Stomatitis in adults: causes, symptoms and treatment
Stomatitis is an infectious inflammation of the mucosa lining the oral cavity. Usually the disease manifests itself in children, since their immunity is still undeveloped and can not withstand pathogenic microbes. However, in recent years it has been recorded in populations of all ages. According to experts, this is due to adverse ecology, which leads to a decrease in the functions of the immune system.
The tactics of treating stomatitis in adults depends on the type of pathogen, severity of symptoms and associated pathologies. Therefore, if you detect the first signs of an ailment, you should consult a doctor.
Content
- Why does stomatitis appear: causes and conditions
- Internal pathology and stomatitis
- Forms and types of disease
- Symptoms and development of stomatitis
- Therapy: general recommendations
- Allergic stomatitis treatment
- Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
- Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
- Treatment of fungal stomatitis
- Stomatitis Prevention
Why does stomatitis appear: causes and conditions
The main culprits of stomatitis are bacteria, fungi and viruses. It is because of their activity that an infectious and inflammatory process originates that affects the fragile mucous membrane of the tongue, palate, throat, gums or cheeks.
The human oral cavity has its own microflora. A huge number of staphylococci, spirochetes, streptococci, fungi and other microbes are in it constantly and from birth. They protect the body from their counterparts from the outside, saving a person from numerous diseases.
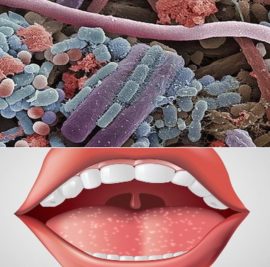 The quantitative and qualitative constancy of microflora is controlled by saliva, which inhibits its reproduction, but does not completely destroy, since the vacant place will immediately be occupied by another pathogenic one.
The quantitative and qualitative constancy of microflora is controlled by saliva, which inhibits its reproduction, but does not completely destroy, since the vacant place will immediately be occupied by another pathogenic one.
An imbalance in the microflora of the oral cavity leads to inflammation of its mucous membrane - stomatitis. Moreover, the causative agent of the disease can be both its own microbes, and those that have penetrated from the outside.
An imbalance in the microflora, leading to stomatitis, occurs under the influence of such factors:
- decreased immunity against the background of a lack of vitamins, stress, chronic or acute internal disease, or a common cold;
- bacteria or fungi entering the mucosa from the external environment, for example, when eating unwashed foods;
- accumulation of microflora in poorly accessible areas: in carious cavities, under crowns;
- defective and irregular brushing;
- uncontrolled intake of drugs that reduce the quality and quantity of saliva;
- inhibition of positive microflora with antibiotics;
- hormonal changes that often occur in women and adolescents;
- prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, or bleeding causing dehydration and decreased saliva.
Internal pathology and stomatitis
The cause of stomatitis often becomes a violation in the work of an organ or system. Most often, the manifestation is facilitated by:
- oncological diseases;
- gastritis, colitis;
- anemia or anemia;
- bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disruptions;
- HIV infection.
Forms and types of disease
By the nature of the manifestation, stomatitis is of three main types:
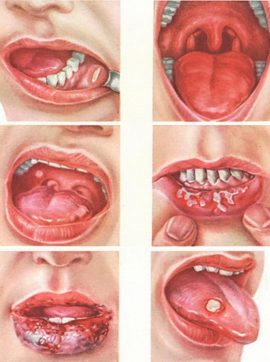 Catarrhal. Signs: dry mouth, burning, teeth imprints on the tongue, bleeding gums, pain during eating, itching, impaired taste and large-scale redness of the mucous membrane.
Catarrhal. Signs: dry mouth, burning, teeth imprints on the tongue, bleeding gums, pain during eating, itching, impaired taste and large-scale redness of the mucous membrane.- Erosive. Accompanied by a sharp pain when chewing food, talking. The area of lips, gums, tongue, palate can swell, blush, become covered with vesicles with transparent exudate. Erosion appears in the lesion focus. Sometimes they merge and form a large-scale single ulcer.
