Swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction: why it appears, how much it holds, how to remove at home
If, after tooth extraction, the cheek is swollen in a child or an adult, there is no need to rush to do anything. You should pay attention to how long puffiness persists, what symptoms accompany this condition. This will help determine whether the edema is a health hazard or is a natural reaction of the body to surgery, whether it is worth visiting a dentist, or you can remove the swelling at home.
Content
How long does cheek swelling last after tooth extraction?
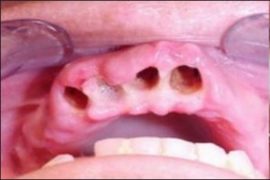
Swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction is a natural phenomenon, since during the operation the doctor injures the soft gum tissue, which causes an inflammatory process. How long the swelling will remain after tooth extraction depends on the physiological characteristics of the body, the tactics of the extraction, which tooth was removed. Normally, postoperative swelling persists for about 7 days.
Since tooth extraction is a micro operation, various side symptoms begin to appear at its completion. The table will help to get acquainted with them:
| Duration after surgery | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Immediately after surgery |
Swelling is observed only if it was present before the operation. If a tooth was pulled out without flux, the cheek will not swell. Since anesthesia continues to act immediately after extraction, there are no other symptoms at this stage. |
| After a few hours | When the effect of anesthesia ends, the cheek swells, a pain syndrome of moderate severity occurs, the temperature may slightly increase, a small amount of the sucrose is released from the hole. |
| The second or third postoperative day | On the second day after the doctor removed the tooth, the cheek may swell and begin to hurt. During this period, buccal edema reaches its maximum volume, but does not spread further. The pain persists, but does not intensify, has a aching character. Temperature readings are normal, a blood tree can ooze from the wound. |
| The third or fourth postoperative day | Swelling is gradually reduced. The pain syndrome is weak, the blood and the uterus do not stand out from the wound, and the temperature will decrease over time. |
| Week after surgery | A week after the doctor pulled out the tooth, the swelling of the cheek subsides, the pain completely subsides. The temperature is normal, there are no discharge from the wound. |
Why does a cheek swell after tooth extraction?
Cheeks can swell after tooth extraction for both natural and pathological reasons. Therefore, if a similar symptom occurs, you should consult your dentist.
Edema, a natural reaction of the body to intervention
Normally, the cheek may swell after the doctor has pulled out a tooth, in the following cases:
- The presence of edema before surgery.
- Removal of the tooth against the background of the inflammatory process. An infection that can provoke swelling of the gums may be present in the hole formed during tooth extraction. To prevent the spread of the inflammatory process, the dentist rinses the wound with an antiseptic solution. To prevent purulent inflammation of the hole, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- Complex tooth extraction.Complex operations that are often performed when removing wisdom teeth include cutting and suturing the gums. Such manipulations lead to the activation of immunity and, as a consequence, the development of the inflammatory process. If the cheek is swollen after removing the wisdom tooth, panic is not worth it. Swelling in the area of the removed extreme molar occurs in 90% of cases. However, it should be borne in mind that it can lead not only to facial asymmetry, but also to difficulty swallowing, uncomfortable and painful opening of the mouth.
- The presence of auxiliary diseases. Some diseases can provoke swelling of the face after tooth extraction. Often postoperative edema is observed with hypertension, neurological and psychoemotional disorders.
- The presence of a focus of inflammation in the gum area where the tooth is removed. In this case, the doctor makes an incision on the gum to remove the pus accumulated in it, due to which the cheek is swollen. Edema present before the operation may increase at the end of the operation.
Health Edema
Tumor of the cheek after tooth extraction may pose a health hazardTherefore, if you find such a symptom, it is better to consult a doctor. With proper diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, the risk of developing many serious complications will decrease.
Situations in which medical intervention is required:
- Edema persists longer than the prescribed 7 days, every day its increase is observed. A similar phenomenon indicates a progressive inflammatory process. Puffiness spreads over a large area of the face, deforming it and giving it asymmetry.
- There is an intensifying severe pain syndrome.
If, after tooth extraction, the cheek is swollen, the gum hurts, and there is a tendency to intensify these symptoms, it is urgent to consult a doctor. Especially if the pain syndrome is pulsating, cutting or oppressive.
- The temperature rises, general weakness is observed, there is no appetite, headaches occur.
- Untimely appearance of puffiness. Normally, edema occurs on the first day after surgery. A swelling that manifests itself a few days after the removal of the tooth unit may indicate a gradual development of alveolitis - inflammation of the socket.
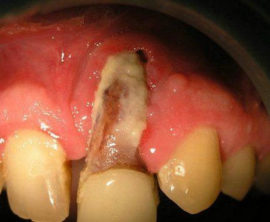
- There was a hematoma. Sometimes, at the end of tooth extraction, a small hematoma (lump) appears on the gum. By itself, it does not cause much discomfort, but with suppuration it provokes the occurrence of pain and an increase in swelling of the cheek.
Possible complications
The phenomenon, when the swelling increases, increases in volume, is accompanied by auxiliary symptoms, indicates the occurrence of some pathological process. In order to see a doctor in time and prevent complications dangerous to health, you need to know how much the tumor usually holds after tooth extraction, and what manifestations it is accompanied by.
