Stomatitis in the mouth in adults: whether it happens, how and with what to treat
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity. The disease is of several types and is characterized by different symptoms. Before treating stomatitis in the mouth, it is necessary to correctly diagnose the pathology.
Content
Does stomatitis occur in adults, a description of the disease
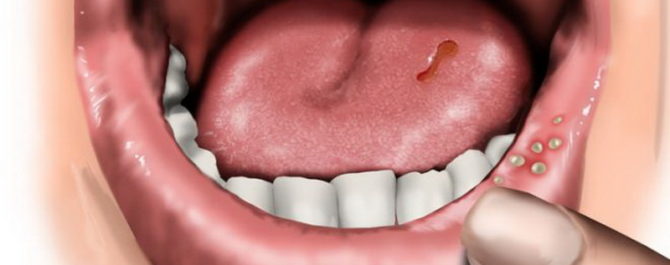
Contrary to the existing association between stomatitis and childhood diseases, it can be diagnosed in adult patients. Being an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, stomatitis can occur on the inside of the lip or cheek, on the tongue, palate, gum. The disease is quite painful.
Timely and correctly diagnosed stomatitis is treated quickly and without complications, while neglected stomatitis develops into a chronic or necrotic form that is difficult to treat.
Pathology develops due to viral, bacterial, fungal infections. Since there is a microflora of its own in the human oral cavity, consisting of billions of microorganisms, the inflammatory process can occur both due to external influences and against the background of serious internal disorders leading to a malfunction of the immune system.
The balance of the microflora of the oral cavity can be disturbed for the following reasons:
- allergic reactions of any etiology;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- lack of vitamins of group B;
- systemic decrease in immunity;
- unbalanced diet;
- tobacco and alcohol addiction;
- consequences of taking antibiotics;
- complications of gastrointestinal diseases, viral or chronic pathologies.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the affected soft tissues redden and swell;
- itching, burning, soreness;
- salivation increases;
- lymph nodes increase;
- sores appear in the lesion;
- body temperature may rise.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults should be carried out medically under the supervision of a dentist. For faster recovery, medications can be used in conjunction with traditional medicine.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- Viral and bacterial diseases, for example, scarlet fever, the herpes simplex virus of the first type.
- Inadequate or unbalanced diet. The diet of a healthy person should be balanced, enriched with vitamins and minerals. The daily menu must necessarily include foods rich in B vitamins, iron, zinc, protein, and folic acid.
- Injuries Stomatitis can be caused by various types of trauma to the oral mucosa. Mechanical damage is possible while eating rough food, in the presence of sharp edges of artificial crowns or fragments of teeth. Thermal - when eating very hot food or drinks. Chemical - due to burns with acid or alkali.
- Incorrectly selected, improperly installed or made of allergenic materials dentures.
- Neglect of hygiene rules: washing hands, fruits, vegetables.
- Decreased immunity due to prolonged antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy, and other aggressive therapies for cancer.
- Frequent use of sodium lauryl sulfate toothpaste.
- Anemia, hormonal pathologies, gastrointestinal diseases, dehydration.
- Allergic reactions.
If you have symptoms that indicate stomatitis, you do not need to try to diagnose the disease yourself and treat yourself at home. Stomatitis is a rather insidious disease, therefore it is necessary to treat it under the strict supervision of a specialist.
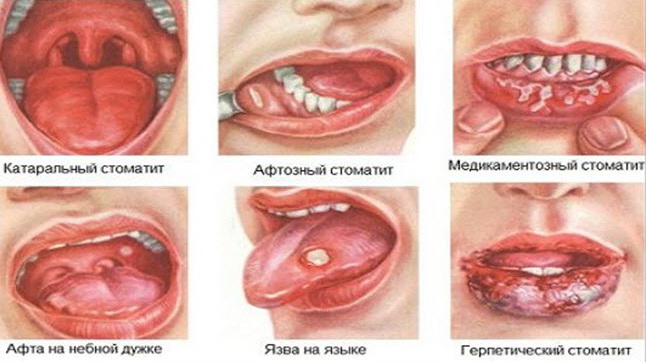
Types of stomatitis and treatment features
Depending on the causative agent, the disease is classified into 4 types:
- Bacterial stomatitis. It occurs with infection of the oral mucosa with staphylococcus, streptococcus. It is characterized by the appearance of purulent sores.
