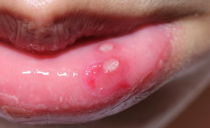
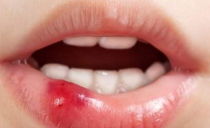
Cheilitis on the lips: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Cheilitis is a fairly common disease, which is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the red border of the lips. The disease is characterized by a long recurrent course. In young people, this pathology proceeds favorably, and in older people it can be a precancerous condition, therefore A dentist or dermatologist should diagnose and treat cheilitis on the lips.
Content
Causes of cheilitis on the lips
According to the generally accepted classification of diseases, cheilitis on the lips belongs to the group of dermatitis. The inflammatory process is localized on the skin of the lips and the periubical area and can appear against the background of various diseases, for example, psoriasis, red lichen, erythematosis.
In addition, the following factors can lead to inflammatory damage to the red border:
- Exposure to adverse external conditions - cold or heat. In dry, hot or frosty windy weather cheilitis occurs much more often than in climatic conditions with normal humidity and temperature.
- The use of low-quality cosmetics. Substances contained in lipstick are able to clog skin pores, which is accompanied by their inflammation.
- Tendency to allergies. Exposure to even a small amount of allergen can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lips.
- Impaired immune or endocrine systems. Endocrine disorders lead to disorders of local immunity, which, in turn, leads to local inflammatory reactions.
- Vitamins. A lack of vitamin A and B vitamins always strongly affects the condition of the skin, and even more so on the condition of the lips.
- Stress. The release of stress hormones helps to weaken the protective functions of the skin due to vasospasm, which exacerbates the inflammatory process.
Symptoms of cheilitis on the lips
The term “cheilitis” unites a large group of diseases that are similar in clinical manifestations, but having different etiopathogenetic mechanisms of development. This should be taken into account not only in diagnosis, but also when choosing a treatment regimen.
Regardless of the causes, all types of cheilitis have common clinical symptoms, which include:
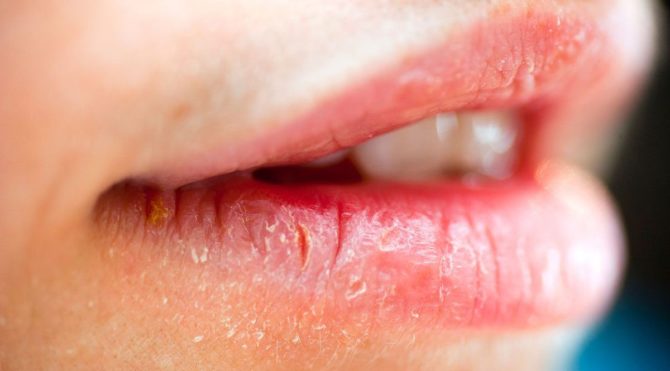
- dry lips;
- burning (itching) of the skin around the mouth and peeling;
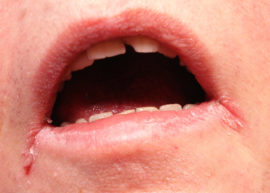
- the appearance of cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- wet skin near the mouth;
- sores on the border of the lips.
Depending on the prevalence of certain manifestations, several types of cheilitis are distinguished.
Exfoliative cheilitis
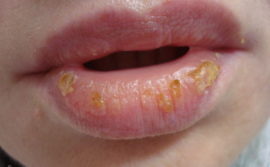 With this form of the disease, mainly the red border is affected, which is manifested by its peeling. The risk group includes women experiencing frequent and intense stress.
With this form of the disease, mainly the red border is affected, which is manifested by its peeling. The risk group includes women experiencing frequent and intense stress.
A number of studies indicate the relationship between endocrinopathies and the indicated type of disease, on the basis of which one of the main causes of cheilitis is hyperthyroidism. The disease is characterized by a long recurrent course and the inability to self-heal.
A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is that peeling does not extend to the oral mucosa or the skin surrounding the mouth.
Glandular cheilitis
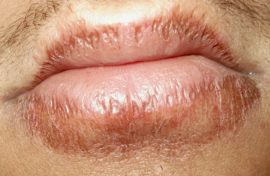 Involvement of the small salivary glands in the pathological process is inherent in this type of disease.It is with their infection that the onset of the inflammatory process on the surface of the lips is associated. Both men and women suffer from the disease with the same frequency, in 80% of cases only the lower lip is affected.
