Cancer of the tongue: how to recognize the disease at an early stage, types, causes, symptoms, treatment
The epidemiology (prevalence) of tongue cancer is an average of 5 cases per 100 thousand population. Among recorded cases of oral tumors, it accounts for up to 60%. Despite the relatively simple diagnosis of this disease, advanced cases occur - people often do not notice signs or ignore symptoms of cancer of the tongue.
Content
Etiology - causes of cancer of the tongue
The main cause of tumors in the tongue, like any other oncological diseases, is a genetic malfunction in the cells. In this case, these are epithelial cells - the tissue forming the mucous membrane. Several key factors contributing to this process have been identified:
- Exposure to carcinogens. A huge amount of harmful substances is contained in cigarette smoke and in chewing mixtures (nasvay, betel nut). It is smokers and weavers who are most often diagnosed with cancer of this localization, and in men it is detected 3 times more often than in women. Alcohol enhances the effects of carcinogens.
- Occupational hazards. The incidence of oncology of the tongue in people employed in hazardous industries is much higher. Salts of heavy metals (mercury, lead), asbestos, oil products can also be classified as carcinogens in nature.
-
Exposure to viruses. Recent studies have shown a direct link between chronic viral infection and the incidence of cancer. The human papillomavirus, herpes simplex virus and HIV are able to transform the cell genome, turning them into cancer cells. According to statistics, up to 70% of women are carriers of HPV. The mechanism of oncogenic effects of viruses is associated with their ability to suppress antitumor genes.
- Chronic trauma to the oral cavity. They can be associated with improper installation of dentures, improper processing of the filling, or chronic biting of the mucous membrane.
Long-term exposure of these factors to the mucosa is accompanied by damage to the DNA structure of epithelial cells. As a result, papillary hyperplasia (excessive proliferation) develops, which looks like a tightening at the sides, or dysplasia (improper development) of the mucous membrane.
Further exposure to these causes leads to the development of precancerous conditions: leukoplakia, Bowen's disease, hyperkeratosis and papillomas. Subsequently, these conditions are transformed into oncology.
Tongue cancer stages
There are several stages of the disease, each of which has its own distinctive features.
Initial Stage of Tongue Cancer (First)
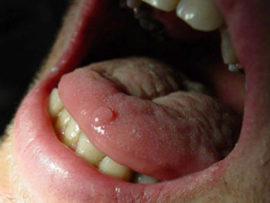
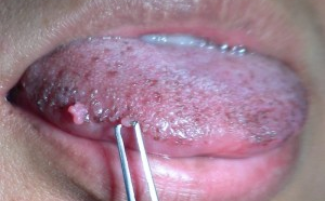
It is characterized by a low-symptom course - practically does not bother patients. It appears whitish spots on the mucosa, the so-called papillary outgrowths. Often they are mistaken for plaque, which is located on the lateral surface of a muscle organ.
On examination, doctors often take these formations for manifestations of other diseases: glossitis or stomatitis. Pain at this stage is absent.
Stage of clinical manifestations (second)
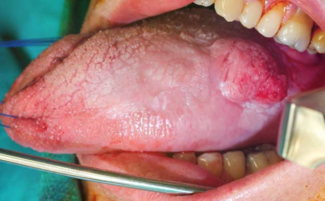
As the disease progresses, “plaque” gradually turns into a seal in the tongue, which, if untreated, transforms into a tumor in the tongue. At this stage, the pain syndrome appears, the pain is spilled or local in nature, very often radiating to nearby organs (in the neck, temple, ears).
Patients at this stage often complain of the appearance of halitosis, which is caused by infection and suppuration of the tumor. Difficulty swallowing, articulation disorder, swelling and numbness of part of the tongue join the clinical picture. Perhaps metastasis to the surrounding tissue and nearby lymph nodes - submandibular, cervical.
Degree Completed (Third)
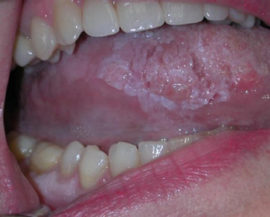
You can bring the disease to this stage if you completely ignore the symptoms of the initial and second stages of cancer of the tongue. It is manifested by aggressive invasive (penetrating the thickness of the organ and surrounding tissue) growth, accompanied by tissue decay.
Terminal Stage (fourth)
In this phase, distant metastases occur - in the bone, liver, lungs. Treatment of advanced cancer of the tongue is unsuccessful and the prognosis is very questionable. Patients who start the disease before the terminal stage rarely live more than a year. Only palliative treatment is used - the fight against pain and cancer intoxication.
Types of Tongue Cancer
The disease is classified by localization - the location of the neoplasm in the language:
- Cancer of the body of the tongue - more than 2/3 of all cases of this pathology.
- Tongue root cancer - 1/5 of all cases.
- Cancer of the lower surface - all remaining cases (about 10%).
According to the principle of tumor growth, the following clinical forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Exophytic - a tumor grows mainly in the oral cavity. Sometimes this form of the disease is called papillary.
- Endophytic (infiltrative) - growth is directed into the thickness of the organ. Endophytic growth is a characteristic symptom of root cancer of the tongue. Very often, this form of the disease leads to swelling and difficulty in the movements of the tongue or to its complete immobility.
