;
- hormonal changes in the body associated with pregnancy or menopause;
- thyroid pathology;
- the use of removable dental prostheses;
- hormonal medication;
- sore throat;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
In addition to these reasons, the gum near the wisdom tooth may become inflamed due to gingivitis or stomatitisaffecting the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Symptoms of inflammation of the wisdom tooth
Symptoms of gum inflammation near a wisdom tooth are hard to miss; they include:
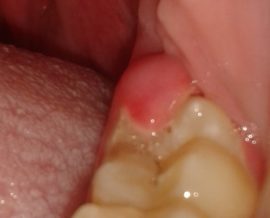 prolonged pain;
prolonged pain;- hardening of the inflamed gum due to overgrowth of bone tissue;
- swelling of the gingival mucosa;
- swelling of the cheeks and lips;
- precariousness of molars, including those adjacent to the figure eight;
- exit from the gum fistulas, from which pus often comes out;
- bleeding, redness, blueness, or blanching of the gum tissue;
- hyperthermia of the site of inflammation;
- increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of halitosis;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- difficulty opening the mouth when talking or yawning, sometimes it becomes painful to swallow;
- burning and throbbing in the jaw.
But sometimes there are no concomitant symptoms: the patient simply has a gum pain near the wisdom tooth when biting food, and soft tissue swelling is observed. In this case, it is necessary to go to the dentist, since the absence of auxiliary symptoms may indicate the presence of a chronic pathological process in the jaw.
If a person suddenly has a gum swelling near the wisdom tooth, and it hurts to swallow, you need to call an ambulance. Such symptoms may indicate a serious infection of the body.
Most often, the gum about eight swells in patients aged 20-30 years. In the older generation, these molars have already come out, and in children there are no eights at all - there are no milk teeth of wisdom.
What can be done at home if the gum is swollen
The first thing to do if the gum hurts near the wisdom tooth is to go to the dentist. If it is not possible to go to the dentist in the next few hours, you can:
- take an analgesic: Analgin, Ketanov, Tempalgin;
- lubricate the gums with therapeutic gel: Holisal, Kalgel, Solcoseryl;
- rinse your mouth and throat with an antiseptic: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Lugol;
- remove dentures (if possible).
If a person does not have serious problems with the liver or kidneys, he can remove the inflammation of the soft tissues near the wisdom tooth by taking Nimesulide or Nise, a powerful anti-inflammatory and pain medication that is often prescribed by dentists. Nimesulide and Nise are powerful drugs that negatively affect the organs of the excretory system, so they should not be abused.
It is impossible to take antibiotics or narcotic analgesics at home, even if the gums near the wisdom tooth are very swollen and sore. Serious medications should be prescribed by a doctor.
It is not recommended to relieve pain if the patient plans to go to the dental clinic in the next few hours. Taking analgesics will lubricate the clinic of the disease and make diagnosis difficult.
A classic treatment for gum disease near a wisdom tooth
The tactics of treatment for gum inflammation near the wisdom tooth depend on the severity and etiology of the disease. If the pathological process has developed due to changes in the hormonal background, you should restore it - you do not need to remove the inflamed molar.
Inflammation of the soft tissues in the oral cavity can be a consequence of the stress experienced, such patients need high-quality psychological assistance and sedative medications.
Drug treatment
With gum inflammation due to trauma, the doctor may prescribe the following procedures to the patient:
- applications by Retinol and Befungin;
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic drugs: Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Mefenamine (these same drugs will help cure gingivitis);
- taking vasoconstrictor drugs: vasopressin, ephedrine, naphthyzin.
The cheek and gums can swell with severe inflammation inside the body. In this case, antibiotics are indicated to avoid sepsis.
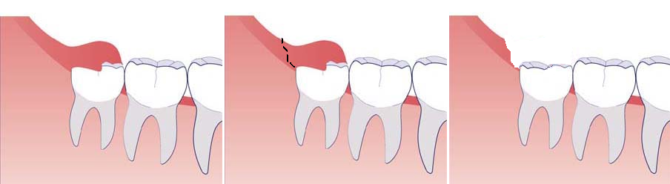
Pericoronitis treatment
If the gum near the last tooth hurts due to pericoronaritis, treatment will occur in several stages:
- Anti-inflammatory therapy using appropriate medications.
- Installation of drainage on the gum, if ulcers have formed on it.
- Opening the hood over the figure eight.
- Further actions depend on the state of the wisdom tooth:
- if it is damaged or affected by caries, it will be removed;
- if everything is in order with the tooth, the doctor will remove the gum hood and treat the wound with an antiseptic.
How to treat a wisdom tooth
If the gingival tissue around the wisdom tooth becomes inflamed and swells due to caries, the dentist may not remove the “wise” tooth, but cure it. But only if the molar has an antagonist, or if in the near future it is planned to install a prosthesis attached to the figure eight.
Manipulation is carried out under local anesthesia. Procedure:
- isolation of the third molar from the soft tissues of the jaw;
- purification of its surface from saliva and pus;
- treatment of the caries-affected area with an antiseptic;
- drilling caries-affected tissues;
- applying insulating material to the bottom of the cleaned cavity;
- filling the tooth cavity with polymer;
- grinding fillings.
The treatment of caries on a wisdom tooth is no different from the treatment of other molars. The only difference is that more effective anesthesia is used during the procedure. You need to be prepared for the fact that within 2 days after the manipulations made, the eight will ache.
If, after some time after the treatment of the wisdom tooth, the gums swell around it and pain begins to swallow, it is necessary to go to the dentistry clinic again. This symptom may indicate the development of inflammation due to errors during treatment. Most often, repeated inflammation of the healed wisdom tooth causes its removal, since the gum near the molar does not cease to fester until the source of infection is destroyed.
Prevention of problems with wisdom teeth
There are several preventive measures that can prevent gum inflammation near the wisdom tooth:
- daily brushing
- reduction of stressful situations;
- balanced diet;
- vitamin therapy (vitamin C is especially needed, since it helps to cope with increased bleeding gums);
- regular gum massage at home;
- rejection of bad habits;
- toothbrush replacement every 3 months.
In addition to all of the above, dentists recommend rinsing your mouth with plain water after each meal.
If the gum is inflamed and swollen near the wisdom tooth, you need to go to the dentist, regardless of the presence or absence of pain. Any dental pathology requires medical intervention, and some of them are dangerous to human health and life.