Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity in humans: causes, list of names with photos and descriptions
The list of dental diseases is huge., and all of them are characterized by specific symptoms and arise for certain reasons. Despite the fact that you can find out the exact diagnosis only by visiting the clinic of dentistry, each person is familiar with the signs of the most common dental diseases. Such information will help to recognize the disease at an early stage and consult a doctor in time.
Content
Causes of the development of diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
Dental diseases can occur due to the harmful effects of one factor or a combination of several. Most dental diseases develop for the following reasons:
- Violation of the rules of hygiene. It is not only a complete disregard for hygiene, but also irregular or improper brushing. The accumulation and hardening of soft plaque provides rapid development in the oral cavity of bacteria, the vital products of which destroy even the hardest tissue in the body - enamel.
- Infectious diseases. Pathogens can penetrate the dental tissue from the oral cavity, in which inflammation proceeds, through cracks in the crowns. In addition, bacteria can be introduced into them with a blood stream from any diseased infected organ.
- Inadequate supply of dental tissue with nutrients with improper nutrition.
- Excessive intake of certain elements, for example, fluoride.
- Taking medication.
- Metabolic disorder or a shift in hormonal levels.
- Low immunity.
- Hereditary predisposition to dental diseases and congenital malformations.
- The effects of radiation and chemicals in contaminated living areas or in hazardous industries.
- Injuries.
The main reasons for the development of dental diseases in children are the use of pacifiers and a bottle with a pacifier, the habit of sucking a finger and pulling dirty objects in your mouth.
Dental Diseases: List and Symptoms
Most dental diseases, photos and descriptions of which will be given below, have an infectious nature. Pathologies from this list are highly interconnected and often develop sequentially if treatment is not started in time.
| Diagnosis | The essence of the disease |
|---|---|
|
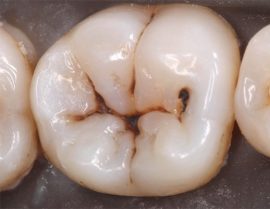
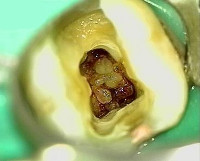
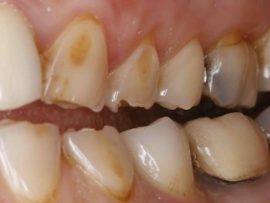
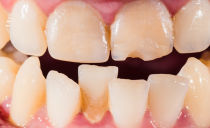
Caries |
It manifests itself as small faded spots on the enamel, which darken over time and are destroyed. Most often provoked by poor hygiene, leading to an accumulation of plaque in the oral cavity, poor nutrition, and sometimes injuries. The superficial stages of the disease are accompanied by hyperesthesia - increased sensitivity. Deep caries is characterized by the appearance of holes in the hard tissues of the tooth, causes more acute pain and spoils the appearance of the dentition. Bottle caries in children is associated with prolonged use of pacifiers and nipples, as well as with the delay of food debris in the mouth after nightly feeding. |
|
Pulpitis |
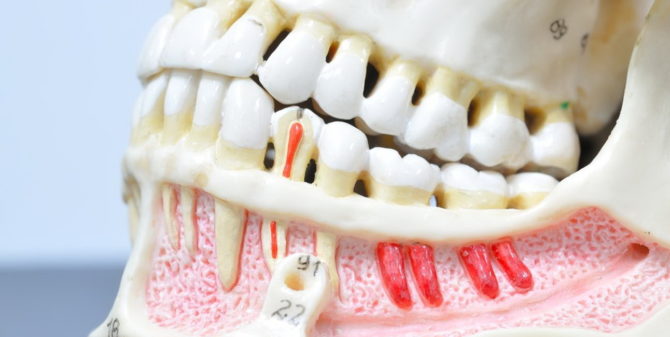
