Inflammation of the salivary glands: causes, symptoms and treatment
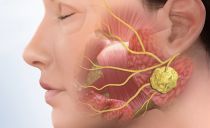
Sialadenitis is an inflammation of the tissues of the glands. Most often, the disease affects the parotid glands, slightly less sublingual and submandibular. It can develop in both adults and children. But for each age group, a certain type of inflammation of the salivary gland is characteristic, they all differ in both symptoms and treatment approach.
Content
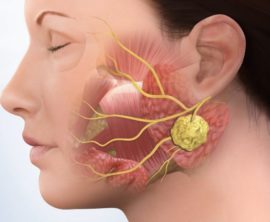
Brief anatomical information
The salivary glands are located in the oral cavity, due to which saliva is released. Large pairs include three pairs: parotid, submandibular, and hyoid. They have an irregular shape, a dense texture and a paired arrangement. Their main functions are hormone secretion, filtration of the plasma part of the blood, as well as excretion of decay products.
The most common salivary gland pathologies include:
- Sialadenitis is an inflammation that develops when an infection penetrates into the gland or against the background of a violation of salivation.
- Mumps is an infectious disease caused by paramyxovirus that affects the central nervous system and glandular organs.
Etiology of the disease
More often, the disease affects children, but sometimes adults also get sick. The latter have a severe course of sialadenitis, especially in men.
Inflammation of the salivary gland occurs for various reasons under the influence of many factors, so the disease is polyethiological. But one condition always precedes the pathological process - the presence of a pathogen, an infectious agent. In most cases, these are either viruses or bacteria.
 The most common prerequisites for inflammation of the salivary glands:
The most common prerequisites for inflammation of the salivary glands:
- any focus of infection that is located in the mouth and ear;
- carriage of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microorganisms;
- tuberculosis, syphilis, HIV;
- metabolic disorders;
- any immunodeficiency conditions;
- scarlet fever, rubella, measles and other infectious pathologies;
- viral diseases such as influenza, cytomegalovirus;
- mycoses;
- pneumonia, bronchopneumonia;
- oncological diseases;
- benign lymphoreticulosis.
The most common transmission mechanisms for this infectious disease are: airborne, contact, blood contact, monotonous.
Diseases of the salivary glands: types and symptoms
Different stages and types of inflammation of the salivary glands are characterized by various clinical signs.
Mumps or mumps
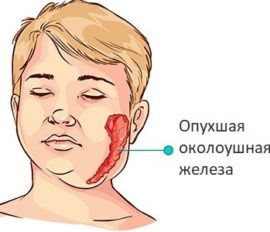 This type of viral inflammation of the salivary glands often manifests itself in children. It begins abruptly: amid complete prosperity. It occurs with an increase in body temperature up to 40 ° C.
This type of viral inflammation of the salivary glands often manifests itself in children. It begins abruptly: amid complete prosperity. It occurs with an increase in body temperature up to 40 ° C.
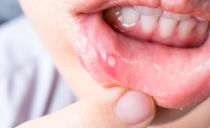
Inflammation usually affects the parotid salivary glands., which is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling of the cheek and parts of the neck on one or two sides (see photo), swelling of the neck, a sharp pulsating pain, aggravated by eating, chewing, opening the mouth.
Sialadenitis
Symptoms of the disease differ depending on the location of the infectious lesion:
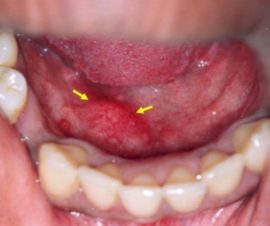
- With inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland, the area under the chin swells. There is acute pain when swallowing, especially under the tongue, with discharge of pus from the duct. The defeat of the submandibular salivary gland is accompanied by a lack of appetite, weakness and fever.
- Inflammation of the submandibular gland can be calculous in nature, that is, it proceeds with the formation of stones. In this case, the duct is blocked by a stone and becomes impassable. The cause of the pathological process is an excess of calcium in the human body. The symptoms of iron inflamed under the jaw are indicated by the following symptoms: stitching, paroxysmal pain during eating, opening the mouth, organ enlargement, which is accompanied by swelling of the neck, pus, and fever.
- Inflammation of the hyoid gland is extremely rare and is more often a complication of an abscess of odontogenic origin.
- Among the chronic forms, a special type of sialadenitis - dry Sjogren's syndrome - should be distinguished. It is directly related to connective tissue pathology and an autoimmune reaction.
- Sialodochitis is a lesion exclusively of the salivary ducts. It occurs more often in elderly people, characterized by hypersalivation and the formation of cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Depending on the clinical picture and the severity of the disease, the disease is divided into 3 main types: serous, purulent and gangrenous.
Serous sialadenitis
This stage of inflammation is characterized by a slight increase in temperature, dry mouth, swelling and a slight tightening in the ear canal and neck. Sometimes there is a slight feeling of fullness and pulsation.
On palpation, the salivary glands of a person will produce secretions in small quantities. At this stage, home treatment is acceptable. - This is the most favorable variant of the course of sialadenitis.
Purulent sialadenitis
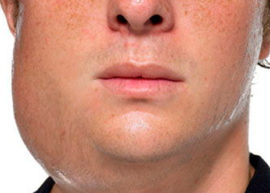 It appears as a complication after serous. It is accompanied by increased pain, asthenic syndrome, autonomic dysfunctions. Insomnia is characteristic, which occurs against a background of elevated temperature.
