Antibiotics for gum and tooth root inflammation
Oral health has a big impact on the condition of the whole organism. Therefore, if inflammation begins on the gums, you need take action immediately to eliminate it. These diseases can be cured with the help of special anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents - sprays, ointments, therapeutic baths, rinses and lozenges. An antibiotic for inflammation of the gums and teeth can be used if a bacterial infection has become a cause of malaise.
Content
Types of diseases of the oral cavity
Gingivitis - inflammatory processes on the gums, in which the connection with the teeth is not disturbed. In this case, they are used only when other treatment measures have not had the desired effect. Often appears in those people whose immunity is weakened. At risk are pregnant women and children.
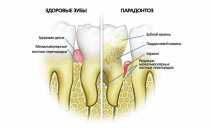
Periodontitis - An inflammatory process in which the gingival joint is disturbed. In this case, it is necessary to use drugs.
Periodontitis - These are inflammatory processes in the periodontal region (bundle-like ligaments that consist of connective fibers that fix the tooth in place). Sometimes this is called inflammation of the upper edge of the tooth root.
Periostitis - inflammatory lesion near the periosteum. In some cases, it appears as a result of exacerbation of periodontitis.
Common causes of gum disease in adults:
- decreased immune defense;
- the presence of chronic diseases;
- wrong diet;
- smoking; alcohol abuse;
- blood flow problems;
- painful tooth growth;
- congenital malocclusion;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- calcium deficiency;
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- polluted environment;
- exposure to radioactive contamination;
- constant stay in a state of stress and depression.
Symptoms of the onset of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity:
- pain that is felt on the roots of the teeth, gums, mucous membrane of the cheeks;
- excessive sensitivity to external stimuli - cold, or hot food, drinks, sweets;
- the formation of a bad smelling plaque, small wounds, sores;
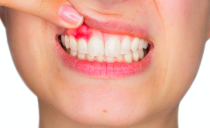
- secretion of pus, blood, or mucus;
- the appearance of edema, swelling;
- body temperature rises (in some cases);
- state of physical weakness;
- bad breath.
When antibiotics are prescribed
Antibiotics are used only as a last resortwhen treatment with antiseptic bactericidal agents did not bring the expected result.
Other indications for use:
- as a result of inaction, the patient's condition worsened significantly;
- the development of inflammatory processes is so rapid that conventional treatment will be ineffective;
- need to act in a short time;
- bleeding wounds and sores form in the mouth, pus goes.
Antibiotics for gum and tooth inflammation
What antibiotics to take for gum and tooth inflammation? For these purposes, tablets or capsules are suitable. First you need to crush them into powder, and then make a solution in warm clean water in the calculation of 5-6 tablets at a time per 1 liter. This therapy has a local effect, kills pathogenic bacteria, while the intestinal microflora is not exposed to negative effects.
In no case should you rinse your mouth with medicines in the form of a solution for injection - this provokes intoxication of the whole body. Do not swallow the rinse mixture.
In the case when gum inflammation develops rapidly, dentists most often prescribe antibiotics of the natural penicillin group as a treatment (for example, Ampisid, Arlet, Amoxil). To enhance the impact, it is recommended to take a drug called Metronidazole, which will help to kill pathogenic organisms in the shortest possible time and normalize the patient's condition.
 Semi-synthetic substances of the macrolide group are considered safer for the healthy work of the stomach and intestines in dentistry: Ecosositrin, Kleramid, Vilprafen and others.
Semi-synthetic substances of the macrolide group are considered safer for the healthy work of the stomach and intestines in dentistry: Ecosositrin, Kleramid, Vilprafen and others.
According to the doctor’s prescription, the patient can rinse the gums with the help of “Tetracycline” in the form of tablets, or preparations of the cephalosporin group - “Sulceph”, or “Hepacef”. High efficiency is distinguished by funds belonging to the group of linkosamides - “Linkomycin” and its analogues. These antibiotics are often prescribed for gingivitis in combination with the Metronidazole drug. They are well suited when local inflammation of the gums and teeth has become extensive and threatens with changes in the structure of the periosteum and even loss of a pair of teeth. In no case should you skip the daily rinse - this will reduce the effectiveness of the drug, and the treatment of the disease will drag on for a long period.
When using antibiotics of the lincomycin group in adults, the use of additional drugs is prohibited.
If severe inflammation of the tooth occurs in the oral cavity with the release of pus and soft tissue necrosis, or periodontitis begins, it is recommended to rinse it with Ciploleta-A, Sparfloxacin, or an ointment called Oflokain. Antibiotics belonging to the group of thyrotricins - Grammidin, Gramitsidin S, have a similar effect in dentistry.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe the effective drugs Aztraebol, Aztreonam, or Microcid to his patient. In the event that the treatment is complicated by the presence of pathogens of the fungal infection in the oral cavity, it is recommended to rinse the gums with the help of Nystatin, Tetracycline, Levorin, or an ointment containing the substance amphoterecin.
 With a strong and abundant formation of pus, inflammation of the root of the tooth, you can start treatment with antibiotics called Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin (an additional active substance is clavuranic acid). In order to strengthen and consolidate their action, you need to take Metronidazole and Tarivid.