- Herpetic stomatitis. The disease manifests itself with activation of the herpes virus and is accompanied by the occurrence of itching, vesicles. It is possible to combine several ulcers in one erosive wound.
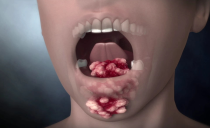
- Fungal stomatitis. It occurs due to the use of antibiotics during the treatment of other diseases and with a decline in immunity. Candidiasis stomatitis is often manifested in children. It is recognized by the cheesy white coating in the mouth. Painful ulcers form under the coating.
- Allergic stomatitis. It occurs as a reaction of the body to an allergen, weakening local immunity, which makes it possible to infect the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Gums may become inflamed after tooth extraction. An infection can penetrate into the postoperative wound, in which case traumatic stomatitis develops.
Depending on the nature of the course and external manifestations, stomatitis is divided into 3 more types:
- Catarrhal.
- Ulcerative.
- Aphthous.
Catarrhal
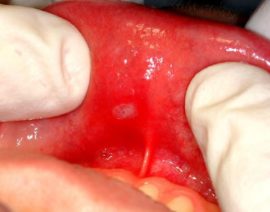 With catarrhal stomatitis, only the superficial layers of the oral mucosa become inflamed. Pathology occurs due to neglect of hygiene. With this form of the disease, redness of the affected tissues is observed, discomfort occurs, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is covered with a whitish film, pink spots appear on top of it. The temperature usually does not rise.
With catarrhal stomatitis, only the superficial layers of the oral mucosa become inflamed. Pathology occurs due to neglect of hygiene. With this form of the disease, redness of the affected tissues is observed, discomfort occurs, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is covered with a whitish film, pink spots appear on top of it. The temperature usually does not rise.
Catarrhal stomatitis in adults can be treated with regular rinses. But therapy based on the use of herbs helps to defeat only mild forms of the disease. In case of severe illness, consult a doctor.
Ulcerative and ulcerative necrotic
If you ignore the treatment, catarrhal stomatitis can develop into a purulent ulcerative. If during the illness secondary infection of the soft tissues occurs, the natural microflora in the mouth is completely destroyed. In the affected area, deep wounds with a red border appear. The following symptoms join:
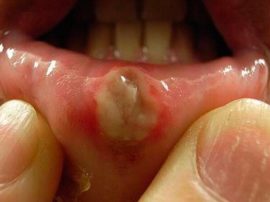 enlarged lymph nodes;
enlarged lymph nodes;- burning in the mouth;
- temperature increase up to 39 ° C;
- the appearance of a headache.
Over time, the infection penetrates into the deeper layers of the epithelium. The treatment period for advanced ulcerative stomatitis in the mouth is long - from two weeks.
The temperature with ulcerative stomatitis in adults does not always increase. But the more neglected the disease, the more its symptoms manifest themselves.
If untreated, the ulcerative form of stomatitis can develop into a purulent ulcerative necrotic, representing a serious threat to health: the infection can spread to internal organs.
Aphthous
The nature of the occurrence of an aphthous type of inflammation of the oral mucosa is still being studied. According to research, aphthous stomatitis can indicate various problems with the immune system, gastrointestinal tract diseases, and allergic processes.
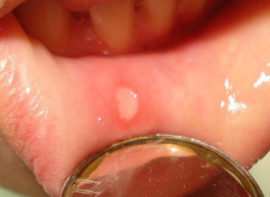 Usually the disease proceeds in a chronic form. During relapses of aphthous stomatitis on the tongue, cheeks, lips or palate, single or numerous rashes appear in the form of round aphthae of white or yellow color. Aphthae is extremely painful, heal for a long time. After recovery, scars often remain in their place. Temperatures can rise up to 38 ° C, and sometimes even higher.
