Enamel hypoplasia: causes, symptoms, forms, diagnosis and treatment methods
Enamel hypoplasia is the underdevelopment of the surface layer of temporary or permanent teeth. The disease is easy to recognize because it seriously impairs the appearance of the dentition. But much more important is that the disease is incurable and can lead to serious complications.
Content
- The main symptoms and photos
- Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in newborns
- Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children and adults
- Types of tooth enamel hypoplasia
- Forms of tooth enamel hypoplasia
- Consequences of the disease
- Differential diagnosis of tooth enamel hypoplasia
- Treatment of tooth enamel hypoplasia
- Prevention
The main symptoms and photos
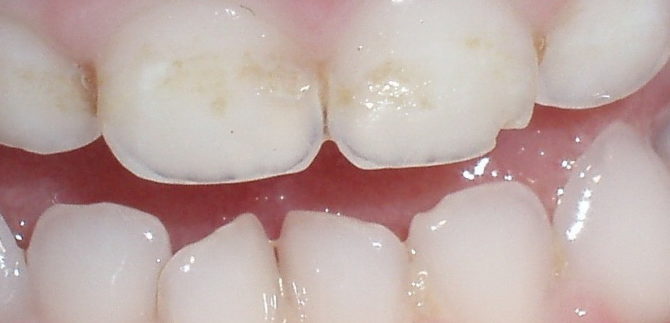
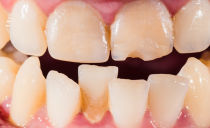
Such enamel damage can be recognized by the appearance of the teeth. Sometimes it’s not even necessary to contact a specialist. Most a characteristic clinical manifestation of the pathology is a change in the color of tooth enamel, the appearance of spots on its surface.
Sometimes changes also affect the shape of the teeth. Grooves or simply small indentations may appear on the protective layer. The remaining symptoms depend on the form of hypoplasia.
Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in newborns
The disease can affect the teeth before they even erupt. This is due to maternal health problems during pregnancy. The cause of the development of hypoplasia of the rudiments of the milk teeth of a child in the womb can be:
- severe toxicosis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- rubella;
- incompatibility of the blood of the mother and baby by the Rh factor.
Certain forms of hypoplasia occur for reasons that are not related to the gestation period:
- prematurity;
- congenital allergies;
- birth injuries;
- asphyxiation during childbirth.
Usually those dental units that developed during the influence of a negative factor suffer from the disease. Therefore, a specialist can determine at what week of gestation a hypoplasia of enamel of milk teeth appeared in a child.
Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children and adults
The disease affects milk teeth, but the first signs of the disease can be noticed even when the bite changes. Sometimes the symptoms of the disease can be detected only on molars in adulthood. Usually this means that hypoplasia affected the tooth enamel after birth. Most often, the development of the disease occurs in the first months of life. At this age, many factors can affect the body:
- poor metabolism;
- disturbances in the endocrine system;
- problems with the stomach and intestines;
- insufficient bone mineralization;
- infectious diseases and their improper treatment;
- lack of protein in the diet;
- congenital syphilis.
If hypoplasia of tooth enamel appeared in a child older than one year, then the reasons for its development could be as follows:
- violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism;
- excess fluoride in water;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- severe diathesis;
- severe allergies;
- taking certain medications;
- tooth injuries still in the process of their growth;
- heredity.
Many of these factors result from poor child nutrition. Therefore, parents who carefully monitor the diet of their baby are less likely to encounter enamel diseases.
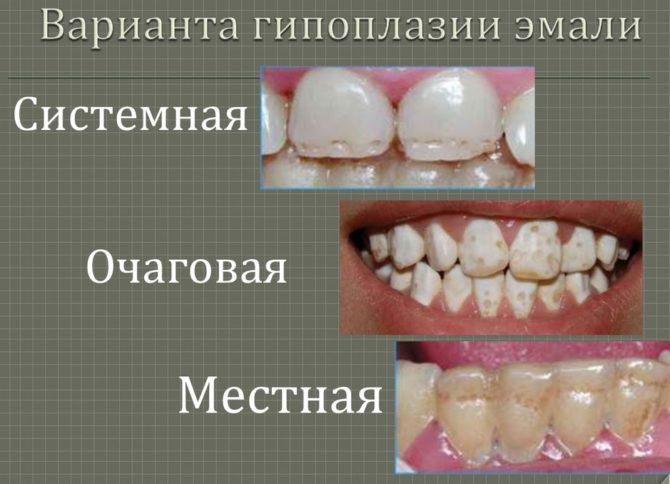
Types of tooth enamel hypoplasia
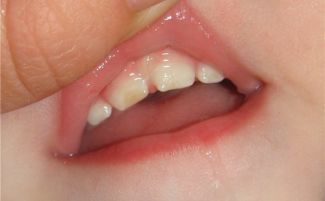
There are two main types of disease: local and systemic. Differentiating them is very simple. Local enamel hypoplasia differs in the defeat of only a few teeth, most often premolars. It manifests itself in the case when negative factors affect a child already in a fairly adult age. Such a disease cannot appear during fetal development. Therefore, a disease found on permanent teeth, most often refers to the local type.
Most often, the local form of the disease manifests itself in the form of pink spots. The shape of the teeth also suffers: recesses and grooves appear on their surface. All this negatively affects the overall sensitivity of the dentition and can lead to a number of negative consequences.
Systemic lesion differs in that it spreads immediately to all the teeth of the child. It is the most common type of disease, since it is formed either at a very young age, or with the development of the fetus. At this time, the enamel coating is more susceptible to negative effects.
Forms of tooth enamel hypoplasia
Systemic hypoplasia is divided into three forms, each of which differs in a number of symptoms:
- superficial lesion;
- underdevelopment of moderate enamel;
- severe systemic hypoplasia of enamel (aplasia).
