Inflammation of the root of the tooth and dental canals: signs, symptoms and treatment
Severe toothache for no apparent reason, a sharp increase in the sensitivity of enamel and a deterioration in well-being indicate the onset of the inflammatory process in the tooth root. With inflammation of the root of the tooth, surgical and drug treatment in dentistry is necessary. It is impossible to cope with the inflammatory process at home, unprofessional independent actions will only aggravate the condition. As a result, time will be lost, and the pathology will become chronic.
Content
Symptoms of tooth root inflammation
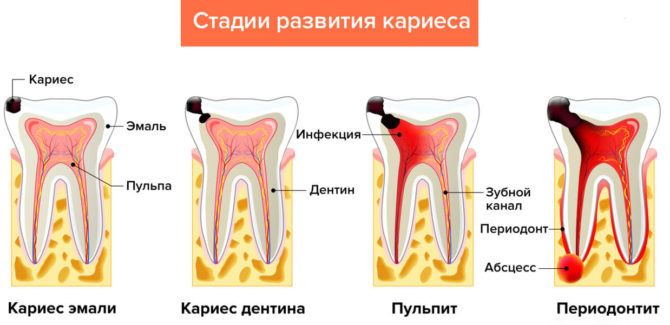
Inflammation of the tooth root or periodontitis is acute and chronic. In the early stages of the disease, the patient suffers from bouts of acute pain of a spasmodic nature that occur during eating and when touching an inflamed area. At this stage of inflammation, changes in the root of the tooth are not visible on the x-ray.
With timely treatment of periodontitis, the risk of developing an abscess and the spread of inflammation to the bone tissue is minimal. If therapy is not started after the first symptoms of the disease are manifested, the inflammatory process will spread from the pulp and dental canals to nearby bone tissue.
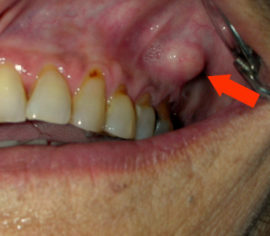
As inflammation in the tooth root worsens, suppuration begins in the soft tissues, accompanied by severe swelling of the gums in the affected area, which is discernible even from the outside of the cheek. Purulent cysts develop at the root. The pain syndrome intensifies, which becomes difficult to remove even with the help of strong painkillers. The general condition of the patient worsens: the temperature rises, weakness occurs, appetite disappears, sleep worsens, performance decreases.
If untreated, the symptoms of periodontitis gradually subside. As pain decreases, the patient mistakenly believes that the disease has receded. But in fact, the subsidence of symptoms indicates that the acute form of the disease becomes chronic, which poses a great danger to health. For some time, the pathology can be asymptomatic, at times exacerbating and subsiding on its own.
In chronic periodontitis, the pathogenic effect on the dental periodontium progresses, destroying bone tissue. Each subsequent exacerbation is more difficult to tolerate, cysts, fistulas, abscesses and other purulent formations in the root zone join the standard symptoms. The patient feels a pronounced taste and smell of pus in his mouth. You can recognize chronic inflammation of the tooth root by the following signs:
- Lack of pain at rest and discomfort when pressing on the tooth.
- Change in color and structure of periodontal tissue adjacent to the root.
- The presence of persistent halitosis.
The chronic form of periodontitis is treated with strong antibiotics. If necessary, the affected areas of the tooth tissue and bone are removed.
If periodontitis is not treated, exacerbations will be repeated, and the affected area will extend to the roots of neighboring molars. The tooth mobility will increase, which will ultimately lead to the need to remove it and increase the risk of removal of adjacent dental units.
Causes of tooth root inflammation
The root cause of tooth root inflammation is the pathogenic microflora that has penetrated the periodontium. The penetration and spread of bacteria deep into the tooth can lead to:
- Running infectious diseases of the teeth and gums: pulpitis, periodontitis, caries. Under the influence of microorganisms, enamel and dentin are destroyed, and bacteria penetrate deep into the pulp, canals, and periodontium.
- Poor dental treatment. Failure to comply with the rules for processing canals, the installation technique of fillings leads to the multiplication of pathogens inside the tooth and their entry into the periapical region.
