Signs, symptoms and treatment of pulpitis of the tooth
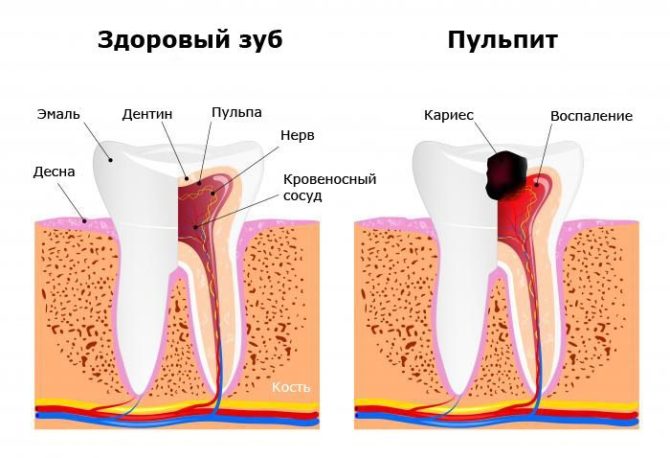
A pulp is called the inside of a tooth that contains a neurovascular bundle. Normally, it is protected from the external environment by hard dental tissues. If enamel and dentin are affected by infection and caries or injured, the pulp chamber loses its integrity and its contents become inflamed. This is how tooth pulpitis develops, about the symptoms and treatment of which everyone needs to know, because this disease is very common.
Content
Causes of tooth pulpitis
A pulp of a tooth can become inflamed under various circumstances. Most often, this is a consequence of the progression of caries, which penetrates deep into the tooth. But there may be other reasons:
- Fractures and chipped teeth with damage to pulp tissue.
- Careless provision of dental services with tooth decay or incomplete removal of dead tissue.
- A complication of other dental diseases in which the infection does not spread from the side of the crown, but from the side of the root, which provokes the development of retrograde pulpitis.
- A rare non-infectious form of pulpitis - calculus - occurs in older people due to the accumulation of deposits in the root canals, as a result of which the pulp is compressed.
First, a protective immune response, inflammation, develops in infected soft tissues. More blood is added to the infected tooth so that the immune cells contained in it can destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The inflammatory process is expressed by pain and an increase in local temperature.
Further progression of the disease leads to tissue death and decay, therefore, with the advanced stages of the disease, it is already impossible to cure pulp inflammation - it must be completely or partially removed from the tooth.
Symptoms of acute tooth pulpitis
Acute pulpitis is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues in the closed tooth cavity and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Acute severe pain that occurs at any time of the day, especially when exposed to irritants - food, drinks. After eliminating the irritant, the discomfort does not subside for a long time - this symptom distinguishes pulpitis from caries. When tapping the tooth, the patient may not feel pain intensification - this distinguishes this disease from periodontitis.
- Headaches and pain may occur in the ear near a diseased tooth.
- Inflammation can cause swelling of the lymph nodes located nearby.
- A violent inflammatory process can cause an increase not only in local, but also in general body temperature. Pulpitis can reach temperatures up to 38 ° C.
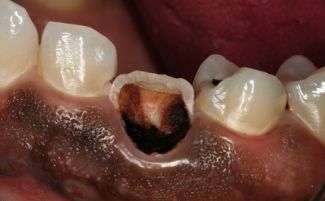
- Due to the destruction of the inside of the tooth, a dark gray spot is visible under the enamel.
Forms of acute pulpitis of the tooth and their manifestations
The initial stage of acute pulpitis, which occurs in the absence of suppuration, is called serous. If acute pulpitis passes into a purulent form, a person notices a peculiarity in the manifestation of pain: it intensifies when exposed to heat due to activation of local blood circulation and calms down under the influence of cold. Purulent-inflammatory phenomena can be accompanied by a halitosis.
Acute pulpitis is divided into focal and diffuse.The difference between these two varieties of the disease can be determined by the nature of the pain: with focal pulpitis, the patient can feel exactly which tooth is sick, with diffuse pulpitis - painful sensations spread along the jaw along the trigeminal nerve.
Signs of chronic tooth pulpitis
The chronic form of pulpitis is most often diagnosed in patients as an acute complication. It happens that acute pulpitis does not precede chronic, then the disease can develop slowly and asymptomatically.
Chronic pulpitis develops in three successively changing forms, which differ in the features of the processes occurring inside the pulp chamber:
| Form of chronic pulpitis | Features of the flow, how the tooth hurts with this form of pulpitis |
|---|---|
| Fibrous | The pulp chamber may be closed or have a hole. It is asymptomatic or accompanied by aching toothache from eating hot or cold food. |
| Hypertrophic | It often develops in childhood. The tooth hurts due to the filling of the inner chamber with tissue, which is popularly called wild meat. The tissue is irritated when chewing food. |
| Gangrenous | If the pulp chamber is closed, then the tooth hurts badly, the temperature may rise. If the cavity is open, symptoms may be mild. The process of necrosis of inflamed tissues can be expressed by an unpleasant putrefactive odor from the mouth. |
Signs of pulpitis under the seal
If the patient has visited dentistry for the treatment of caries, some time after filling he may feel discomfort. This happens if the infection gets under the filling material and destroys the tooth, which happens when the enamel and dentin affected by caries are not completely removed.
