A bump on the lip from the inside and outside: what is it, treatment
If the eyes are a mirror of the soul, then by the appearance of the lips you can make an impression of the general condition of the body, health, habits, lifestyle of a person. Diagnosis of many diseases pays special attention to this body.
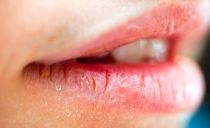
A large number of nerve endings and a thin layer of the upper epithelium increase sensitivity many times in comparison with the fingertips, so the slightest changes in the integrity of tissues, especially the bump inside the lip, are more acute.
Content
The reasons for the appearance of a cone-shaped seal
A bump on the lip is not only an aesthetic problem. The resulting growths cause discomfort, difficulty speaking, eating. They can also signal the manifestation of a disease.
Normal lip condition: the surface is plain, plastic, smooth, holistic, with clear boundaries.
Deviations from the normal state of the lips: the presence of nodules, vesicles, seals, spots.
Violation of the integrity of the tissue structure is possible due to physical, chemical or biological factors. Damage to the tissues of the oral cavity is dangerous because several agents are involved in their formation (the so-called combined species), and a secondary infection is easily attached to the root cause.
If a seal appears on the lip, two approaches are possible here: the first - the person does not believe that the growth should be treated and postpones the call to the doctor, the second - begins to study it, twist the lip, bite - and damages the cyst.
To clarify the nature of the origin of the neoplasm, it is necessary see a doctor. The local therapist, dermatologist, dentist can consult. Only a doctor can collect an anamnesis, explain why a lump appeared on the lip and cure it. The specialist examines the likelihood of a viral origin of the formation. About 90% of the population is infected with the herpes virus, which is embedded in the genetic apparatus of the cell and manifests itself in relapses.
Viruses
Many viral diseases are detected in the oral cavity caused by herpes simplex viruses, Coxsackie viruses, enteroviruses, vesicular stomatitis virus, herpes zoster, and others. Of particular importance is herpetic infection. There are household names: fever, colds.
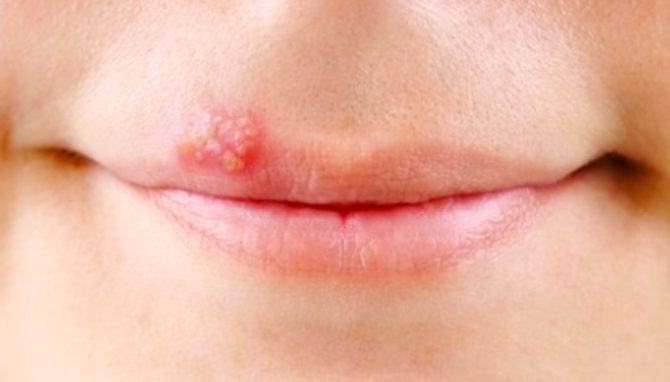
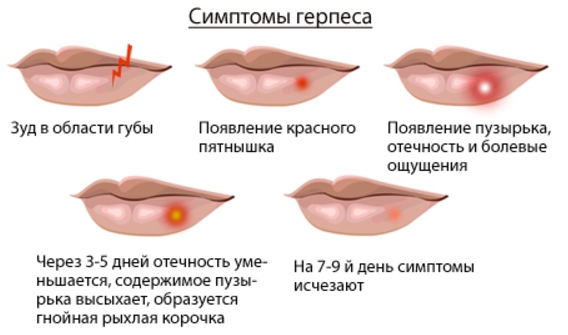
The rash of grouped small painful vesicles is accompanied by itching, burning, fever. The localization site first swells and the bump that appears on the lip looks inflamed. After that, small blisters appear, filled with transparent contents. A few days later they burst. On the epithelium (skin and red border) an erosive formation is formed, covered with a crust. On the mucous membrane, the appearance of a crust is impossible, there the ulceration is delayed by a yellowish fibrin film.
Infection pathways: airborne, generic, genital, contact. An extremely viable virus is transmitted by talking, sneezing, and shaking hands. It is able to encapsulate on items of individual household use (towel, handkerchief, toothbrush) and move to the next recipient.
In addition to the common symptoms, atypical are possible. Clinical manifestations: precursors in the form of burning, tingling, itching. A bump can jump on the lip from the inside. Classical signs (bubbles) may not come out.In cases of diagnosing HSV, even blurry classic symptoms, without blisters, are treated with the usual protocol.
Relapse of herpetic manifestations is caused by:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia (overheating);
- infectious diseases;
- stress
- an injury.
Mechanical damage
A bump on the inside of the lip does not necessarily indicate a cold sore. The main function of the epithelium and mucosa is protection. Damage to this system opens the door for the penetration of pathogens. Chronic phenomena of this nature can develop into systemic diseases or, in especially severe cases, become malignant. Injury and microtrauma of soft tissues provoke a lump that appeared on the lip.