- Violation of the operating life of dentures and orthodontic structures. A worn design can become loose and dislodged, as a result of which microbes can enter the pulp cavity.
The following injuries can lead to an inflammatory process in the dental root:
- Incorrect distribution of filling material, resulting in an uneven distribution of chewing load on periodontal tissues.
- Cracking of the root during dental procedures.
- A tear of the neurovascular bundle, due to which tooth mobility arose.
- Rupture of the connecting fibers holding the tooth in the alveolus.
- Dislocations, fractures, cracks in crowns and roots, as well as mechanical injuries of the oral cavity associated with sports and professional activities, accidents.
Characteristic signs of inflammation in different areas of the tooth
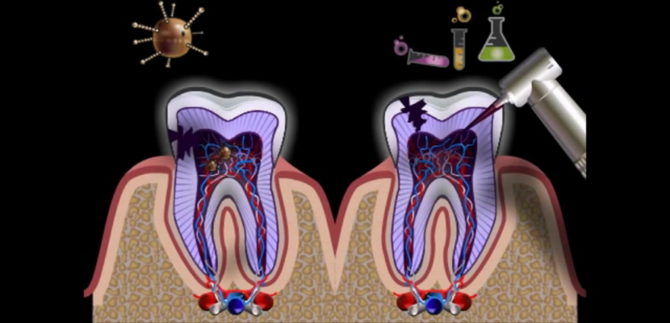
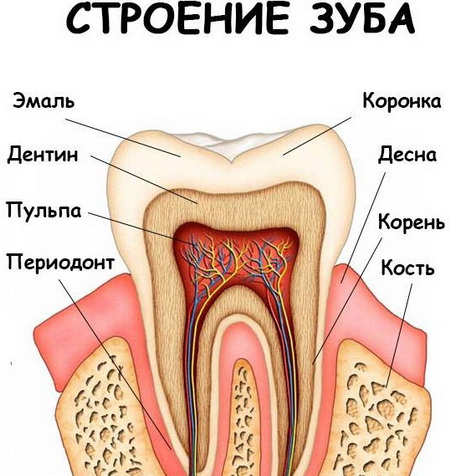
The teeth have a complex structure. Soft bones are hidden under hard bone tissue - pulp. The pulp contains nerve endings, lymphatic and blood vessels. Nutrients enter the pulp through canals passing through the roots of the tooth. Inflammation can begin in the pulp or in the canals, and in the absence of treatment, inflammatory and necrotic processes spread to the bone tissue.
Inflammation of the canal and pulp of the tooth
Under the influence of adverse factors, the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the tooth canals and pulp becomes possible, which provokes inflammation, causing severe toothache and the development of purulent formations at the base of the tooth. Root canal treatment is a complex operation requiring jewelry accuracy from the dentist.
Causes of dental canal inflammation:
- Neglected caries. The most serious complication of caries is the penetration of infection through enamel and dentin into the pulp. As a result, there is an infection of the vessels located in the channels.
- Running periodontal disease. Inflammation of the gums opens the way to the dental canals, as a result of which they become inflamed.
- Dentist error. Poor and untimely filling of the channels entails secondary inflammation of the tissues located in them.
Bone inflammation
Inflammation of the bone tissue surrounding the tooth leads to destruction of the bone and loss of the dental unit. Bone tissue becomes inflamed in the chronic form of periodontitis, when the nerve and root are already affected by bacteria, and a purulent formation has developed at the root of the tooth. Running the disease at this stage is life-threatening: cysts can grow in the maxillary sinuses, spread the infection to the heart and other internal organs, become infected with an infection of healthy teeth, and develop osteomyelitis.
