Teething sequence in children: scheme and timing
All parents expect the growth of baby teeth. They are preparing for this event from the very first days of the baby’s life. Some study teething patterns to know in what order teeth should appear in children. Others do not leave the dentist’s office; their child should be only a few days behind schedule.
In fact all terms are relative. Someone will have the first incisor at 6 months, and someone at 8. And the development of both babies will occur within normal limits. However, there are also serious anomalies, for example, adentia, in which the dentition is incomplete or completely absent. This happens infrequently - some cases out of a hundred, but parents worry quite reasonably.
Content
- How teeth grow in children and adults: features of anatomy
- When to wait for the first tooth to appear in the baby
- The correct order of appearance of primary teeth: scheme
- Teething terms of temporary teeth: table
- How infants teeth are cut: symptoms and photos
- How to help a child
- When does permanent tooth growth begin and how long does it take
- In which queue should molars get out: scheme
- Oral hygiene: the basic rules
How teeth grow in children and adults: features of anatomy
A child is born toothless. The first teeth begin to erupt at a time when coarse food appears in the baby's diet, which requires chewing - about half a year. However, they are laid much earlier - during pregnancy. That is why obstetrician-gynecologists advise expectant mothers to eat foods rich in calcium, phosphorus and vitamins.
Milk teeth are cut in pairs and first on the lower jaw, and only then on the upper. That is, if the parents found one lower central incisor in the child, then the second will soon appear. And after him - the upper brothers of the same name. According to this principle, the growth of all milk teeth in children occurs, except for lateral incisors and canines. They begin to climb from above.
Only 20 teeth are placed on the jaw of a child. By the age of 5–7 years, its size increases, which can be seen in the growth of interdental spaces. At this age, temporary incisors, molars and fangs begin to fall out, and in their place permanent ones appear. The jaw continues to grow, and by the age of man can boast 32 teeth. Although 28 is not considered a pathology, since third molars or, as they are popularly called, “wisdom teeth,” some people may not crawl out. And that is the norm.
When to wait for the first tooth to appear in the baby
According to statistics, teething begins in the period between the fifth and eighth month of life. However, in those children who drink mother’s milk, the first incisor appears a few weeks earlier than the “artisans”. Frequent attachments to the chest stimulate gum tissue thinning., so the top of the tooth is easier to break out.
However, do not forget that the timing of teething in children is relative and depends on many factors:
- from how quickly parents will introduce complementary foods;
- from the composition of baby food;
- from climatic conditions;
- from the presence of chronic diseases;
- from heredity.
Therefore, do not worry if the first tooth has not appeared at the indicated time. Show your baby to a pediatric dentist. Most often, anxiety is baseless.
It is interesting! A baby can be born with several front teeth. Such cases are rare, but should not be disturbing, since they do not belong to deviations from the norm.