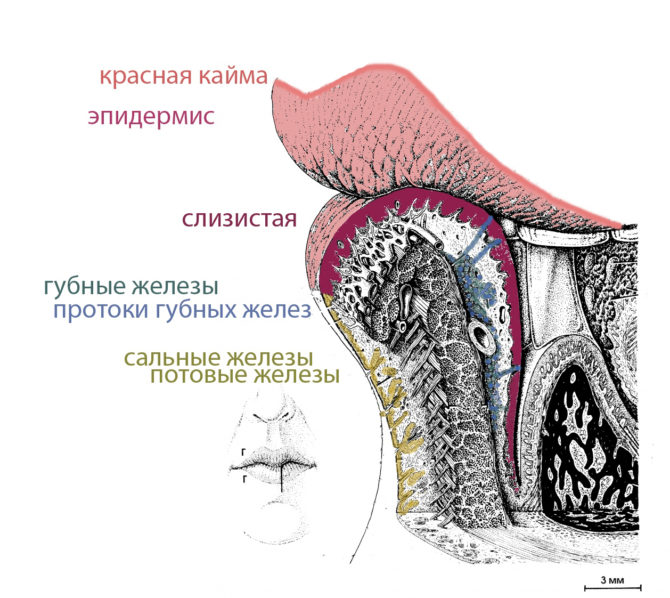
The outer, outer surface is covered with several layers of keratinized epithelial tissue, inside of which there are sweat, sebaceous glands with ducts and hair follicles. In the intermediate part, the squamous epithelium passes into the mucous membrane. The ducts of the mixed labial glands are located on the mucosa (sometimes they are called small salivary glands).
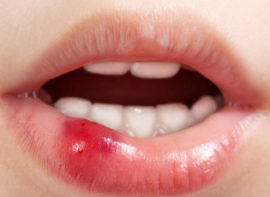
If you bite your lip, a ball may form: such an injury often causes the membrane of one of the many glands to rupture and release their secretion into the surrounding tissue. Then, the damage to the duct channel seals the gland inward and for some time a ball in the lip accumulates mucus, stretches the walls, and bulges from below.
He bit his lip, a bump formed - a rather frequent phenomenon. Clinically, such damage speaks only of post-traumatic edema, can disappear on its own. If the wound remains for more than 3-5 days and even increases - this is a symptom of a retention cyst and an occasion to consult a specialist.
What may cause injury:
- hit;
- inflammation;
- the habit of biting lips with teeth;
- smoking (chronic burn);
- wearing bracket systems;
- dentures;
- piercing.
Types of tumor-like formations
A bump came out on my lip - what does it mean? The doctor will definitely clarify whether this is a primary seal or relapse. In addition to collecting an anamnesis (according to the patient), an examination is carried out. The seal is examined first from the outside, then the lip moves back and turns out to examine the mucous membrane.
The tumor can crawl out in any part of the oral cavity, however, it is most often observed as a lump on the lower lip inside. The seal, which originated deeply, remains at the bottom or leaves in the upper layers with an asymmetric thickening, wart, lump, ulcer. The neoplasm can be filled with a clear white liquid, or have a bluish-bloody hue. Depending on the clinical picture, distinguish:
- viral rash;
- benign tumors (cyst, papilloma, nevus, connective tissue tumor, vascular);
- cancer.
With complaints that a ball appeared inside the lower lip, 9 out of 10 patients in megalopolises turn to (Moscow). Of benign tumors, a cyst is more common. The main difference between a cyst and a virus is painlessness, lack of burning, growth. Spontaneous or independent opening of the cyst will lead to repeated growth.
You can not pierce or bite a cyst on your own. Removing the contents along with the membrane will prevent complications and relapse.
The growth of even a benign cyst can trigger the process of malignancy. The transition to lip cancer, from a clinical point of view, goes unnoticed.
Injury, crack, sore are no less dangerous: they require observation. The appearance of a white bump on the lip may indicate leukoplakia - a precancerous condition. The disease is a violation of keratinization. Change occurs painlessly, slowly.
Keep in mind that only a doctor can assess the danger of overgrowth. Doubtful tissues are subjected to cytological and, if necessary, histological examination and biopsy.
Treatment methods
In addition to observation, modern medicine offers two ways to treat bumps inside the lip: conservative and radical.
Conservative traditional therapy includes:
 Immunotherapy Prescribing immunomodulators and immunoregulators.
Immunotherapy Prescribing immunomodulators and immunoregulators.- Antiviral therapy. Suppression of virus replication and inhibition of the stages of the interaction of the virus with the cell.
- Physiotherapy. UV treatment, oxygen therapy, dosed hypothermia.
- Drug therapy. Irrigation, creams, ointments, vitamins.
- Antibiotics. A sensitivity test is needed.
- Folk medicine. Medicinal plants (Kalanchoe, aloe, chamomile, etc.) in the form of decoctions, solutions, lotions.
- Vaccination. Lesions of a viral nature are easier to prevent with vaccine therapy.
A cystectomy of a retention cyst is performed by a dentist using a surgical scalpel, laser, ultrasound or radio frequency devices.
Cases in which treating bumps on the lip from the outside involves surgery:
- Relapse of the cyst. The cyst needs to be removed completely (the shell along with the contents). Otherwise, she may jump up again.
- Very active tumor growth. Untimely treatment exacerbates the pathological process and the tumor seeks to enter neighboring tissues.
- Seal of the cyst. Stagnation creates favorable conditions for the degeneration of cysts in scar tissue (fibroadenoma).
Prevention
There are a number of rules, observing which you can avoid or minimize the risk of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity:
- Compliance with personal hygiene.
- Healthy lifestyle: physical activity, intake of vitamins, proper diet, elimination of damaging factors due to smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Routine preventive examinations.