Baby teeth in children: timing and pattern of loss
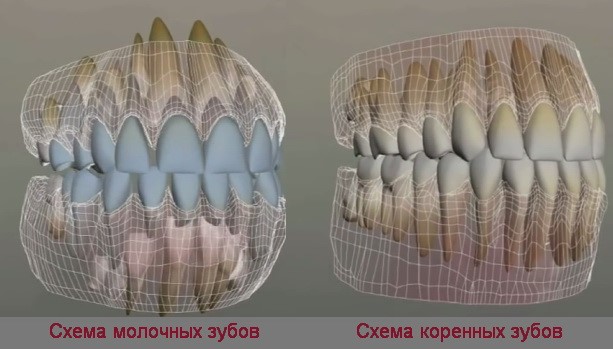
Only 20 baby teeth can fit on the jaws of a small child, and all of them should appear before two years. Over time, the size of the jaw will increase. And when the baby is five or six, the tops of the first molars called “sixes” will appear along its edges.
At the same time, the child will begin to lose milk teeth, which will occur in the same way as teething. But the process will last longer: permanent teeth will replace temporary ones only after six to seven years. And the remaining two pairs of molars, which should be the last in a row, will grow only by 13 years.
Content
How teeth are replaced and laid
When children have milk teeth, they are not hurt. Many even gladly help the crown part with the gum, boast of another loss to friends and look forward to the next one staggering to lure the Tooth Fairy's present.
Temporary incisors and fangs have roots, but they dissolve long before the permanent teeth begin to grow. Therefore, at the right time, milkmen lose their attachment, become loose and fall out freely. But their "shift" is arranged differently.
Root incisors, molars and fangs have a denser structure, strong roots, sensitive nerves, hard enamel and have excellent endurance. They can slowly and painfully collapse, but do not fall out. At least as easily as their predecessors.
Temporary teeth are laid before birth - between the fourth and fifth week of fetal development. Indigenous people form later, but their rudiments form even at the moment when the baby is in the womb. Therefore, during pregnancy, the expectant mother should eat well. Increase the amount of cottage cheese, milk, cabbage, shrimp, nuts and other foods that are rich in calcium.
During teething, bone tissue continues to grow. The baby is no longer receiving beneficial elements with breast milk, so it's time to introduce complementary foods into his diet. Now the child needs calcium more than ever. Indeed, soon milk teeth will change to permanent. And even then, the importance of the entry of the element into the children's body will not decrease, since the enamel will form over many more years and even in adolescence.
Attention! Temporary teeth affected by caries must be treated. The infection can spread to the rudiments of the molar, which will grow at the site of the patient. For the same reason, you need to teach your baby hygiene from the first year of life. And it is advisable to control this process so that it is performed properly.
How teeth fall out: signs
To predict when milk teeth will begin to change for permanent, you need to follow a few signs:
- The expansion of the interdental spaces. Due to age-related enlargement of the jaw, temporary incisors, molars and fangs are moving away from each other. If this does not happen for a long time, the molars will grow crooked due to lack of space. The orthodontist is able to help solve the problem. He will take a picture of the jaw and check if the baby has an anomaly.
-
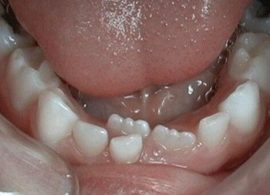
Punching a permanent central incisor next to a temporary one.The molar can peep out from under the gum tissue even before its predecessor falls out. If the process of changing the dentition does not work out within three months, you should contact the clinic as soon as possible. The baby may develop such an anomaly as “shark teeth” (see how the defect looks in the photo). It is fraught with the formation of a curved row, malocclusion and requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Reeling crowns. Temporary roots begin to dissolve 12 months before the appearance of lifelong teeth. When the process reaches the neck of the "young", its upper part loosens and falls out.
Which teeth change and which grow from scratch
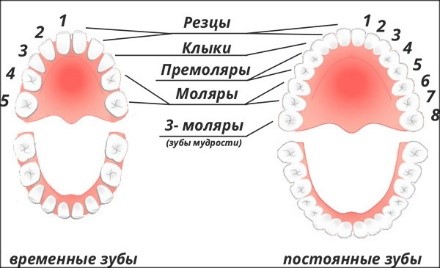
All milk jugs, which should be exactly 10 pieces in each jaw, fall out to give way to permanent ones. "Four" and "five" - units that many call indigenous also drop out. But teeth erupted in place of molars will be called premolars.
The first molars grow in a child a year before milk teeth begin to fall out. They occupy the free areas of the jaw, which appeared as a result of its age-related increase. And they are the sixth in a row. The second will only erupt at age 13, when the entire time series will be replaced by a permanent one.
A complete set of teeth in humans should consist of 32 units. But the last four can appear only at 16 or 20 years old, and in some people it will never erupt and remain in the form of an embryo in the gum. It’s not worth worrying because of the absence of “wisdom teeth” or third molars, since this is the norm.
In what order teeth fall out: scheme
The sequence of tooth changes may vary for each person. But usually milkmen fall out in order of priority:
- At five, the resorption of the roots of the central incisors begins. A little later - the side. And at six - the first molars. The process of separating the crown from the base lasts about 24 months.
- The loss of milk teeth begins in children from the age of six. First, a pair of lower central incisors leaves the gum, and a little later, the namesake is on top.