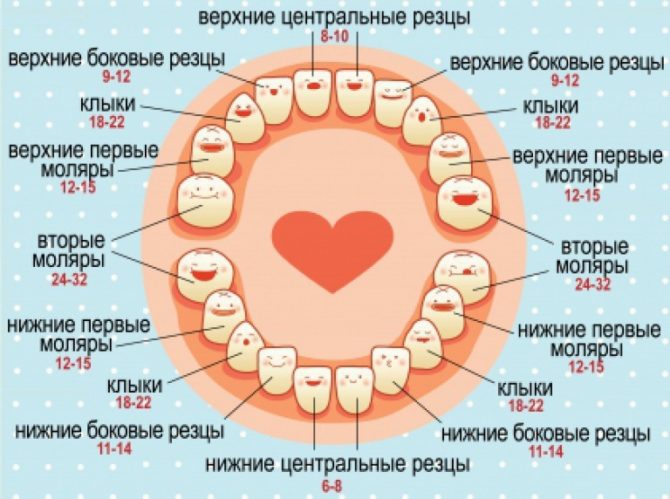
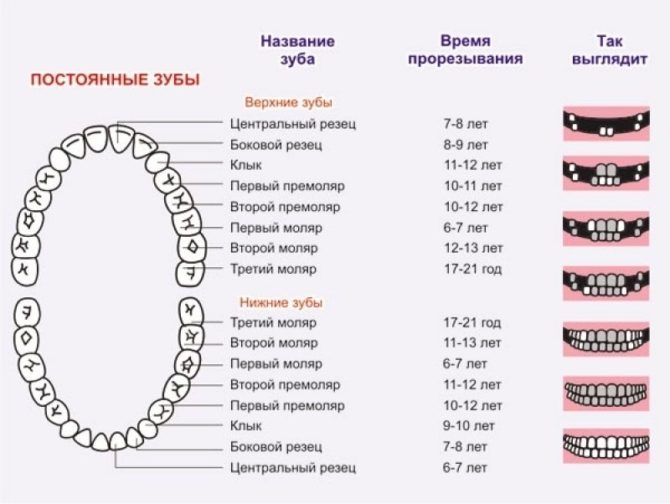
The correct order of appearance of primary teeth: scheme
If the timing of the development of the dentition is individual for each child, then the sequence is always the same. In the first year of life, 8 incisors should grow in the baby, which are designed to bite off food and are located in the middle of the jaw. Such teeth come out in pairs, the order of appearance is as follows:
- central lower;
- central upper;
- lateral upper;
- lateral lower.
If the baby is 12 months old and the incisors have not appeared, you need to see a doctor to exclude the likelihood of developing endocrine diseases and other pathologies that are accompanied by metabolic disturbances. The complete absence of teeth in a one-year-old baby may be a symptom of rickets or adentia, but medicine knows situations where children remained toothless for up to 15 months, but were completely healthy.
When the newborn is 1 year old, he will start to grow paired chewing teeth: the first and second molars. And also fangs, which are designed to tear solid food into small pieces. During the growth of fangs, the baby is naughty more than usual, because their sharp tip injures soft tissues. The process may be accompanied by an increase in temperature. up to 39 ° Cswelling of the gums, profuse salivation.
The order of teething in children in the second year of life:
- upper first molars;
- lower first molars;
- upper fangs;
- lower fangs;
- lower second molars;
- upper second molars.
At two years old, the child must smile with at least 16 teeth. And at three - at 20. If the time series has not formed by this age, you need to consult a specialist.
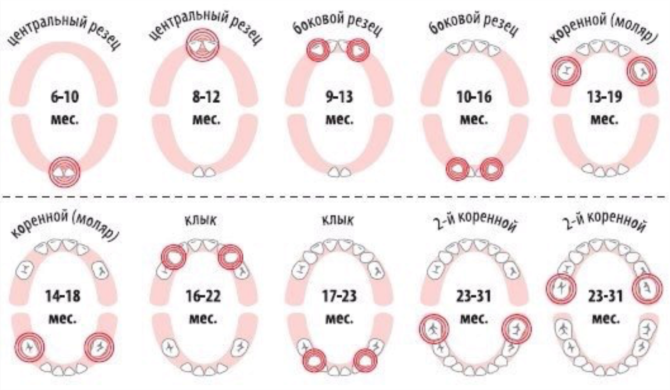
Teething terms of temporary teeth: table
| Couple name | Location (B - upper, H - lower) | Age of the child (in months) |
|---|---|---|
| Central incisors | H | 5–8 |
| B | 8–12 | |
| Side incisors | B | 9–13 |
| H | 10–16 | |
| First molars | B | 13–19 |
| H | 14–18 | |
| Fangs | B and H | 15–24 |
| Second molars | B and H | 23–31 |
How infants teeth are cut: symptoms and photos
During teething, the child experiences terrible discomfort, so his behavior may differ from the usual for parents. This is a bad mood, a desire to gnaw something, refusal to eat, moodiness. Signs of something wrong can be noticed long before the first incisor begins to peck - in 1-2 months. Therefore, in order not to worry about the health of the baby, you need to know the symptoms of tooth growth. What will happen:
- salivation will increase;
- decreased appetite;
- the gum will swell and turn red;
- the child will often cry and be capricious;
- body temperature rises;
- a wet, rare cough, runny nose will appear;
- possible constipation or diarrhea;
- the area of the baby's mouth is covered with a rash.