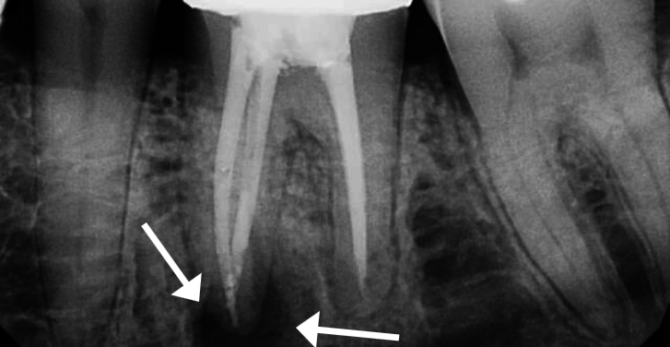
X-ray diagnosis of periodontitis
In the early stages of the disease, when decay processes have not yet developed, x-rays are little informative and rarely used by dentists. At this stage, inflammation of the root of the tooth is diagnosed not by a radiographic photo, but on the basis of the general clinical picture: after examining the oral cavity and voicing complaints.
But in the diagnosis of chronic forms of periodontitis, it is the x-ray that is the main method for determining the nature, stage of the disease and localization of the purulent sac. An x-ray helps the doctor choose the appropriate treatment tactics and correctly prepare for the operation.The most indicative is fluoroscopy, which allows the doctor to assess the change in the structure of dental tissues in dynamics.
What to do if the root of the tooth is inflamed
The inflammatory process in the tooth root never begins spontaneously. There is a reason that provoked it, and until it is eliminated, the pathology will progress, presenting an increasing danger to health.
To find out how to safely and effectively remove inflammation in the root of the tooth, you need to consult a doctor. Attempts to relieve pain with analgesics may succeed in the acute form of the disease, but it is impossible to regard the subsidence of pain as the removal of the inflammation itself - destructive processes continue inside the tooth.
Treatment of inflammation of the root of the tooth can be carried out at home, but only if treatment measures are prescribed by a dentist.
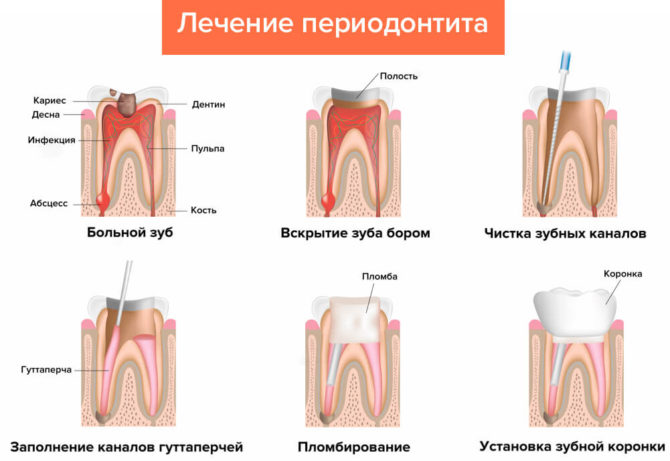
The main stages of the treatment of inflammation of the root of the tooth
What to do with inflammation of the root of the tooth, the dentist decides on the basis of the cause and stage of the disease, the degree of tissue damage and the development of complications. Each patient who has a tooth inflammation is given antibiotic therapy. It helps relieve inflammation and blocks the spread of infection. The type of antibiotic and the optimal dosage are selected individually by the doctor.
Periodontitis treatment is carried out in stages under local anesthesia. They begin treatment only when the doctor accurately determines the localization of the lesion by radiography.
The treatment regimen for periodontitis:
- Channels leading to the lesion are drilled. Special swabs soaked in an antiseptic are placed in them.
- To maintain sterility, a temporary seal is installed on the crown.
- The doctor prescribes an antibiotic, explains whether any procedures should be done at home, and allows the patient to be treated on an outpatient basis.
- The next appointment with the dentist will take place after 2-3 days. If at this point the patient has no pain attacks, swelling, hyperemia and swelling, the temporary filling is removed, the canals are re-flushed with an antiseptic and a temporary filling is established again.
- The second temporary filling is removed 2-3 months after the patient takes an X-ray, according to which the doctor can judge the dynamics of root restoration.
In the case of successful treatment and the absence of relapse, a temporary seal is removed, the doctor again flushes the canals and establishes a permanent seal. So that the root does not inflame again, after filling, an X-ray examination is again performed. According to the picture, the doctor can make sure that the channels are completely flooded with a solution, and the procedure is performed efficiently. A control visit to the dentist should take place 4 months after the installation of a permanent seal.