With a strong and abundant formation of pus, inflammation of the root of the tooth, you can start treatment with antibiotics called Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin (an additional active substance is clavuranic acid). In order to strengthen and consolidate their action, you need to take Metronidazole and Tarivid.
If the disease is too neglected, then the doctor may prescribe a strong antibiotic Gentamicin. This is done when inflammation in the periosteum began and signs of osteomyelitis are visible. During the administration of drugs, it is recommended to additionally drink special probiotic drugs to maintain a healthy balance of microflora in the intestine. Patients with diabetes should always consult a doctor before taking it..
With gum disease, antibiotics can be taken from 5 to 10 days.
Antibiotics for diseases of the teeth and gums:
| Type of disease | Antibiotic name | How to drink |
|---|---|---|
| Gingivitis |
|
1,2 - rinse your mouth with a solution of water and crushed tablets 3 - internally as an injection |
| Periodontitis |
|
1, 2, 3, 4 - rinse the oral cavity with an antibiotic solution |
| Osteomyelitis | Gentamicin | Rinse gums several times a day with a solution of water and an antibiotic |
Rules for taking antibiotics for treating gums and teeth:
- It is forbidden to violate the schedule of admission during the illness, this will reduce the effectiveness of the course of treatment.
- Together with the main therapy, you need to take the drug "Metronidazole" - it will enhance the effect of antibiotics.
- The use of alcoholic beverages during the entire treatment period is strictly prohibited.
- In order to be effectively treated, smoking patients must at least temporarily get rid of their bad habits. Nicotine strongly dries mucous membranes and can inflame them.
- Dosage and time of administration cannot be adjusted independently. Only a doctor prescribes a treatment regimen.
- Unauthorized administration of any antibiotics by intramuscular, intravenous or oral route is prohibited.
- Despite the rapid emergence of a lasting result, the course of treatment must be completed to the end according to the schedule and follow what the doctor prescribed.
In order to avoid and prevent inflammatory processes on the gums, you need to regularly take the following measures:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, thoroughly removing plaque and food debris.
- Use dental floss and mouthwash.
- From time to time, massage the gums with a soft synthetic brush.
- Once every six months, be examined in dentistry, carry out preventive measures - remove plaque, clean from stone, heal caries.
Essential oils help well when the oral cavity begins to become inflamed. Several times a day, it is recommended to apply tea tree oil, sage, chamomile, or calendula to the wound using the spot method.
Additional methods to combat inflammation
Antibiotics for inflammation of the gums and teeth to enhance the therapeutic effect should be taken in parallel with special dental baths for the oral cavity. The solution must be typed in the mouth and kept in it for several minutes, and then spit.
For these purposes, well suited:
- Plain iodine, which kills many microorganisms.
- Hydrogen peroxide, which further disinfects the oral cavity.
- "Furazidine" - it destroys almost all types of pathogenic bacteria.
- "Triclosan", "Hexetidine."
- "Chlorhexidine."
Additionally, it is possible to treat places near the damage with a regular cotton swab dipped in Metrogil-Dent. This will help to quickly remove inflammation and start regenerative processes.
Other treatments
 Special antiseptic sprays - “Stomatophyt”, “Stop-angina”, “Anti-angina” and others — have shown high efficiency in the treatment of gums and tooth roots. In addition, wounds or sores can be treated with the good antiseptic agent “Miramistin”. Its advantage is that it is absolutely safe and can be used to treat not only adults, but even pregnant women, or small children.
Special antiseptic sprays - “Stomatophyt”, “Stop-angina”, “Anti-angina” and others — have shown high efficiency in the treatment of gums and tooth roots. In addition, wounds or sores can be treated with the good antiseptic agent “Miramistin”. Its advantage is that it is absolutely safe and can be used to treat not only adults, but even pregnant women, or small children.
Some throat lozenges have a good analgesic and regenerative effect on the oral cavity. These include the Septolete,
Forbidden with inflammation of the oral cavity:
- To smear places of damage to soft tissues (sores and wounds) with aggressive antiseptics in their pure form. These include iodine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, etc. If this rule is ignored, serious diseases and burns of the mucous membrane can occur.
- Rinse your mouth with alcohol, vodka - this greatly dries the oral cavity. In addition, aggressive alcohol components can react with the active substances of drugs, the consequences of which will be unpredictable.
- Warm the part of the face that is near the lesion. Bacteria reproduce best in a warm, humid environment, so this action will contribute to the rapid growth of infection, its spread throughout the body and will cause gums to become inflamed even more.
You need to be extremely careful when using traditional medicine methods in parallel with the main treatment of the disease. It is recommended that before taking any remedy, be sure to consult a doctor.The components of the first drug can react with natural substances, and those, in turn, slow down the effect of the drug.
If treatment with antiseptic agents and even antibiotics did not help with gum disease, then in such cases urgent intervention is necessary - special physiotherapeutic and ultrasound methods. If all this turned out to be useless, then you should seek help from a surgeon.
In combination with antibiotic treatment for inflammation of the gums and teeth, use antiseptic solutions, therapeutic pastes, painkillers gels. During the period of the disease, it is recommended to eat intensely, as well as drink an additional vitamin and mineral complex.