Foamy, viscous and viscous saliva in the mouth - causes and treatment
Consistency is one of the characteristics of salivary fluid in the mouth, which few people think about for no reason. Most often, that it can be modified, a person learns when metabolism is disturbed in his body. However, saliva in the mouth can become viscous and sticky for a variety of reasons, and the treatment of a defect directly depends on what exactly served as a prerequisite for its development.
Content
Saliva is normal
The salivary glands of an adult healthy person produce from one to two liters of secret daily. The objective of this fluid is to lubricate the oral cavity to facilitate chewing and speaking. Thanks to the secret, the digestion of food begins already at the moment of chewing, because the active enzymes are part of the saliva. The perception of the taste of the products also depends on the degree of processing with salivary fluid.
Drooling is the first natural antiseptic available. That is why small wounds in the mouth heal much faster than on the skin.
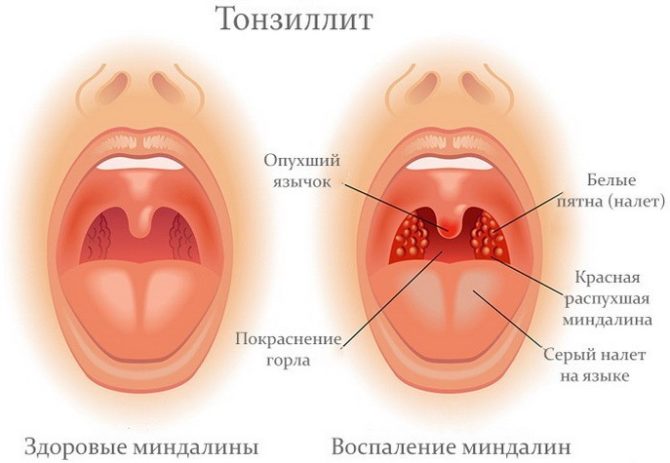
In order for all these processes to proceed exactly as needed, salivation should be sufficient, and the discharge should be transparent or slightly cloudy, liquid and imperceptible to humans. Violation of the usual consistency of saliva cannot be overlooked, since an obsessive feeling of discomfort is created, speech and the usual rhythm of life are disturbed, digestion, teeth and oral mucous membranes are possible.
What should alert
Typically, patients' complaints are related to the fact that in the morning their saliva becomes not as usual: thick, sticky or foamy. In such cases, concomitant symptoms may be observed:
- violation of taste perception;
- persistent dry mouth and throat;
- feeling of not passing thirst;
- tingling sensation on the tongue;
- difficulty and pain when chewing and swallowing food;
- sore throat and hoarseness;
- cracks on the lips;
- rapid plaque formation on the teeth;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and gums.
All these phenomena can be the result of changes in the composition, amount and viscosity of saliva. To make sure of the validity of such suspicions or to dispel them will help a simple test, which you can take yourself on an empty stomach in the morning. To do this, you need to get a pipette with applied divisions and a stopwatch.
First, you need to draw a milliliter of ordinary water into a pipette and observe how long it will flow out. Then you need to do the same with salivary fluid. It remains to compare two indicators - normal, they should be approximately the same.
But self-examination is a subjective thing, therefore, for any suspicion of a serious malfunction in the body, you should contact specialists for accurate laboratory tests. Doctors determine the consistency of saliva norm with the help of a viscometer device. If he confirms that the patient has really too thick saliva in his mouth, the doctor will determine the cause of the defect and prescribe the necessary treatment. For the diagnosis, additional analyzes and consultations of narrow specialists will be required, therefore self-medication in this situation is unacceptable.
Why saliva is viscous and viscous
Symptom like thick saliva, often causing dehydration due to insufficient fluid intake and intoxicationaccompanied by vomiting and diarrhea. In addition, the cause of thick saliva can lie in the side effects of medications.Diuretics and choleretics, antihistamines and antidepressants, as well as a number of painkillers, radiation and chemotherapy can cause the salivary glands to malfunction. In these cases, cancellation or replacement of the drug is sufficient to solve the problem.
Smokers with experience often encounter dry mucous membranes of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the appearance of viscous, sticky saliva. For some, such a violation accompanies a complete abandonment of a bad habit.
The cause of the appearance of viscous or foamy saliva can be a natural hormonal imbalance that occurs during pregnancy, menopause, or adolescence. No drug therapy is required in these cases.
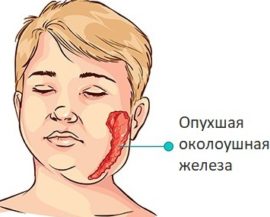
When the root of the problem lies in internal diseases, determining the true cause can be very difficult. Some diseases directly complicate the salivary glands.: with mumps, Mikulich’s diseases and sialostasis, the glands enlarge and become painful, secretion production is significantly reduced, and salivary stone disease and neoplasms can even lead to their surgical removal. In any of these cases, saliva can acquire an unusual consistency. Cystic fibrosis, scleroderma, Sjogren's syndrome, HIV, retinol deficiency, anemia can also occur in a similar way.
