Syphilis in the mouth: ways of infection, signs and auxiliary symptoms, treatment
Syphilis in the mouth - this is a serious disease caused by the Treponema pallidum bacterium (pale treponema). The disease is a sexually transmitted infection, so the attitude towards syphilitics is usually sharply negative. However, in order to become infected with syphilis, it is not necessary to lead a wild lifestyle.
Content
Infection pathways
The entry into the human body of pale treponema occurs as follows:
- sexually;
- in utero;
- through non-sterile medical instruments in dentistry;
- household way: through toothbrushes and other personal care products;
- through wounds on the oral mucosa.
The first variant of infection with syphilitic infection is the most common. Moreover, the causative agent of the disease can penetrate the body even through a kiss, especially if there are cuts or ulcers on the oral mucosa.
Syphilis can be congenital. The baby becomes infected with it from the mother during intrauterine development. With timely medical intervention and full medical monitoring of the pregnancy, intrauterine infection with syphilitic infection can be avoided.
Syphilitic infection can be infected during dental treatment procedures or during surgery. In this case, pale treponema enters the body through poorly processed medical instruments.
A special risk group for contracting a sexually transmitted infection includes doctors. The causative agent of syphilis in the tongue can penetrate into their body if the basic precautions are not observed during the examination and treatment of the patient’s teeth and oral mucosa.
Stages, signs and symptoms of syphilis in the mouth
There are three main stages of syphilitic infection. The first is easy to treat, but finding it on time is quite difficult. The last two stages of the disease usually proceed in a chronic form and can cause irreparable harm to the body. Complete healing in the last stages of the development of the disease is impossible.
In addition to the three main stages of the infectious process, an incubation period is distinguished. At this time, the patient does not yet show symptoms of syphilis in the mouth.
Incubation period
The incubation period lasts 2-3 weeks from the moment of infection with syphilitic infection. Many attribute this period of the development of the disease to primary syphilis, but since it is almost impossible to detect the disease within the specified period, experts distinguish it in a separate stage.
The incubation period of syphilis in the oral cavity can last longer if:
- the patient takes antibiotics in connection with other diseases: cold, flu;
- the infected person has good immunity, able to fight the pathogen for a long time.
In women, the visible signs of syphilis in the mouth usually appear later than in men, since they have a longer incubation period for the disease.
Primary stage
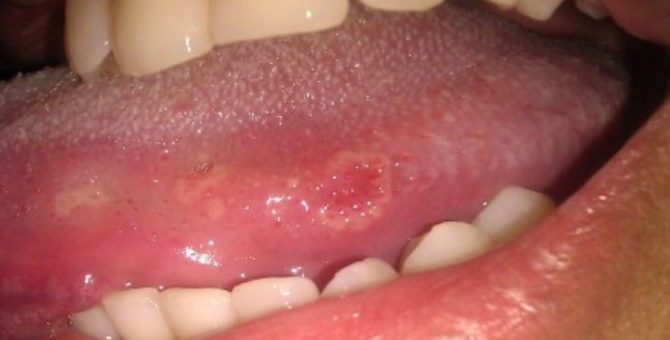
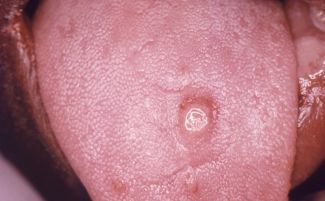
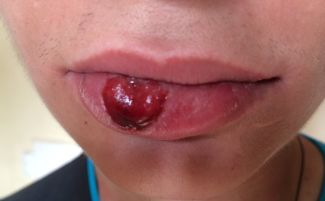
The main manifestation of the primary stage of syphilitic infection is the formation of a hard chancre on the tongue, palate, or lip. If the infection occurred through the damaged mucous membrane of the oral cavity, then the seal forms exactly in the place where the wound is located. At first, the chancre looks like ordinary redness.
The affected area gradually grows and can reach several centimeters in diameter.In the center of the lesion, erosion appears, which has a bright red tint. Up to this point, the chancre does not cause the patient any discomfort, so it is difficult to detect it at the first stage of the development of the disease.
The chancre in the mouth is far from the only symptom of a sexually transmitted disease. The disease can be accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. This means that syphilitic infection has reached them. In turn, such a lesion leads to general malaise, weakness, and painful reactions.
Secondary stage
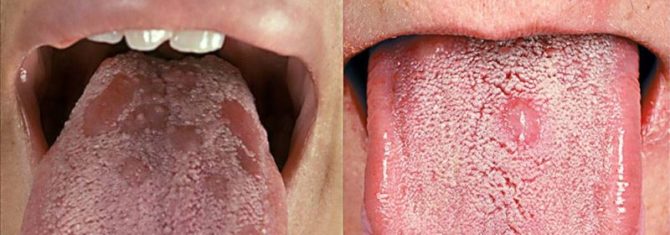
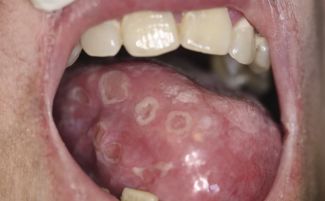
If treatment is not started within two months after infection with syphilis, the disease will go into secondary form. At this stage of a sexually transmitted infection, formations in the form of roseola and papules appear in the oral cavity.