Tongue cancer refers to squamous in 95% of cases, and only in 5% it is another histological form: carcinoma or basal cell cancer.
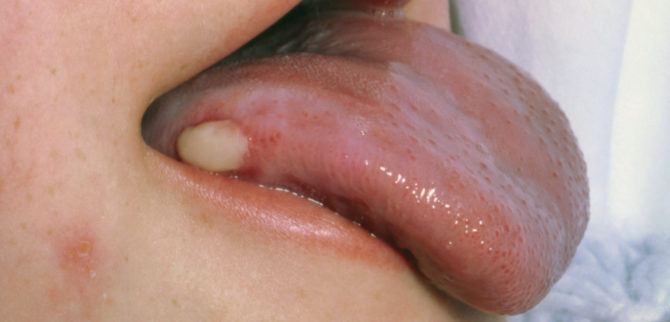
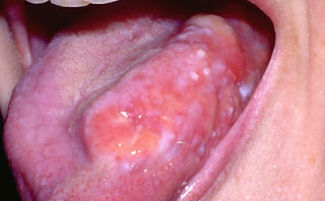
By the appearance of the tumor, papillary and ulcerative forms are distinguished. Papillary cancer is the most common type of ailment. It looks like a dense outgrowth, slightly rising above the mucous membrane and covered with "warts".
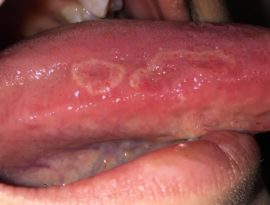
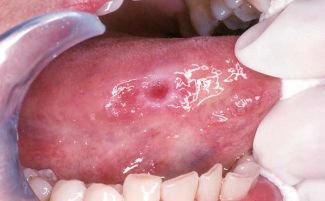
With an ulcer form of the disease, an ulceration appears on the side of the tongue on the side of the tongue or on the back, surrounded by a roller. A characteristic property of an ulcer at an early stage is its complete painlessness. As the ulcer grows, pain appears, bleeding is noted. The attachment of the inflammatory component masks cancer and makes diagnosis difficult.
Tongue cancer photo
Diagnostics
You can only suspect the first symptoms of oncology of this localization on your own. Strange as it may seem, of the doctors most often faced with this pathology are not oncologists, but dentists. This is due to the specifics of their activity - in the course of performing their professional actions, they are the first to notice signs of an early stage of cancer in the form of a seal on the side of the tongue or at the root.
The similarity of the first symptoms of tongue cancer with other diseases of the oral cavity leads to its late diagnosis - most often in the second stage, when a malignant neoplasm of the mucous membrane looks like an ulcer or a pronounced tumor.
Specific diagnostics consists of the following examinations:
- Examination of the smear of the fingerprint in order to detect signs of squamous cell carcinoma in it.
- Tumor biopsy followed by histological examination under a microscope.
- Ultrasound of the tongue and soft tissues of the lower jaw, as well as ultrasound of the neck in order to search for metastases.
- X-ray of the skull or computed tomography - with suspected tumor invasion into the bone.
In order to exclude distant metastases, it is necessary to do an X-ray of the lungs, CT (MRI) of the brain and ultrasound of the liver.
Despite the fact that in women squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue is less common, the frequency of detection at an early stage is much higher in them. This is due to a more reverent attitude of women to the state of the oral cavity.
Tongue Cancer Treatment Methods
Regardless of the cause of cancer of the tongue, combination therapy is used to treat it, including the following methods:
- Surgery. The operation is aimed at radical removal of the malignant tumor: either partial resection (excision) of the tongue or its complete removal (glossectomy) is performed. In advanced cases, when the tumor has grown in the surrounding tissues, they are resected down to the bones of the lower jaw.
- Radiation therapy. Remote therapy is distinguished when the tumor is irradiated at a distance by X-rays, and contact (brachytherapy), when the radiation source (radioactive isotopes) are located in the thickness of the organ. Radiotherapy is carried out both before and after surgery. How many sessions are needed, the doctor determines.
- Polychemotherapy. It is used in advanced cases in the presence of distant metastases, when other methods cannot be used, or the effect of them is insufficient. Patients are treated with cisplatin, methotrexate and other drugs.
Surgery in the late stages of the disease is often crippling - in some cases, it is necessary to remove almost the entire lower jaw. After surgery, patients live with some limitations. In order to create a satisfactory quality of life, they undergo reconstructive medical operations.
Prevention methods, prognosis of tongue cancer
You can reduce the likelihood of a disease by giving up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol and chewing tobacco. In the presence of a tooth pathology that contributes to chronic mucosal injury, the oral cavity is sanitized: the prostheses are reinstalled, fillings are treated, and the bite is corrected.
Compliance with basic oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of cancer. Regarding the prognosis, regular preventive check-ups at the dentist are of importance, during which the first signs of cancer can be noticed, which allows you to promptly refer a person to an oncologist.
With the radical combined treatment of cancer of the tongue in the early stages, the five-year survival rate approaches 90%, in advanced cases it decreases to 60%. If treatment is started at the metastasis stage, five-year survival is less than 35%, even in Moscow.