It appears as a complication after serous. It is accompanied by increased pain, asthenic syndrome, autonomic dysfunctions. Insomnia is characteristic, which occurs against a background of elevated temperature.
When opening the mouth, the patient experiences severe pain, therefore, chewing function is limited. Hyperemia, marked swelling, passing to the cheek area and the lower jaw region are noted. Regional lymph nodes increase, pus is released into the oral cavity.
Gangrenous sialadenitis
In the case of the transition of inflammation to this stage, the well-being of patients worsens, and they are in an extremely serious condition. There is a high risk of death due to sepsis. There is a fusion, tissue necrosis, an inflamed area of destruction is visible above the skin. The enlarged gland becomes an order of magnitude larger.
Diagnostics
If a person has an inflamed salivary gland, you should immediately contact a clinic for professional help. Based on complaints, a thorough medical history and an objective examination, the doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment.
For diagnosis, the following types of laboratory tests are used:
- cytological;
- biochemical;
- general blood analysis;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- gland biopsy;
- microbiological;
- immunological.
In addition, sialometry is used for functional diagnostics. Apply ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
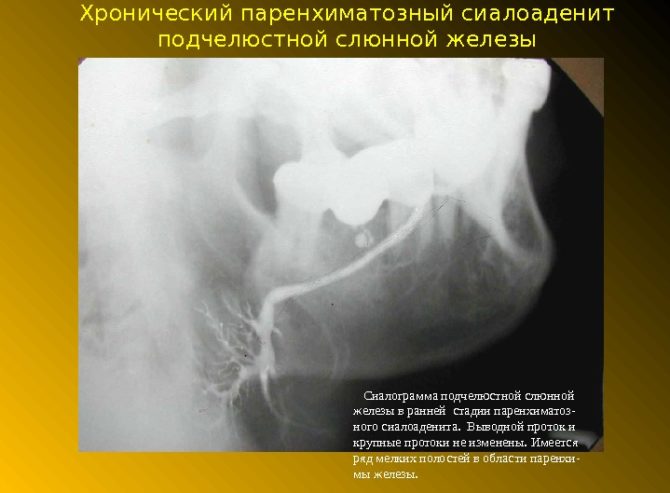
Acute sialadenitis is diagnosed by examination and history. In chronic cases, contrast sialography is necessarily used - an X-ray study with a contrast medium.
Treatment
The tactics and treatment regimen for inflammation of the parotid, sublingual or other salivary gland has its own characteristics and is chosen by the doctor depending on the infectious agent.
- The etiotropic treatment of sialadenitis caused by bacteria involves the appointment of antibacterial agents. Before prescribing antibiotics, be sure to do bacterial inoculation from the source, where the microorganism “activates”, and a test for sensitivity to the drug. Before taking these tests, you can not take potent drugs.
- When detecting mycosis, it is recommended to take antifungal drugs, since antibiotics against the fungus are powerless.
- In the case of the viral origin of the disease, antiviral drugs and interferon therapy are prescribed.
- With a purulent inflammatory process, surgical treatment is indicated with subsequent sanation of the focus.
- In case of narrowing, gland ducts are ducted.
- The calculous process is treated by removing stones by lithotripsy or lithoextraction.
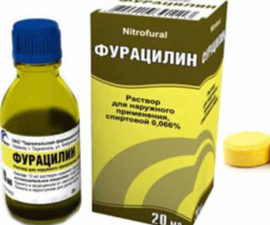 In complex therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are used, such as galvanization, UHF, electrophoresis, massage, and heating of the affected area. Salt compresses are also effective, rinsing the mouth and ear canal with antiseptic solutions is very good. They inhibit the reproduction of antiseptic bacteria called chlorhexidine and furatsillin.
In complex therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are used, such as galvanization, UHF, electrophoresis, massage, and heating of the affected area. Salt compresses are also effective, rinsing the mouth and ear canal with antiseptic solutions is very good. They inhibit the reproduction of antiseptic bacteria called chlorhexidine and furatsillin.
An ideal option would be to use compresses using Dimexidum. To stop allergic reactions, the doctor prescribes antihistamines, for example, with such names as Loratadin, Cetrin.
The patient must strictly adhere to the rules of hygiene, follow a special diet with the use of products in liquid, boiled form. It is forbidden to eat food that provokes salivation, very hot and too cold drinks and dishes, alcohol, smoking.
What can be done at home
Treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands at home is acceptable, but only at the very initial stages of the disease or in combination with traditional methods of therapy. To avoid complications, you must always consult a doctor.
 To speed recovery, you can drink and rinse your mouth with decoctions based on the following herbs:
To speed recovery, you can drink and rinse your mouth with decoctions based on the following herbs:
- chamomile;
- mint;
- raspberries;
- needles;
- eucalyptus;
- feverweed;
- sage;
- elder.
You can use a folk recipe with baking soda. To do this, it is necessary to dissolve a tablespoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water and treat the inflamed oral cavity with a cotton pad soaked in soda solution several times a day after meals.
An excellent folk remedy for reducing pain and inflammation is aromatherapy with essential oils of fir, needles, eucalyptus and many other oils.
Prevention
Preventing salivary gland inflammation is easier than curing. To do this, you need to follow only 4 rules:
- sanitize the oral cavity, cure carious teeth, pharyngitis, tonsillitis;
- remove foci of infection, especially those located near the ear canal and throat;
- stimulate, strengthen the immune system;
- protect your body from stress and less nervous.
The acute process ends with either a transition to chronicity or recovery. Chronic sialadenitis is often complicated by atrophy, sclerotherapy and difficult to treat. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and not to self-medicate.