Papules are rashes of a rounded shape, but without a clear outline. They can appear on the tongue, sky, throat and tonsils. Ulcers can form in one place and thereby form large foci. If the papule appeared on the tongue, sensitive papillae atrophy in this area, a plaque appears, under the surface of which the inflamed red tissues are hidden.
Roseola is a bit like papules. They are spots that most often appear near the teeth, in the sky and tonsils. Due to the bright red color, roseola stand out against the background of the oral mucosa. They do not cause the patient any particular discomfort, so until the papules appear, a person may not even suspect that he has acquired a syphilitic infection.
In addition to the appearance of roseol and papules, the secondary stage of syphilis in the tongue is distinguished by the following:
- it is most contagious to others;
- the rash appears not only in the mouth, ulcerative lesions pass to the skin of the body and face;
- the infection affects the internal organs, so a general deterioration in health is possible.
If a second stage of syphilitic infection is detected, the patient is immediately isolated. All his relatives should be tested for the presence of pale treponema in the body.
Tertiary stage
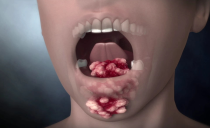
The tertiary stage of syphilis in the oral cavity is characterized by the most striking manifestations: on the gums near the teeth, on the tongue and palate appear tuberous rashes or gum. The last stage of the development of the disease begins only 3-4 months after infection and only in the complete absence of treatment. It is impossible to get rid of a neglected sexually transmitted infection without consequences.
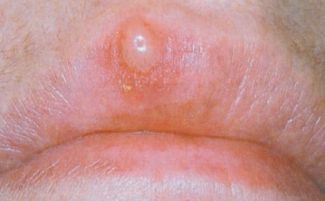
Tertiary syphilis begins painlessly and even imperceptibly. A node (gum) appears on the oral mucosa. Such formations can be everywhere, but most often they are located on the tongue, lip or palate.
The node gradually increases in size, becomes painful and acquires a brown hue. The tissue in the middle of the gum dies away - an open ulcer is formed. Densified tissue around the ulcer rises above the level of the mucous membrane of the affected area of the oral cavity.
With the right treatment the healing process of soft tissues of the oral cavity affected by tertiary syphilis takes from 3 months to six months. In place of the gum, a noticeable scar remains. If the formation has managed to destroy a large area of the soft tissues of the tongue, palate or lip, plastic surgery may be required.
Tuberous syphilitic rashes often appear on the lips. They are localized in groups and at first do not cause much discomfort. With the growth of the tubercles gradually turn into small open wounds. When the ulcers that appear in the mouth during tertiary syphilis heal, scars will remain forever after them.
Consequences of the disease
Syphilis is a dangerous disease that can lead to serious consequences. Among them:
- Extensive damage to the soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity.
- Dead areas of soft tissue in the mouth and noticeable scars in the area of hard chancre, papules and nodes.
- Violations of the cardiovascular system.
- Damage to the muscles of the face and neck.
- Asymmetry of the face.
In the absence of treatment, syphilis spreads to adjacent tissues. The disease can even affect the brain, which is fraught with serious consequences, even death.
Diagnosis of the disease
A dermatovenerologist is involved in the identification and treatment of syphilitic infectious disease. In the second and third stages, the disease is easily detected by external signs. An experienced specialist will accurately distinguish a hard chancre or papule on the lip, palate, gum and other parts of the oral cavity from formations that look similar. Initial syphilis can only be detected with a blood test.
Since syphilis is completely cured only if treatment is started during the first months after infection, tests to identify this sexually transmitted disease are given during any comprehensive examination.
Treatment features
The main goal of therapy for syphilis in the oral cavity is the suppression of the pathogen. For this, the patient is prescribed a number of medications with an antibacterial effect. To improve the action of essential drugs, it is necessary to take drugs that normalize the functioning of the immune system.
Since with secondary and tertiary syphilis, external symptoms appear - papules, ulcers, gum, drugs are prescribed to the patient that improve tissue regeneration. If the patient’s tongue has chancres, roseola or papules, ointments are prescribed for their healing. Usually, preference is given to those drugs that have a healing, antiseptic and analgesic effect.
In the treatment of the tertiary stage of the disease, in addition to drug therapy, surgical intervention may be required. The patient is either restored the affected tissue, or remove scars that impede a full life.
In addition, treatment in the last stages of a sexually transmitted infection differs in the following:
- It will not be possible to completely get rid of syphilis in the oral cavity. You will have to visit a specialist at least once every six months to check your health condition.
- Even if the disease is in an inactive stage, the patient may remain its carrier. Therefore, additional precautions must be taken.
A person who has syphilis should constantly monitor his health. It is better to get rid of all bad habits, start eating right and exercise. All this is necessary to improve immunity and prevent relapse of the disease.