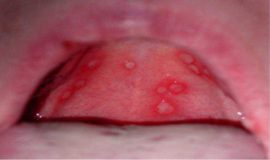
- Aphthous. Most often, it begins with an increase in body temperature, swelling of the lymph nodes. Then the lesion area turns red and becomes covered with individual aphthae, which have smooth, whitish edges. Usually the number of aft does not exceed three.
Depending on the pathogen, due to the fault of which inflammation appears, stomatitis is divided into 5 main types:
- Bacterial. The culprits of the disease are staphylococci or streptococci.
- Traumatic. It occurs due to burns or mechanical damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Fungal. Appears with reduced immunity or after a course of antibiotics. Against this background, the body can not prevent the increased growth of fungi of the genus Candida, which is why inflammation develops.
- Viral. This form of stomatitis occurs due to the activation of the herpes simplex virus or Epstein-Barr.
- Allergic. Reaction to various allergens. For example, the material of the denture, the composition of the paste or rinse aid.
Symptoms and development of stomatitis
Infectious inflammation usually covers the mucous membranes that cover the tonsils, tonsils, throat, upper part of the tongue, inside of the cheeks or lips, gums.
Symptoms of stomatitis are the same in both adults and children. But in the second, the disease is more acute, with signs of general intoxication and high fever. Whereas in the former, only the mucous membrane most often suffers.
Inflammation begins with a slight reddening of the lesion. Then the area around it becomes swollen, painful and swollen. The next day, ulcers, aphthae, or vesicles may appear.
In addition to rashes, bad breath, bleeding gums can occur. Sometimes the body temperature rises. The maximum mark is 39 ° C. Lymph nodes almost always increase, and the tongue is screwed up.
Viral stomatitis
The cause of this type of stomatitis is the pathogenic effect of the herpes simplex virus, chickenpox or influenza. The most common causative agent of the disease is herpes virus. According to statistics, in 90% of cases, infection with them occurs in early childhood. As soon as pathogenic particles get on the skin, they penetrate the replication apparatus of nerve cells and are in it in a latent state for life.
When a person's immunity decreases, the agents are activated and affect either the lips and / or skin on the face or the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In the second case, the favorite places for the localization of the virus are the cheeks, the upper part of the tongue and the palate.
With herpetic stomatitis, the oral mucosa reddens and swells. Over time, bubbles appear on it, filled with a transparent liquid and arranged in groups.
Within a few days, the exudate becomes cloudy, the formations burst, and red erosions appear instead. The latter quickly dry out and become whitish or yellowish.
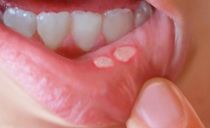
Aphthous stomatitis
The main difference between this form of the disease is the appearance of rounded aft yellow or white with a bright red rim (see what they look like in the photo). The size of the formations can reach 10 mm. The surface is covered with fibrinous plaque.
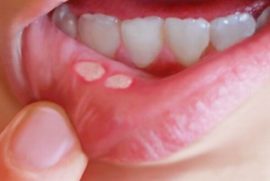 Most often, the disease is chronic (persistent) in nature. If it cannot be cured within two weeks, then the pathology will switch to a different form and ulcerative stomatitis or, even worse, necrotic will begin. This happens not without reason. Most often, this phenomenon indicates serious health problems.: immunodeficiency, radiation, leukemia, poisoning with salts of heavy metals.
Most often, the disease is chronic (persistent) in nature. If it cannot be cured within two weeks, then the pathology will switch to a different form and ulcerative stomatitis or, even worse, necrotic will begin. This happens not without reason. Most often, this phenomenon indicates serious health problems.: immunodeficiency, radiation, leukemia, poisoning with salts of heavy metals.
