Glands and tonsils in the throat: location, functions, causes of inflammation and treatment methods
Adults and children are faced with unpleasant painful sensations in the area of the throat where the glands are located. Immediately after the onset of the first symptoms - pain and dryness in the throat, shortness of breath, high fever - the sick begin to be treated on their own.
Self-medication and an incorrect diagnosis lead to the transition of the disease to a severe form and complications. To avoid tonsillectomy, you must consult a doctorwho will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe competent therapy.
Content
Functions and structure of tonsils
Tonsils are organs of the body’s immune system. Their main function is antibacterial protection against pathogenic microbes that penetrate the oral cavity by airborne droplets and provoke inflammatory diseases. The second, no less important task of lymphoid cells, colloquially called glands, is hematopoietic. They supply lymphocytes to the blood stream and control their content in the required quantity.
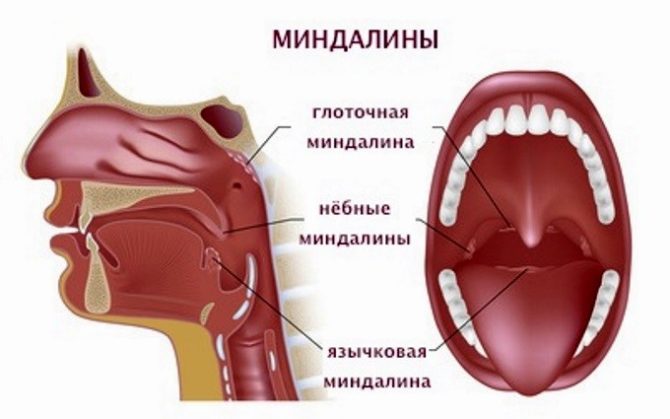
In total there are six tonsils:
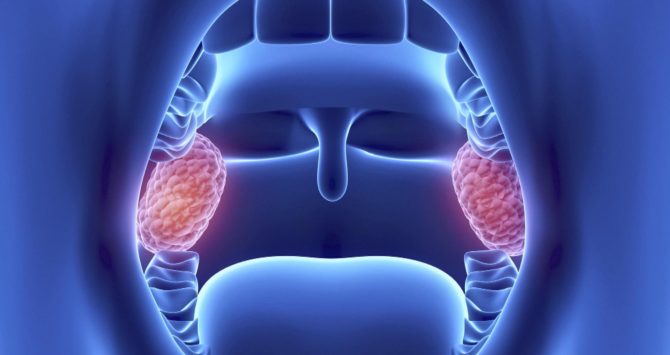
- A pair of palatines. As seen in the photo below, palatine tonsils are the largest from available. They are placed on the sides of the pharynx in tonsillar niches. To see where the glands are, you should open your mouth wide and look in the mirror. The free surface of the lymphoid formations, covered with several layers of the epithelium, is turned to the pharynx. In every formation there are crypts - gaps. The other side of the palatine tonsil fuses with the lateral surface of the pharynx using a capsule.
- A pair of tubular located in the nasal cavity at the mouth of the auditory tube. Normally, small organs in case of hypertrophy block the connection between the nose and middle ear, causing otitis media and hearing impairment.
- Pharyngeal. It is almost impossible to independently see the location of the tonsil, called the nasopharyngeal or pharyngeal. The organ located in the back of the nasopharynx can be detected only with a significant increase in it and in the position hanging over the tongue.
Overgrown adenoids - the so-called inflamed pharyngeal tonsil - are especially dangerous for babies. Children cannot breathe fully, hearing impairment occurs, otitis media develops. If drug treatment fails, adenoids are removed.
- Lingual. Where the tonsil is located is clear by name - it is located at the root of the tongue. A rough formation with tubercles is covered with lymphoid tissue. With inflammation, the tonsil interferes with eating and hurts when talking.
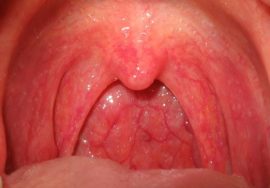
How healthy tonsils look and where they are
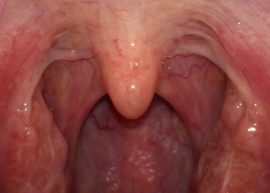
The glands of a healthy person are of medium size, usually they do not extend beyond the arches of the pharynx. But exceptions are possible - in some people, large glands are found due to the anatomical features, and not the disease.
The surface structure of the tonsils uneven by nature should not be pronounced and bumpy. The color of healthy glands is indicated by their color, usually it is uniform, pinkish in color, without red furrows and inclusions.
The back wall of the oral cavity, palate, tongue with healthy glands are evenly colored and have no signs of inflammation. The mucous pharynx should be free of edema, a pronounced vascular pattern.On the surface of the glands themselves there should not be purulent deposits, unhealthy plaque.