It can develop as a result of untreated deep caries, when the damage reaches the dentin, and then to the pulp chamber containing the neurovascular bundle. Sometimes the pulp becomes inflamed due to the penetration of the infection from the side of the root, where it can be carried with the flow of blood from other organs. Pulpitis is accompanied by severe pain, sometimes with fever and pus. |
|
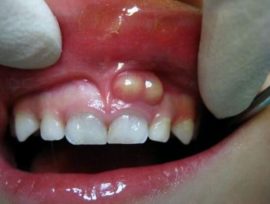
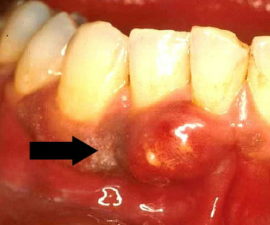
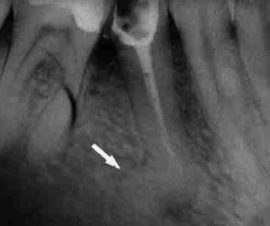
Tooth cyst |
A cyst is an inflammatory process characterized by proliferation of tissues near the root. It develops as a complication of inflammatory diseases - pulpitis, periodontitis. Accompanied by pain and swelling of the gums. |
Periodontal disease: names and description
Dentists call periodontal tissues of the jaw that surround the tooth root and fix it in the alveolus. A list of periodontal diseases with names and photos is given in the table:
|
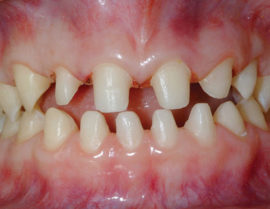
Periodontitis |
Inflammation of the periodontium - the structure that holds the root in the jaw alveolus. It provokes purulent inflammation, fever, tooth mobility. |
|
Periodontitis |
Periodontal inflammation, manifested by bleeding and accumulation of pus in the gingival pockets. |
|
Periodontal disease |
The gradual loss of a strong connection between the root and the jaw due to atrophy of the dental process of bone tissue. Pus accumulates in the gingival pockets, and the neck is gradually exposed, until the tooth is completely lost. |
Anatomical diseases of the teeth
Such diseases can occur at any time, but some of them are laid back in the period of embryonic development. They are associated with improper formation of the dentofacial apparatus or a change in its anatomical structure in the future. Below are the most famous abnormal dental diseases with photos and descriptions.
| Diagnosis | The essence of the disease |
|---|---|
|
Adentia |
An acquired or congenital defect in which a person does not have all or some of the teeth. |
|
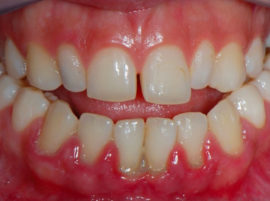
Anomalies of the dentition and the teeth themselves |
Incorrectly formed dentition:
|
|
Microdentia |
Too small tooth size. |
|
Macrodentia |
Atypically large tooth. |
|
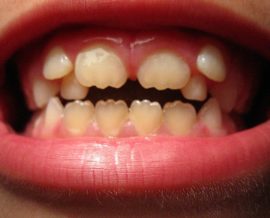
Imperfect amelogenesis, dentinogenesis |
Improper tissue formation - enamel or dentin. It is shown by darkening of enamel, fragility, increased sensitivity. |
|
Hypercementosis |
The growth of the cement layer with thickening of the roots. |
|
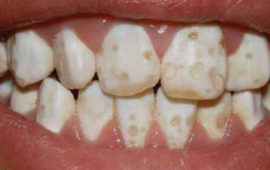
Enamel Hypoplasia |
Underdevelopment of enamel, manifested by the appearance of stains or a change in the shape of the entire tooth: Getchinson's teeth, Pfluger. |
Other diseases: names and essence
The list of dental diseases associated with the action of chemicals, impaired cell division or jaw injuries is shown in the table:
| Diagnosis | The essence of pathology |
|---|---|
|
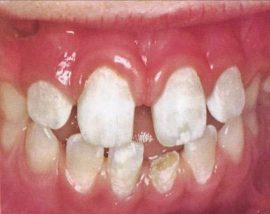
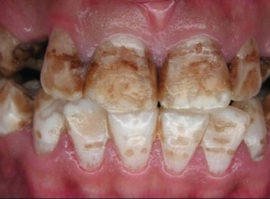
Tetracycline teeth |
Violation of the structure and dark color of the enamel in children whose mothers took antibiotics during pregnancy. |
|
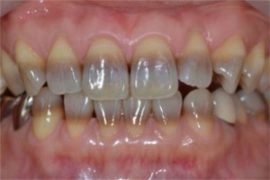
Fluorosis |
Violation of the structure and color of enamel, dentin in people whose body gets too much fluoride. |