Bacterial stomatitis
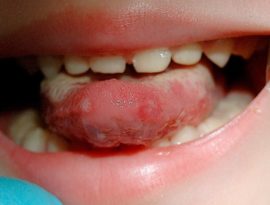 The mucous membrane is covered with a coating of gray or yellow. Vesicles should appear on the affected areas, from which bloody contents or pus is released. Rashes have a smooth, rounded shape, red color, elastic walls and clear boundaries. Gums swell and hurt. There is a putrid breath.
The mucous membrane is covered with a coating of gray or yellow. Vesicles should appear on the affected areas, from which bloody contents or pus is released. Rashes have a smooth, rounded shape, red color, elastic walls and clear boundaries. Gums swell and hurt. There is a putrid breath.
The clinic lasts no longer than one week. Then the symptoms disappear, but it’s not worth hoping that the adult’s bacterial stomatitis will go away without treatment. Against the background of weakened immunity, the pathology undergoes chronicity.
Fungal stomatitis
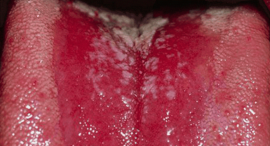 This form of stomatitis is most pronounced. The mucous membrane is covered with a characteristic plaque, which has a white color and a curdled texture. The skin under them is covered with ulcers. If you try to clear the affected area, it may begin to bleed.
This form of stomatitis is most pronounced. The mucous membrane is covered with a characteristic plaque, which has a white color and a curdled texture. The skin under them is covered with ulcers. If you try to clear the affected area, it may begin to bleed.
Candida stomatitis in the tongue, palate, gums and cheeks is localized. At the initial stage, plaque covers the mucous membrane topically. At the latter, a continuous film is formed.
Therapy: general recommendations
A common cause of catarrhal stomatitis in the mouth is poor hygiene. A mild form of the disease provoked by such a factor can be treated at home. Use antiseptic agents, rinsing with decoctions of herbs - and in a week the manifestation will disappear.
However, with a severe course of the disease and serious forms: aphthous, ulcerative, herpetic, you should contact the therapist. Since there is a high risk of complications.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults is to eliminate the cause and symptomatic manifestations. Usually it consists of a whole range of measures to reduce discomfort and prevent the progression and transition of the disease into a chronic relapsing form.
Painkillers
If the soreness of the ulcers prevents the patient from leading a full-fledged lifestyle, eating, the doctor will recommend the use of local anesthetics. These include:
- Anestezin - tablets for the preparation of powder. Stop the pain in the lesion.
- Hexoral tabs - antiseptic lozenges based on benzocaine and chlorhexidine. In addition to the analgesic effect, they have an antimicrobial effect.
- Lidocaine Asept - a means with a local anesthetic. Often included in therapy for aphthous stomatitis and erosive lesions.
- Lidochlor is a combination preparation in the form of a gel. It has antimicrobial and analgesic effects.
- Kalanchoe juice, decoction of calendula, sage, chamomile.
All medicines have a number of side effects and contraindications, therefore they should be used only after agreement with the doctor.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Regardless of the cause of stomatitis in an adult, therapy must necessarily include rinses, ointments, sprays, absorbable lozenges, and antimicrobial tablets:
- Cholisal is a dental gel with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Kamistad is an antiseptic and anesthetic gel, which includes pharmacy chamomile and lidocaine.
- Evkarom, Ingafitol - herbal preparations for rinsing and inhalation containing eucalyptus leaves.
- Stomatidine is an antiseptic with a weak analgesic effect and pronounced antimicrobial.
Drugs aimed at eliminating the pathogen
| Type of stomatitis | What funds are assigned | Medication options |
|---|---|---|
| Candidiasis | Antifungal |
|
| Herpetic | Antiviral |
|
| Allergic | Antihistamines |
|
| Bacterial | Antibiotics |
|
Mucosal healing accelerating agents
- Solcoseryl is a dental paste that stimulates tissue regeneration and improves trophism.
- Katorolin is a solution with antioxidant properties.
