Treatment of stomatitis in children up to a year and older at home
Everyone has stomatitis at least once in his life, but for many, acquaintance with him begins literally with diapers. The pediatrician determines the treatment regimen for stomatitis in children up to a year and older, but treatment of the disease is carried out at home.
Content
Stomatitis in children: types and symptoms
How and what it will be necessary to treat stomatitis in a child’s mouth at home depends not only on the age of the small patient, but also on the type of disease. Stomatitis happens:
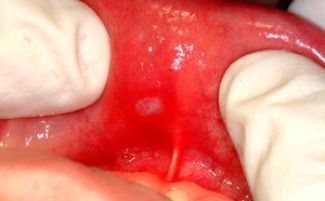
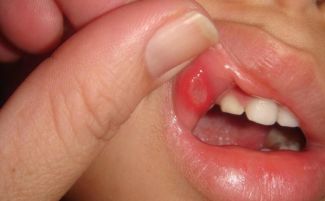
- Aphthous. It is accompanied by the development of ulcerative formations on the mucous membranes of the mouth called aphthae, mainly rashes appear in the lips and cheeks. Aphthae are surrounded by a red outline, covered with a white or grayish coating and are very painful, especially with meals. With this form of the disease, a slight rise in temperature is possible. It manifests itself with a weakening of immunity due to infections, chronic or acute diseases, lack of vitamins.
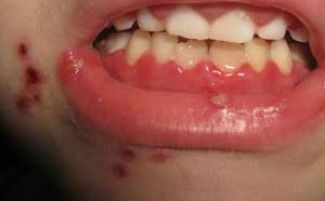
- Herpetic. Caused by the herpes virus, manifests itself in a characteristic rash in the form of watery vesicles-papules on the lips and gums. The temperature can reach 38.5 ° C, the child feels weak, lack of appetite and other symptoms of intoxication, along with a feeling of irritation from sore rashes.
- Catarrhal. It is expressed by inflammation of certain sections of the oral mucosa without visible superficial damage - glossitis on the tongue, cheilitis on the lips or gingivitis on the gums. It occurs as a symptom of internal systemic diseases, in infants it often manifests itself with teething.
- Candidiasis, known as thrush. Caused by Candida yeast, manifested by the appearance of cheesy plaque on the tongue, cheeks and tonsils. Painful erosion is concentrated under the coating. This form of the disease can cause inflammation or atrophy of the papillae of the tongue, lead to the formation on its surface of grooves or folds covered with plaque. The causes of the disease are immunodeficiency states, dysbiosis after antibiotics, diabetes mellitus, hormonal failure.
The course of stomatitis can be acute and chronic, mild and complicated, when an inflamed or ulcerated surface becomes an environment for the multiplication of other pathogens. Severe, advanced forms of stomatitis in children, especially aphthous and herpetic, are treated in a hospital. If treatment is started on time and passes under the supervision of a pediatrician, in most cases it is possible to get rid of this disease in a few days.
With stomatitis, a fever and a runny nose are possible - because of these signs, the disease is often mistaken for acute respiratory viral infections.
Photo of different types of stomatitis
Home treatment
The parents of a sick baby have two tasks: to quickly eliminate the irritating manifestations of stomatitis with topical drugs and strengthen children's immunity to defeat the disease from the inside and prevent relapse. The choice of drugs and methods of treatment depends not only on the form and stage of the disease, but also on the age of the victim: the younger he is, the greater the number of medicines is contraindicated for him.
How to help babies
Thrush often attacks the gums, throat and tongue of children in their first year of life.Breasts are especially susceptible to this disease, because they have not yet formed their own immunity, they are more prone to infectious pathologies and allergies, and a tendency to pull unwashed toys and fingers into their mouths has been developed. Very often the disease manifests itself during teething.
To quickly cure stomatitis at home in a baby, it is necessary to act immediately after the appearance of white plaque and slight redness in the mouth. The choice of treatment methods is limited, since the baby is still unable to rinse his mouth or make a therapeutic bath. But there are effective, time-tested remedies for such patients:
- Soda solution (teaspoon per glass of warm water) or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate (3 crystals per 0.5 l of water). When treating the mucous membrane with a cotton pad dipped in a healing fluid, white plaque is well removed, and at the same time the surface of the tongue or gum is disinfected. The same solutions treat the nipples, soothers and breasts of the mother before feeding.
- If the disease is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal medications are indicated: Candide solution, drugs based on nystatin, levorin.
- If the doctor diagnosed a herpetic form of stomatitis in a baby, it is necessary to include antiviral agents in the treatment regimen: Acyclovir, Tebrofenova or Oxolinic ointment.
- Local anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs: Calgel, Baby Dent.
- Healing ulcers and erosion agents: Solcoseryl, Vinilin.
Treatment of the affected mucosa is carried out 3-4 times a day (after each meal). The use of folk remedies will help consolidate the effect of pharmaceuticals - warm black tea, decoctions of chamomile or calendula in the form of lotions or irrigation from a syringe. During treatment, the baby needs to drink more liquid - better than pure water.
The baby’s recovery from stomatitis will help speed up the cleanliness of the house, regular treatment with bottles of boiling water, toys and teething. If complementary foods have already been introduced, the food should be liquid or puree-like consistency and a comfortable temperature - not overheated. It is necessary to exclude from the diet acidic foods that irritate the already inflamed soft tissues of the oral cavity, and sweets that “love” fungi and bacteria.
How to treat an older child
Children under the age of one and a half - two years are treated according to the same scheme as infants up to a year. But children of the third year of life and older can already brush their teeth and rinse their mouth, so the arsenal of drugs used to treat pediatric stomatitis at home is expanding. A sick child is recommended:
- Rinse your mouth after eating with solutions of soda, potassium permanganate, Furatsilina, hydrogen peroxide, decoctions of herbs chamomile, sage, yarrow, calendula, pharmacy herbal collection Stomatophyte.
- After rinsing, treat the oral cavity with the antiseptic Miramistin, Hexoral, Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine or Acyclovir (with the viral form of the disease), fungicide Nystatin, Candide or Diflucan (with fungal infection).
- Lubricate sores with Lugol's solution, propolis water tincture, sea buckthorn oil, Kalanchoe or aloe juice.
For local anesthesia, Kamistad, Kholisal gels are used, from 10 years old - Lidochlor. To relieve swelling and itching - antihistamines: Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil. To restore local immunity of the oral cavity - Immudon.
Nutrition during the treatment period should be balanced, saturated with valuable substances, but as sparing as possible for inflamed mucous membranes. Soups, mashed potatoes, cereals, mashed vegetables and fruits (citrus fruits are excluded), dairy products, nonfat soft or chopped meat, fish, eggs are suitable. By agreement with the doctor, you can use vitamin complexes to strengthen the child's body. It is necessary to strictly monitor the observance of oral hygiene by patients and carefully process the dishes used by them.
Preventative measures
At home, it is not always possible to completely cure stomatitis in a child - the course of the disease can become chronic or recurring (with periodic exacerbations). To avoid chronicity of the disease, it is important not to self-medicate and coordinate each action with the pediatrician. It is necessary to complete the prescribed treatment course, and then rehabilitation.
It is very important to identify the true cause of childhood stomatitis and its type. If inflammation is a symptom of a systemic disease, you need to undergo a therapeutic course to eliminate it. If the exacerbations are associated with unstable immunity, you will have to adjust the lifestyle of the child, and maybe the whole family: visit the dentist more often, monitor the cleanliness of your home and personal belongings, do physical education and hardening, balance nutrition and daily routine.