Each degree of pathology is characterized by certain symptoms. The superficial form of the disease manifests itself in the form of a discoloration of the upper tissues of the tooth. Small, sometimes quite invisible spots of yellow and white shades appear on it. They have a clear boundary that will not change all their lives. The affected areas are formed not only on the visible part of the tooth, but also behind.
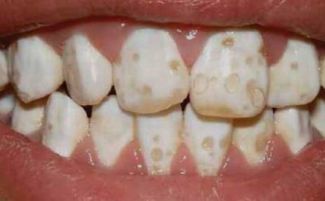
Moderate hypoplasia is sometimes called spotted, and this is a more serious violation of the structure of enamel. With this pathology, the tooth relief noticeably changes. On the entire surface of the enamel, small dots appear in the form of dots. Their color can be very dark, which is why the spotted form of enamel hypoplasia is often confused with caries.
Less often, small seals appear on the teeth, called rollers. The middle stage of the development of the disease can also be furrowed, then recesses appear in the form of clear stripes on the enamel. It seems that the teeth in this place have been erased.
Aplasia is an extremely serious stage of the disease. With it, areas appear on the teeth where the enamel is completely absent. The degree of sensitivity is seriously increased. A person experiences discomfort and pain under the influence of almost every stimulus.
Aplasia occurs only in the absence of treatment. In this case, the patient may encounter other complications.
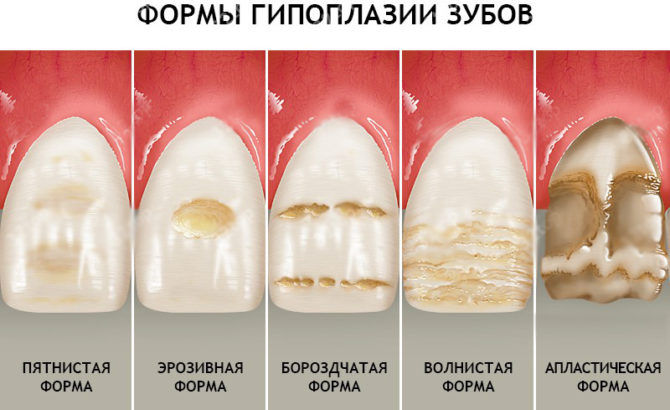
According to the shape of spots on enamel, hypoplasia is classified into the following types:
- spotty;
- erosive;
- furrowed;
- wavy;
- aplastic.
Consequences of the disease
The first stage of milk tooth hypoplasia seems completely harmless, but if the disease is not treated, it leads to terrifying consequences:
- exposure of dentin - the next layer of tooth after enamel;
- serious carious lesions;
- malocclusion;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract due to malnutrition.
All this sounds intimidating, but often they forget to include the main consequence on this list. It is about constraint and complexes. Smile for a photo or laugh in the company becomes a real test. Problems with self-esteem in childhood will also manifest themselves in adulthood, therefore, diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be taken very seriously.
Differential diagnosis of tooth enamel hypoplasia
The main method for detecting enamel hypoplasia is differential diagnosis. It lies in the fact that the specialist, at the sight of the first manifestations of tooth damage, first eliminates all other possible causes. This method is effective due to the fact that the early symptoms of the disease are similar to signs of other diseases of the oral cavity. Similar spots can occur during caries or due to the use of certain medications.
To diagnose hypoplasia directly, a specialist needs to do the following:
- Conduct a complete and thorough examination of the oral cavity.
- Identify at what exact age the first symptoms appeared.
- Read all the information about the course of pregnancy.
- Explore the lifestyle of the child and parents.
All this requires effort and time. Therefore, it is easier to conduct a differential diagnosis and first rule out other diseases with similar symptoms.
Treatment of tooth enamel hypoplasia
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia is simply not possible. You can not take any pills or carry out a procedure that would relieve this disease. Instead, attention is paid to preventing the further development of the disease.
If during differential diagnosis hypoplasia was detected at the initial stage of development, the specialist gives the patient recommendations for dental care. So that the enamel does not deteriorate further, it is very important to clean it of plaque in time, regularly strengthen and do professional cleanings. For this, cabinet procedures are used, as well as special pastes and gels.
If the enamel has already become spotty, aesthetic dentistry is included in the therapeutic course. In the presence of recesses, composite compositions are used, with which the specialist levels the enamel surface. The same material is used in the presence of rollers. Only at first the dentist removes them, and composites are used in order to restore the protective function of enamel.
With aplasia, more serious measures are required. Without a protective layer, a tooth cannot perform its functions, therefore, external correction will not solve the problem - crowns are placed on such teeth. Since after the prosthetics the same dental procedure will have to be carried out all his life, this method is resorted to only in the most advanced cases.
Prevention
Since with children’s tooth enamel hypoplasia full treatment and recovery is not possible, more attention should be paid to the prevention of the disease. It can be divided into two stages: during pregnancy and after birth.
During the bearing of the baby, the mother must observe the following rules:
- eat right;
- be careful when taking any medications (this can only be done after consulting a specialist);
- always to the end to undergo treatment of any diseases that occurred during pregnancy.
All these measures are necessary to prevent systemic enamel hypoplasia. To prevent local damage, the following is required:
- proper balanced nutrition of the child;
- accustoming to oral hygiene from a very young age;
- regular visits to the dentist from 2 years;
- avoidance of dental injuries and timely treatment when they occur;
- complete treatment of any diseases, especially acute forms of chronic ailments.
In 40% of cases, completely healthy people suffer from hypoplasia. Therefore, you should not think that in the absence of risk factors you will not come across a similar diagnosis. Dental health should always be treated with special attention.