Such symptoms appear in all children. The temperature and cough will disappear on their own within a few days. But if this does not happen, immediately consult a doctor.
How to help a child
 When a baby has milk teeth, it experiences pain and discomfort. But each parent has the power to alleviate his condition. First of all, you can buy special cooling teething. They will reduce swelling of the gums, and at the same time its soreness. A lot of children's gels are sold in pharmacies to help relieve itching. Among the most common:
When a baby has milk teeth, it experiences pain and discomfort. But each parent has the power to alleviate his condition. First of all, you can buy special cooling teething. They will reduce swelling of the gums, and at the same time its soreness. A lot of children's gels are sold in pharmacies to help relieve itching. Among the most common:
- Calgel.
- Baby Doctor.
- Carmolis.
You can give the child a syrup known to everyone - Ibufen. It performs 2 functions at once - antipyretic and analgesic, which allows not to use a separate medicine to bring down the temperature.
Caution! Any procedures and drugs must be agreed with the pediatrician, as they may have contraindications and restrictions. In addition, parents do not know how to choose the right dosage.
When does permanent tooth growth begin and how long does it take
Teething of permanent teeth occurs in strict order. This process lasts a long time - from 7 to 9 years.At first, the first radical molars appear - about six months before the young growth begins to fall out. They grow in empty places, which are formed in connection with the age-related increase in the jaw. When the baby is five, the change of central incisors, which are located below, will begin. And then those on top. At six, the side will be updated. In 7–10 - the first and second milk molars. And only 11 - fangs.
The timing of the appearance of permanent teeth in children is very extensive and approximatebut if the child does not fit into them, you will have to consult a doctor. Up to four years, milk cutters, molars and fangs do not fall out and do not stagger. A loose tooth is a sign of a lack of vitamins, caries, or other pathology. In case of premature prolapse, an implant can be installed that protects the integrity of the dentition.
Another reason for going to the dentist is the long absence of molars. If the dairy has fallen out, but the constants have not grown, you need to do an x-ray. This procedure will help to identify possible anomalies, for example, when the root grows in the wrong direction.
In which queue should molars get out: scheme
The process of teething occurs in the following sequence:
- The first upper and lower molars. They are the biggest.
- Permanent central incisors.
- Side incisors.
- Lower fangs.
- The first, and then the second premolars.
- Upper fangs and second molars.
- Teeth of wisdom or third molars.
Oral hygiene: the basic rules
It seems to some parents that monitoring the health of primary teeth is useless, because they will still fall out and be replaced by new ones. This is fundamentally wrong judgment. Root incisors, fangs and premolars begin to be laid already from birth. therefore caries, which develops on the "young", can affect the condition of permanent teeth. According to statistics, this disease is detected in 73% of children over 5 years old.
How to properly care for the baby's oral cavity:
- You can not try food from the spoon of an infant and lick its dummy. So you can cause caries.
- It is necessary to reduce the number of sweet foods and drinks in the diet of babies.
- It is necessary to clean the baby's oral cavity after each feeding before bedtime. To do this, you can give him a drink of water or use a damp cloth.
- You need to teach your child to brush your teeth from early childhood. Children are still imitators. Show the kid how to use the brush, and he will happily follow you.
Remember that baby teeth fall out painlessly. Indigenous growth is also imperceptible: there is no gum swelling, nor an increase in body temperature. Therefore, those parents who did not pay proper attention to hygiene often find out that the first molar was replaced by a molar in the dentist's office when they come to fill in a damaged tooth.
Follow the child’s oral hygiene and he will thank you so much when he grows up.