Usually the disease proceeds in a chronic form. During relapses of aphthous stomatitis on the tongue, cheeks, lips or palate, single or numerous rashes appear in the form of round aphthae of white or yellow color. Aphthae is extremely painful, heal for a long time. After recovery, scars often remain in their place. Temperatures can rise up to 38 ° C, and sometimes even higher.
Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive, usually therapy includes:
- taking antihistamines;
- local treatment of aft with antiseptics and gels;
- strengthening immunity;
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- compliance with hygiene procedures.
To prevent the occurrence of relapses of aphthous stomatitis, it is necessary to cure all concomitant chronic diseases and strengthen the immune system.
How and with what stomatitis in the mouth is treated in adults
Stomatitis in the mouth in adults is treated differently. The treatment regimen depends on the form of the disease and the degree of spread of inflammation. That helps with stomatitis of one form or another, you need to find out from the dentist. After studying the results of the tests, the doctor will establish an accurate diagnosis, identify the pathogen and prescribe a suitable treatment regimen.
It is strongly recommended that you do not treat stomatitis without consulting a doctor, since at home it is impossible to determine the causative agent of the disease.
| Form of stomatitis | Approximate treatment regimen |
|---|---|
| Bacterial |
|
| Herpetic | Drug therapy is indicated, including the administration and topical use of such drugs:
|
| Fungal |
|
| Aphthous |
|
| Allergic |
|
In the treatment of any form of stomatitis, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease that caused it to occur. Otherwise, the disease will turn into a chronic form.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of stomatitis in adults should be carried out comprehensively. Drug therapy can be completely replaced by traditional medicine only in the initial stages of the catarrhal form of the disease.
As an addition to the basic treatment, the following folk remedies can be used:
- Blue iodine diluted in a ratio of 1: 1. A cotton swab dipped in this agent should be applied to inflamed sores 3 times a day.
- Rinse your mouth with diluted apple cider vinegar. Helps to eliminate symptoms in a shorter period.
- Alcohol tincture of propolis. It is applied to dry areas of soft tissues affected by infection, facilitates the acute course of the disease.
- A solution of chamomile and a few drops of boric acid. It is used to rinse the mouth.
- Myrrh oil. Used in the form of applications for lesions. It helps relieve swelling, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and prevents the spread of infection to the ENT organs.
- Thyme oil. This remedy is recommended to be treated for any diseases of the oral cavity. It is taken orally by dissolving in honey, juice or kefir.
- Ginger root, grated and boiled in boiling water. Suitable for rinsing, eliminates inflammatory processes in the mouth.
- A decoction of blueberries.You can rinse your mouth with this tool for any form of the disease, since it has an antiseptic effect and is harmless.
- Green tea with honey. Rinsing the mouth with this tool will help eliminate mild forms of inflammation on the tongue, gums, cheeks.
- Lemon peel infused in boiling water. Disinfects and promotes rapid healing of ulcers. Tincture is used in the form of rinses.
- Lotions of freshly pressed onions and garlic. Onions can be mixed with a few drops of Kalanchoe, and garlic is recommended to be mixed with yogurt.
- Chamomile, calendula, mountaineer serpentine, celandine, St. John's wort, linden flowers. Herbs are used to prepare decoctions for rinsing the mouth.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Heals damaged soft tissues and anesthetizes. It is applied in the form of applications.
Preventive actions
Treatment of stomatitis in adults is a difficult and lengthy process. Prevention of the disease will help get rid of unwanted relapses. Preventing the disease is easier than curing; just follow a few rules:
- wash hands with soap after walking and before eating;
- monitor the condition of the teeth: on time to carry out the treatment of caries and removal of stones;
- monitor the condition of the digestive tract;
- establish a healthy balanced diet;
- artificially increase immunity in the autumn-winter period;
- do not interrupt the treatment of infectious pathologies;
- Responsibly approach the choice of toothpaste, rinse aid, brush.