Diseases that occur when the glands are disturbed
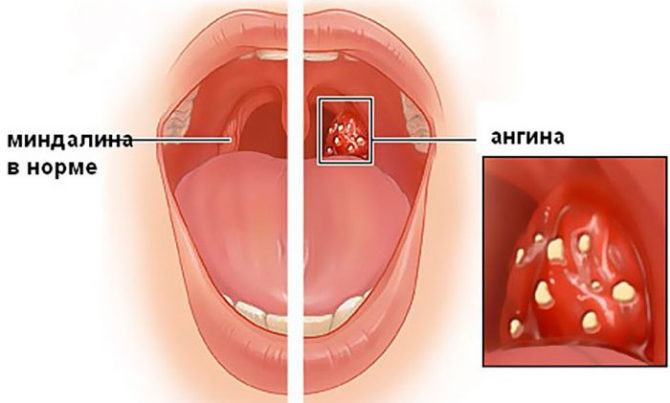
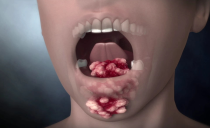
- Angina, accompanied by high fever, swollen lymph nodes, headache, weakness, severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing movements. When infected with herpetic sore throat, purulent vesicles appear on the tonsils, eventually turning into small sores.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa. With pharyngitis, only the palatine arches and the back of the larynx swell. Palatine tonsils may not change.
-
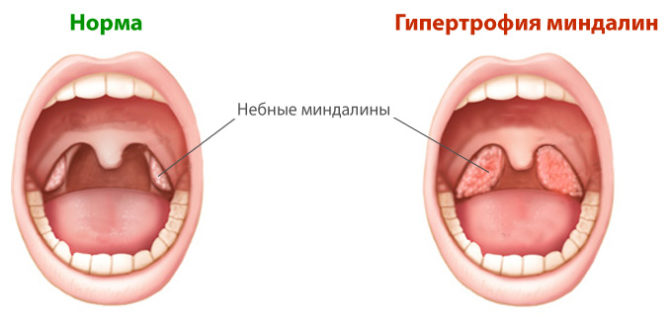
Hypertrophy is a disease in which normal tonsils increase in size. Adults rarely have an illness, most cases are recorded in childhood.
- Tumors, neoplasms, cancer or a cyst of the nasopharynx are diseases that require a general diagnosis of the picture and rapid treatment of the disease. The risk of gland cancer increases in adults older than 50 years. During medical commissions, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is necessary, especially in the area where the glands are located.
First aid
It is difficult to swallow, the temperature has risen, when examining the throat, redness or pustular rashes are found - call a doctor. Before the arrival of a specialist, patients should not take pills that lower the temperature, but only if it does not exceed 39 ° C. High temperature will help the body cope with the infection and destroy harmful microorganisms.
Relief scheme for the patient:
- A plentiful warm drink.
- Gargling with salt water, decoctions of herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula).
- Rinse with diluted water Furacilin, Miramistin, Dioxidine and other means recommended by your doctor.
- Absorption of lollipops with a calming and analgesic effect.
- Bed rest.
Take antibiotics, and preferably all other drugs, should only be prescribed by your doctor.
Reasons for the increase in tonsils
Tonsils are enlarged in case of infection of the body with strepto-staphylococci or viral infections. This happens as a result of:
- Overflow of usual inflammation into chronic.
- Decreased immunity during hypothermia, stressful situation or due to other reasons.
- Irritation or poisoning by chemicals, allergens, unusually spicy food.
To compare how normal and inflamed tonsils (tonsils) look in the throat, you can see in the photo:
Gland Removal: Pros and Cons
Disputes about the need to remove or preserve tonsils have been ongoing for a long time and with varying success. Those who argue that nature is not involved in the construction of extra organs give the following arguments about the benefits of glands:
- Producing a huge amount of immunoglobulins, tonsils of a healthy person contribute to the proper development and protection of the body from viral infections.
- The porous surface of the glands serves as a barrier to pathogenic microorganisms seeking to enter the throat and the internal environment of the body. Once in the center of the immune cells, the harmful bacteria die.
Proponents of surgical intervention believe that even normal tonsils can eventually cause big health problems:
- During some diseases, for example, chronic sore throat or acute tonsillitis, malfunctions and irreversible changes occur in the proper functioning of lymphatic formations. The glands are constantly inflamed, do not allow breathing freely, the elimination of harmful bacteria does not occur.
- Frequent purulent sore throats can cause a throat abscess, a general infection of the body.
- Constantly enlarged glands lead to hearing impairment or impaired respiratory function.
Most doctors agree with the removal of the tonsils in the most severe cases: if the body is unable to respond to medication treatment.
Disease prevention
Strengthening the immune system does not allow the development of inflammatory processes. In order to prevent the development of diseases, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle: get rid of bad habits, eat right, monitor the general condition of the body. To keep the tonsils normal, it’s enough:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Refuse cold drinks.
- Eliminate all possible sources of infection: sinusitis, caries, sinusitis.
- At the first sign of infection, contact a health facility.