When removing incisors, fangs and molars, the following complications may develop:
-
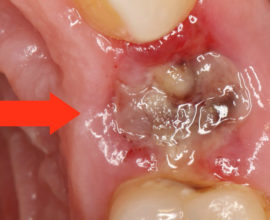
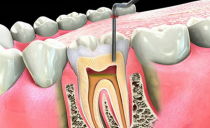
“Dry hole” is a pathology caused by the loss of a blood clot from a hole formed at the site of a torn tooth. Coagulated blood mass performs a protective function, so its absence contributes to the development of the inflammatory process and the appearance of pain. The wound does not heal for a long time, an unpleasant aftertaste appears in the mouth, pain remains for a long period.
- Alveolitis is a pathology caused by infection and suppuration of the hole. The disease can develop with the formation of a "dry hole". Most often it occurs when the molars are removed on the lower
jaw and teeth with cysts. In addition to the cheeks, other parts of the face swell with alveolitis: eyes, cheekbones. The disease is accompanied by fever, the appearance of bad breath, general weakness.
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent inflammation of the jawbone.With the disease, there is a pronounced increasing swelling of the cheek at the extraction site, which is accompanied by severe pain in the jaw, extending to the entire dentition. If tooth extraction was performed on the lower jaw, not only it will hurt - the pain can spread to the upper jaw, cheekbones, ears, eyes. With osteomyelitis it is painful to talk, open your mouth. A high temperature appears, accompanied by a headache, impaired appetite, and weakness. The disease can be complicated by blood poisoning.
-
Neuritis is a pathology caused by damage to the facial nerve and accompanied by severe pain. May occur when teeth with long or winding roots are torn out. The disease leads not only to swelling of the cheek, but also to numbness of the cheeks, palate, tongue, and partially the larynx.
- Flux is an inflammatory process that affects the periosteum. Symptoms: swollen cheek from the extraction side, fever, long-lasting pain syndrome.
- Abscesses affecting the soft gingival tissue. With this pathology, the cheek swells, fever rises, pain in the jaw occurs.
What to do to remove the tumor after tooth extraction
If swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction is caused by natural physiological processes, it can be reduced at home. Such a tumor should not last longer than 7 days and be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms. Otherwise, it is better to consult a doctor to identify the cause of the pathology and its treatment.
The following folk recipes and tips will help remove the tumor that has formed after tooth extraction,
- Cold. Swelling is reduced with the help of cooling masks. You can apply pieces of ice in a plastic bag to the swollen cheek. Swelling can be removed by applying a compress of natural fabric or gauze soaked in cold water. The compress should be kept in a sore spot for 1 to 2 minutes. The procedure is repeated several times a day - four for adults, two for babies.
- Water-salt solution. A compress with this composition quickly removes swelling after tooth extraction, moreover, it is easy to do at home and can be applied to the cheek every hour. A piece of cotton wool is saturated with a water-salt solution (2 teaspoons of salt per glass of water) and applied to the gum for 15 minutes.
- High pillow. To edema sleep faster, you should sleep on a high pillow. During such a sleep, the outflow of excess fluid from the tissues increases, as a result of which the tumor passes several times faster.
Stressful situations and excessive excitement should be avoided. In a normal psycho-emotional state, postoperative edema decreases much faster.
Preventative measures
To prevent swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction or to facilitate the early removal of an already formed tumor, the following preventive rules should be observed:
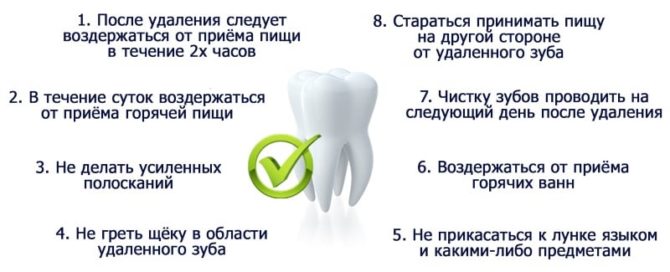
- Mouth baths. In the first day after surgery, you can not rinse the oral cavity in order to avoid violation of the integrity or removal of a blood clot. To reduce the risk of infection of the hole, it is permissible to carry out only oral baths - holding the solution in the mouth.
- Anesthetics. To reduce or completely remove postoperative pain, you must take medications prescribed by your doctor. Typically, dentists are advised to take Ibuprofen, Next or Ketanov - drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. It is not recommended to exceed the prescribed dose.
- Proper nutrition. In the first postoperative day, it is necessary to exclude solid, rough, hot food from the diet. Such food can injure the gums and cheek, which are already swollen after tooth extraction. For a whole week, you should eat only soft, warm and mild food. Until puffiness passes and the hole heals, it is better to chew food slowly and on the opposite side of the extracted tooth.
- General hygiene. You can not take a hot bath, because when it is taken, blood pressure rises, which is fraught with the opening of a hole in the bleeding.
- Oral hygiene. Teeth should be cleaned carefully, avoiding the operated area. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptics is indicated. If there are none, you can rinse your mouth with a herbal decoction.
During the period of elimination of postoperative puffiness and in order to prevent its occurrence, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia and overheating. It is worth canceling trips to the sauna, to the solarium, to the beach. Physical activity should be minimal. It should limit the use of alcohol, smoking cigarettes.
Swelling should decrease a few days after surgery. If this does not happen, you need to contact the dentistry clinic. The doctor will examine the oral cavity, analyze the general condition and, if necessary, conduct additional diagnostic tests. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor will determine what caused swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction, and tell you how to remove it.