- Sea buckthorn or rosehip oil. They have a healing effect.
- Vinylinum (Shostakovsky's balm). Helps to cleanse wounds, epithelization and regeneration. It also reduces inflammation and inhibits the growth of bacteria.
Allergic stomatitis treatment
This disease is not considered as a separate one, since it can begin only against the background of a general allergic reaction and is only one of its manifestations. Treatment of adults comes down to eliminating the allergen and eliminating the signs of stomatitis. For this, antihistamines are used. For example, Suprastin, Tavegil.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
With viral stomatitis, complex therapy begins, which includes taking:
- Anesthetics - Lidocaine Asept, Lidochlor.
- Anti-inflammatory - Holisal, Solcoseryl, rosehip oil.
- Antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin.
- Antiviral - Oxolin, Zovirax, Acyclovir.
- Immunomodulators - Cycloferon, Immunal.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
It can be difficult to cure aphthous stomatitis in adults, since the disease is prone to relapse. Therapy may include the following items:
- Treatment of rashes with a solution of chamomile and boric acid. For its preparation, 2 tbsp. l decoction of pharmacy chamomile combined with 4 g of acid. The resulting mixture is used to rinse the mouth or to apply applications. Instead of these components, you can take others. For example, furacilin tablets or diluted hydrogen peroxide (1 to 1). For local treatment, sea buckthorn or peach oil is also suitable.
- Detoxification can be treated with sodium thiosulfate, which is administered intravenously once a day.
- To increase the protection of affected tissues from microbes, Lysozyme, Pyrogenal or Prodigiosan are used.
- To improve immunity, vitamin C1, B6, riboflavin, folic and nicotinic acid are taken.
- A treatment program may include sedatives and antihistamines.
- With persistent stomatitis, Decaris is prescribed, which helps to prevent relapse.
- Rough, sweet, spicy food is excluded from the composition of the food. And also limited to alcohol and cigarettes.
A good result is given by therapeutic irradiation of aphths with UV rays. Referral to the treatment room may be prescribed by the therapist.
If inflammation occurs on an ongoing basis, an immunological examination should be performed.. Since the causes of frequent aphthous stomatitis in adults are associated with various pathologies of the nervous, endocrine system, as well as with lesions of the digestive system, treatment of a concomitant disease will be required.
Treatment of fungal stomatitis
In adults, this type of stomatitis appears against a background of reduced immunity or after a course of antibiotics. Therefore, the following method is used for treatment:
- Local or oral antifungal drugs are used - Pimafucin, Fluconazole, Clotrimazole.
- The entire affected surface is treated with antifungal agents - Miconazole, Nystatin ointment.
- If the patient has dentures, then mouth rinses with a solution of Lugol or Iodinol are prescribed.
- Diet is adjusted: easily digestible carbohydrates are excluded.
- And treatment is necessarily carried out aimed at increasing immunity.
Since fungal stomatitis in the mouth in adults often appears against the background of internal diseases, it is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist. They will prescribe an appropriate examination, identify the cause of the disease and form the necessary and competent treatment methodology.
Stomatitis Prevention
After recovery, replace the toothbrush.This will help to avoid the secondary infection of the mucosa. If there are carious lesions in the oral cavity, they need to be healed to prevent relapse.
Periodontal pockets are also a kind of depot for pathogenic microflora.If they are present, stomatitis will often have to be treated, since therapy will only lead to a temporary result.
A huge role in preventing outbreaks of any form of stomatitis is played by hygiene and a proper lifestyle. To maintain oral health:
- Wash hands before eating and after a walk.
- Include foods rich in vitamins in your diet.
- Limit the intake of sugary foods.
- Maintain cleanliness in the home.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Refuse alcohol and nicotine.
- Take care of hygiene.
- Visit the dentist at least 1 time per year.
And at the slightest suspicion that stomatitis or any other disease occurs in the oral cavity, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely treatment will help to avoid many serious problems.