Involvement of the small salivary glands in the pathological process is inherent in this type of disease.It is with their infection that the onset of the inflammatory process on the surface of the lips is associated. Both men and women suffer from the disease with the same frequency, in 80% of cases only the lower lip is affected.
At the initial stage of patients, only dry lips are worried. As the glandular form of the disease progresses, small and then deeper cracks appear on the lips first. In advanced cases, cracks begin to bleed and turn into wide erosion on the lips.
Allergic cheilitis
A type of dermatitis that forms when the lips come in contact with irritating substances. The disease can develop both due to the use of low-quality cosmetics for skin care, and under the influence of harmful production factors.
Very often this type of cheilitis occurs among musicians who, by the nature of their profession, are forced to hold mouthpieces of musical instruments in their mouths for a long time. Sometimes cheilitis on the lips is an allergic reaction to the ointment used to treat other diseases.
The main manifestations:
- swelling of the lips;
- burning or itching in the mouth;
- rashes in the form of small bubbles.
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis intensify immediately after contact with the allergen, so it is quite easy to identify.
Atopic cheilitis
Atopic cheilitis on the lips is a local symptom of another serious disease: neurodermatitis. At the heart of its formation is the failure of some parts of the immune system.
Any allergens act as provoking factors: drugs, microorganisms, and their metabolic products. At first, patients with atopic cheilitis complain of redness and flaking of the lips, and subsequently, they develop jams.
Hypovitaminous cheilitis
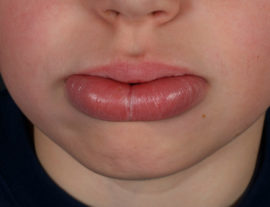 Hypovitaminous dermatitis often occurs in children. This condition develops with a lack of B vitamins in the diet, especially with a lack of riboflavin - vitamin B2. Patients complain of intense peeling of the lips, burning in the mouth and tongue. On examination, small flakes of flaky skin and vertical cracks are clearly visible on the background of dry, hyperemic skin of the lips.
Hypovitaminous dermatitis often occurs in children. This condition develops with a lack of B vitamins in the diet, especially with a lack of riboflavin - vitamin B2. Patients complain of intense peeling of the lips, burning in the mouth and tongue. On examination, small flakes of flaky skin and vertical cracks are clearly visible on the background of dry, hyperemic skin of the lips.
In almost 100% of cases, there are signs of language damage (glossitis):
- swelling;
- raspberry color;
- imprints of teeth.
Candidiasis cheilitis or thrush
 The disease occurs against a background of weakened immunity. The main reason is the seeding of the red border of the lips with fungi of the genus Candida. The clinical picture of the candidal form is not much different from other forms, but it is typical for the appearance of a cheesy whitish coating on the edge and in the corners of the lips.
The disease occurs against a background of weakened immunity. The main reason is the seeding of the red border of the lips with fungi of the genus Candida. The clinical picture of the candidal form is not much different from other forms, but it is typical for the appearance of a cheesy whitish coating on the edge and in the corners of the lips.
Fungal damage to the lips is very often observed in children with the spread of candidiasis from the oral cavity.
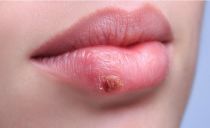
Cheilit manganotti
Cheilit Manganotti - This is nredrakovy condition of a red border of lips. Pathology is dangerous with a high risk of malignancy of the altered skin areas. Most often, this form of the disease is determined in men older than 50 years, especially in smokers and those infected with the herpes virus.
Clinically, the disease looks like one or more painless erosions of irregular shape; in 0.6–5% of cases, they transform into lip cancer.
Macroheilitis
Macroheilitis is one of the symptoms of Melkerson’s disease, in which, in addition to lesions of the red border, facial neuritis is noted. The leading symptom in this form of the disease is swelling of the lips, accompanied by itching. Swelling can spread to the cheek and cheekbones.
Meteorological (actinic) cheilitis
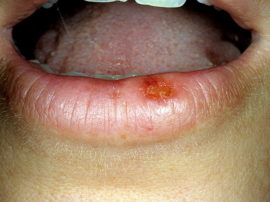 This type of disease is noted in people with hypersensitivity to meteorological factors: wind, solar radiation, cold. At risk are men older than 25 years. When interviewing patients in 80% of cases, it turns out that they suffer from general weather sensitivity.