Such pulpitis can be recognized by the same symptoms that are characteristic of an acute or chronic form of the disease - depending on which way its development goes.
With pulpitis, the enamel surrounding the seal may take on a characteristic gray hue.
Signs of complications
If pulpitis was treated incorrectly or not treated at all, it provokes various complications. Such diseases can be dangerous not only for health but also for life, so you need to be able to recognize their symptoms in time:
| Pulpitis Complications | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Periodontitis | Strong suppuration, which is accompanied by swelling and the appearance of fistulas. |
| Sinusitis | Pain and pressure in the maxillary sinuses, discharge from the nose. |
| Abscess | The inflammatory process in the gums, in which the temperature rises, general intoxication develops. |
| Phlegmon | Widespread purulent-inflammatory process on the jaw and other parts of the face. |
| Sepsis | General severe intoxication of the body with a significant deterioration in the patient's condition. |
How to identify pulpitis
At home, the patient cannot accurately determine the diagnosis. Having identified symptoms similar to the manifestations of pulpitis, you need to go to dentistry, where not only the correct diagnosis will be made, but also effective medical care will be provided.
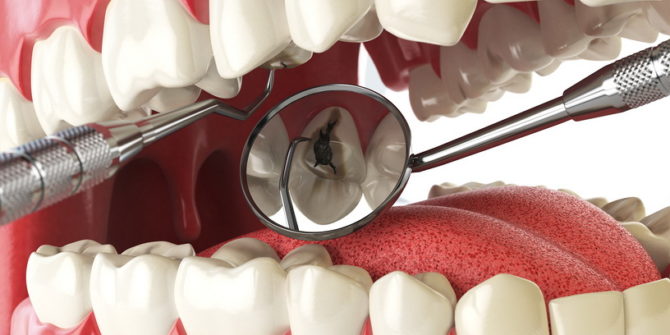
When a patient visits dentistry, the doctor can diagnose his pulpitis by examining with a mirror and probing the tooth with tools. Thus, the state of the tooth is determined: does it have holes in the pulp chamber, can it bleed, and does the jaw hold firmly in the alveolus.
To clarify the diagnosis, you may need an x-ray and EDI, which allows you to assess the viability of a nerve in a diseased tooth.
Without additional hardware methods, it is impossible for even experienced dentists to determine some forms of pulpitis. Difficulties can arise if the disease is provoked not by caries, but by inflammation of the root apex - then the tooth looks healthy outwardly.It can be difficult to detect a diseased tooth when diffuse pulpitis causes pain that extends to the entire dentition.
Tooth pulpitis treatment
The method of treating pulpitis depends on the degree of damage; effective care is possible only in dentistry. If you experience symptoms of tooth pulpitis, you must first make an appointment with the doctor, and not self-medicate. If the tooth hurts badly, you should ask your doctor what painkillers you can take by calling him. Self-select analgesics, and even more antibiotics, is very dangerous for health.
Pulpitis treatment in dentistry can be carried out in several ways:
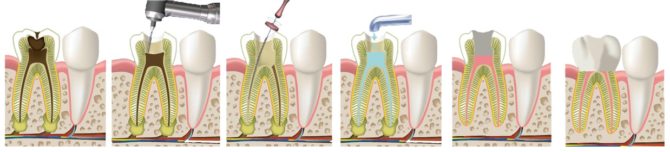
- Conservative or biological method. It is used only for the treatment of young patients in the initial stages of tooth pulp inflammation. It consists in applying a special medicinal disinfectant to a living pulp. After eliminating inflammation, a seal is placed.
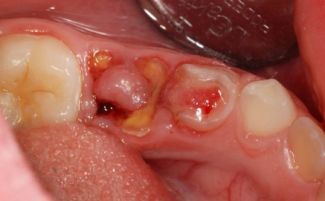
- Surgical methods. They are used for various degrees of tooth damage. The pulp can be removed partially (by amputation method) or completely (by extirpation method). Nerve removal is performed on the day of the visit under the influence of anesthesia (vital method) or after a certain time after nerve sacrifice (devital method). The hole in the tooth after the intervention is closed with filling material.
The advanced stages of pulpitis or complications that threaten the health of the patient can be an indication for the removal of the affected tooth. If inflammation of the tooth pulp has entailed negative consequences, a longer and more complex treatment is needed to prevent or eliminate the general infection of the body.
The appearance of a carious cavity in a tooth and an increase in its sensitivity can be harbingers of pulpitis. Therefore, the state of the oral cavity, healthy and filled teeth should be carefully monitored. The initial stages of the disease are treated faster and with less discomfort than advanced purulent or gangrenous pulpitis, which can cause general intoxication of the body.