The reason for the appearance in the mouth of an unusually thick and viscous saliva may be an injury that caused a rupture of the ducts or tissues of the gland. In this case, you will need the help of a surgeon. Various internal diseases can affect the work of the salivary glands and the properties of their discharge.
- neurological;
- hormonal;
- gastrointestinal;
- autoimmune;
- rheumatoid;
- psychosomatic.
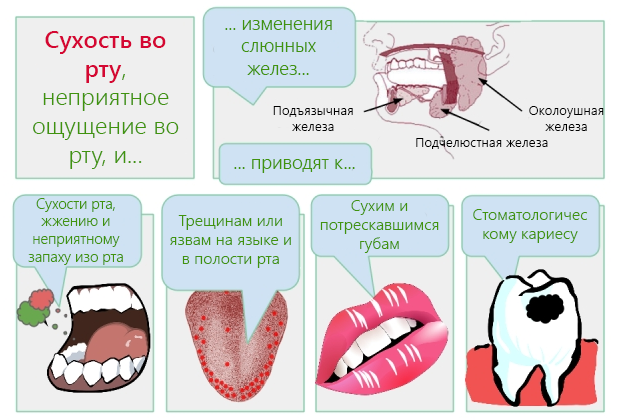
Dryness and stickiness in the mouth, accompanied by a decrease or complete absence of saliva and resulting as a result of deep internal pathologies, is called xerostomia. Concomitant symptoms of the disease are redness of the tongue, cracks and seizures on the lips, soreness in the mouth and throat. Xerostomia develops on an increasing basis, depending on the cause of the occurrence, the pathology can be temporary or permanent - both require timely treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Viscous mucus can look and feel differently. Thick sputum is white, frothy, thick, viscous, can create a feeling of "lump in the throat."
Causes of Foamy Saliva
A condition in which the saliva in the mouth not only thickens, but also changes to a foamy consistency, is due to the action of mucin, a special substance in the composition of saliva that helps form a food lump when chewing. If the salivary glands are disturbed, the mucin content in saliva becomes higher, which explains the foam structure.
Whitened saliva
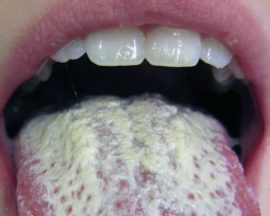
The reason for the appearance of white thick saliva should be sought in fungal lesions of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. Most often, this pathology is observed with candidiasis, known as stomatitis or thrush. It usually develops in children, but sometimes appears in adults.
Salivary fluid is stained white with sediment in the form of a cheesy plaque characteristic of this infection, which covers the mucous membranes of the mouth. To get rid of the disease, apply local and internal antifungal drugs, strengthen the immune system.
Causes of Viscous Saliva in the Throat
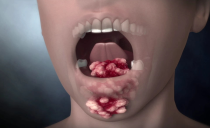
Saliva can not only foam, but also seem to get stuck in the throat. In this case, an examination by an ENT doctor is necessary for damage to the tonsils and larynx. Purulent forms of tonsillitis or tonsillitis are accompanied by the appearance of plaques on the tonsils, which create discomfort and pain, and when opened, they secrete purulent contents in the throat that increase the saturation of sputum.
Gum disease, accompanied by the secretion of pus, can also be an explanation of why saliva became thick, viscous and felt in the throat. Such diseases include periodontitis, periodontal disease, cysts, phlegmon and abscesses.Sticky pus from the affected areas of the gums mixes with saliva and makes swallowing difficult.
How to relieve the condition when saliva is viscous and viscous
A person whose saliva thickens and foams feels a lot of discomfort. In addition to discomfort, outbreaks of diseases of the throat, tongue, gums can become more frequent, and teeth become more vulnerable to caries. Therefore, you need to get rid of such a symptom using conservative and alternative methods of treatment.
Having determined why the saliva in the patient’s mouth has become thick and viscous, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the underlying disease that caused xerostomia, as well as auxiliary methods of local exposure, which will help to return to normal life faster:
- artificial saliva;
- various moisturizers in the oral cavity in a form convenient for use (in the form of a gel or spray);
- specialized rinsing agents;
- special chewing gums and candies;
- plentiful drink.
Of the folk remedies for the treatment of xerostomia, tea from sage or fenugreek, lubrication of the oral cavity with a mixture of peach oil with propolis, inhalation with eucalyptus are used. But these therapeutic methods are best discussed with your doctor.
It will not be superfluous to purchase a room humidifier and refuse tobacco, alcohol, soda and coffee, which additionally dehydrate the mucous membrane. The use of dairy products will also have to be minimized. The daily volume of clean water consumption should be at least one and a half liters. During this period, it is better to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles so as not to injure dehydrated gum tissue.
Do not wait until unusual sensations in the mouth turn into intolerable. Saliva viscosity is one of the serious indicators of the health of the body. If he deviated from the norm, it is necessary to act.