|
Dentikli |
The appearance of solid mineralized particles in the pulp. The disease is asymptomatic or with the appearance of pain due to compression of the pulp. |
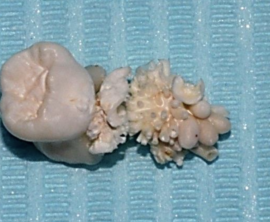
|
Odontoma |
Benign growth of dental tissues. The tumor can become inflamed, bleed. |
|
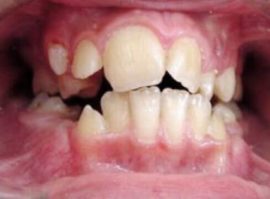
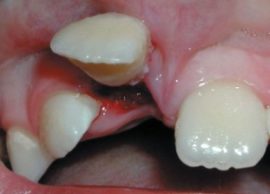
Tooth dislocation |
Traumatic violation of the normal position of the tooth. |
|
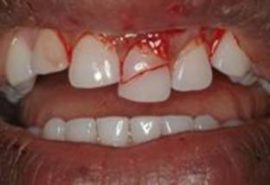
Fracture of the tooth and its root |
A traumatic violation of the integrity of the tooth, which is accompanied by pain and can lead to inflammation due to infection. |
|
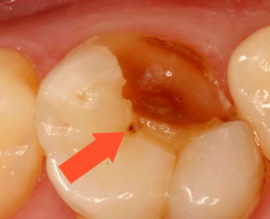
Erosion of teeth |
With erosion, enamel destruction that is not associated with caries occurs. It can develop under the influence of chemicals, manifested by the appearance of spots that lose the gloss characteristic of enamel, and then darken and become hypersensitive. |
Diagnostic measures
Any disease from the above lists should be diagnosed and cured on time. A person should periodically examine the dentition, since the appearance of tangible symptoms - pain, fever, swelling, putrid odor from the mouth - is characteristic of the late stages of diseases, which make it difficult to treat the disease.
The first stages of any dental disease can be asymptomatic or show minor visible defects.
If signs of dental disease have already manifested, you need to contact dentistry. After examining the dentition, the dentist can prescribe additional examinations to clarify the diagnosis:
- X-ray
- MRI
- Electroodontodiagnosis.
If the doctor suspects the presence of internal diseases that could provoke dental diseases, he will refer the patient to the appropriate specialist: pediatrician or therapist, endocrinologist. In this case, the list of examinations can be replenished with blood tests, urine tests and other studies.
Dental treatment
The treatment of dental diseases always takes place within the walls of a dental clinic, at home, only auxiliary procedures can be carried out - rinses, applications, taking tablets - which was prescribed by the doctor. Different pathologies require an individual approach to treatment, but most often such procedures are carried out:
- Filling with preliminary cleansing of destroyed tissue.
- Depulpation - removal of the pulp during its inflammation.
- Installation of prostheses and micro prostheses to eliminate visible defects and strengthen crowns.
- Installation of structures to correct the dentition: braces, orthodontic cap.
- Surgical treatment - removal of the damaged part of the crown, root, tumor, or the entire diseased tooth as a whole. Usually, removal is started if the dentist is unable to cure the disease, or when it is too dangerous for the patient’s health.
Dental problems are not only unpleasant, but also dangerous to health. The result of prolonged development of the disease can be a deterioration in the general condition of the patient, loss of teeth, or the spread of infection into the internal organs. It is impossible to prevent dangerous consequences with improvised home remedies; you need to seek the help of qualified dentists.