This type of disease is noted in people with hypersensitivity to meteorological factors: wind, solar radiation, cold. At risk are men older than 25 years. When interviewing patients in 80% of cases, it turns out that they suffer from general weather sensitivity.
In addition to itching and burning in the lips, with this disease, small vesicles can appear, which independently open and become covered with a crust. A long course of the disease is dangerous in that it can pass into other, more dangerous forms of cheilitis - Manganotti or into hyperkeratosis.
Treatment of cheilitis on the lips
It is easy to diagnose cheilitis - usually a simple examination of the affected lips is enough for the doctor. The main difficulties arise when it is required to conduct a differential diagnosis of cheilitis with other lip diseases (leukoplakia or oncology), in this case, the doctor prescribes a histological examination.
Regardless of how cheilitis is manifested, it is necessary to treat it comprehensively, taking into account the specific form of pathology. General principles of therapy:
- In the early stages (with dry lips), the use of high-quality moisturizing hygienic lipsticks is shown.
- In the period of severe inflammation, the use of anti-inflammatory ointments is indicated. It is allowed to use glucocorticoid ointments, apply them several times a day.
- Elimination of irritating factors: low temperature, heat, allergens.
- Normalization of sleep patterns.
- A balanced diet.
- Vitamin Therapy.
Other therapeutic measures are specific for each form of the disease:
- With common glandular cheilitis, surgical methods of treatment are used. The operation consists in the removal of overgrown salivary glands, electro-and laser-coagulation are considered the most modern methods.
- For the treatment of atopic cheilitis, antihistamines must be included in the treatment regimen. During the treatment of this form of the disease, as well as allergic cheilitis, it is important to adhere to a diet that excludes allergens from entering the body.
- They fight meteorological cheilitis by eliminating provoking factors. Patients with this form of the disease must use protective creams with a high UV absorption coefficient.
 To treat allergic cheilitis on the lips, steroid ointments are used that eliminate contact with the irritant: Fenistil, Actovegin, Actiderm, Forocort. Antiallergic drugs are prescribed: Cetrin, Zodak, Loratadin, Suprastin.
To treat allergic cheilitis on the lips, steroid ointments are used that eliminate contact with the irritant: Fenistil, Actovegin, Actiderm, Forocort. Antiallergic drugs are prescribed: Cetrin, Zodak, Loratadin, Suprastin.- In the treatment of macroheylitis, a key element of therapy is the use of antiviral drugs in combination with immunocorrectors. A positive effect is noted when using laser therapy in the projection of the facial nerve. Macroheilitis can be cured only by coping with the underlying disease.
When diagnosing cheilitis, Manganotti requires advanced diagnostics, including cytological or histological examination. In some cases, surgical excision of the lips is performed, since it is necessary to remove a potentially dangerous area of tissue. If the malignant nature of the disease is not confirmed, conservative treatment continues.
- The treatment regimen for candidal cheilitis necessarily includes antifungal agents.
- Hypovitaminous cheilitis disappears within 2-3 days after the start of vitamin intake.
Treatment of cheilitis on the lips at home
Treatment of cheilitis on the lips at home should be carried out only after consulting a doctor. Only a specialist is able to determine the specific form of the disease, and it largely determines the treatment regimen.
Such folk remedies as decoctions or infusions of herbs are not recommended, as they can aggravate the course of the disease due to additional damaging effects. At home, you can use moisturizing ointments, but only with a dry form of cheilitis, because applying ointment to wet areas increases the risk of infection.
At home, the use of lip balms made on the basis of herbs with an antiseptic effect (chamomile, sage) is effective. But such treatment of cheilitis is aimed only at alleviating the symptoms, for complete healing you need to adhere to the doctor's recommendations.
Prevention
Almost all forms of cheilitis are treated quite simply, but it is better to prevent the development of pathology. To do this, it is recommended to enrich the diet so that it contains the necessary amounts of trace elements (zinc and magnesium) and vitamins (A and E), necessary to eliminate hypovitaminosis.
Patients with weather sensitivity are advised to avoid exposure to precipitating factors (cold and sunlight). In winter, it is necessary to use protective creams and lipsticks, preference should be given to hypoallergenic cosmetics.
The prognosis for cheilitis is usually favorable. Most varieties of the disease can be cured at home, hospitalization in a hospital is only required for the development of a severe form of the disease in young children.