- At seven to eight, the lateral incisors change. But unlike the central ones, in the reverse order: first the upper ones, and then the lower ones. By nine years, the child should have all the permanent incisors in the amount of 8 pieces.
- At ten the first molars change - paired chewing teeth. In their place, indigenous premolars are poked. But not immediately, but only by twelve years.
- At the age of eight years, children begin to drop out the third milk teeth - fangs, which are designed to tear food into small pieces. Their permanent successors will begin to cut at nine, and by ten they will decorate both jaws.
- At eleven, a teenager becomes the owner of the first and second premolars. At about 12 years old, the child has only permanent teeth.
- Large molars, which have another name, “sevens,” are cut last. First, they appear on the lower jaw, then on the upper. "Teeth of wisdom" grow after adulthood or do not appear at all.
When and why teeth change in children
A baby is born toothless because he has nothing to chew. In the early days of life, the infant's diet consists only of mother's milk. But even before birth, root rudiments form in the bone tissue of the jaw of the fetus. The first tooth erupts at about the moment when the baby is six months old. At this age, he is ready to eat more solid foods.
At 3 years old, the child has all the baby teeth in his mouth. They appear in a certain sequence: first, incisors for biting, then chewing molars, and only then fangs for grinding solid food.
As a person grows up, his jaw also increases. If in childhood only 20 cloves were placed on it, then by the adolescent period their number increased to 32.Therefore, baby teeth in children begin to change to permanent. In addition, with age, a person needs a stronger enamel construction, as his diet becomes more diverse and tougher.
How old are the teeth in children: table
Up to 48 months, milk cutters and fangs do not fall out and do not stagger. Reeling is a sign of a lack of vitamins or disease. If you turn to the dentist in time, he will install an artificial implant that will help protect the integrity of the row.
A prolonged absence of molars indicates an abnormality. You will have to take an X-ray, which will allow you to identify a developing disease and eliminate it at an early stage.
Opposite situations also occur. When the milkman is in no hurry to give way to a permanent tooth that has already formed and has begun to erupt. This interference must be removed to avoid abnormal molar growth.
It is impossible to give a clear answer to the question of how old milk teeth change in different children. For some, the process will end by ten years, and for someone only to thirteen. And both children will develop within normal limits. So worry about the fact that peers are already smiling at all 28 “pearls”, and your child is only 20, not worth it. But in case of too long a delay, it is still advisable to go to the doctor. And to find out whether the teeth are behind the schedule, the table will help:
| Name of the pair (top and bottom) | Duration of deciduous tooth (age in years) | Permanent dentition (age in years) |
|---|---|---|
| First molars | ꟷ | 5–6 |
| Central incisors | 6–7 | 6–8 |
| Side incisors | 7–9 | 8–10 |
| Small temporary molars, after the change - premolars | 8–10 | 10–12 |
| Large temporary molars, after the change - premolars | 11–13 | 10–12 |
| Fangs | 9–11 | 10–12 |
| Second molars | ꟷ | 12–13 |
| "Wisdom teeth" | ꟷ | 17–20 |
What to do if the milkman falls early
In childhood, a tooth can be lost due to a banal fall. The roots of temporary teeth are weak and thin. Therefore, situations such as “received from a friend with a spatula”, “landed unsuccessfully from a hill” or “stumbled in a sandbox”, often lead to the loss of a dental unit.
 When the gum is empty, less pressure is applied to it, as the child tries to eat on the other side. As a result, bone tissue begins to dry out, and neighboring roots come together. Such a process can lead to uneven growth of a permanent tooth and pathological changes in the formation of the jaw. And this is fraught not only with a violation of the chewing function, but also the development of digestive problems and facial muscles.
When the gum is empty, less pressure is applied to it, as the child tries to eat on the other side. As a result, bone tissue begins to dry out, and neighboring roots come together. Such a process can lead to uneven growth of a permanent tooth and pathological changes in the formation of the jaw. And this is fraught not only with a violation of the chewing function, but also the development of digestive problems and facial muscles.
The situation is easily resolved if you pay attention to it in time. You just need to go to the dentist and install a special expander in the interdental cavity, which will keep adjacent teeth at the right distance until the shift period begins.
Why didn’t a milk tooth fall out?
Later changes in the dentition should not always be considered a sign of pathology. Often the reason for the delay lies in the banal lack of vitamins. To ignore this phenomenon is not worth it, but there’s no reason to panic. It is enough to contact a pediatrician and consult about vitamin and mineral complexes that can be given to a child based on his age and state of health.
If the baby is eight years old, and milk teeth still have not changed to molars, this is an alarming signal. It is likely that their rudiments did not even begin to form in the bone tissue. But before rushing to conclusions, you should consult a doctor and take a panoramic picture of the jaw. With it, you can see how serious the problem is.
The most common pathologies that cause a delay in the loss of baby milk teeth are:
- rickets;
- genetic abnormalities;
- infectious diseases;
- dyspepsia - a violation of the stomach;
- phenylketonuria is a hereditary ailment that is associated with a violation of the metabolism of amino acids.
Pathologies in which the child's primary teeth do not change are rare. But it is better to play it safe and go to the doctor.After all, the stage of teething of permanent teeth is the most important, since it is the last. And dental procedures, even if super-promising, are very expensive. Especially when it comes to serious defects.