Removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower and upper jaw, consequences and possible complications
Wisdom teeth are the eighth large molars closing the dentition. They owe their name to the fact that they are cut out already in adulthood - usually not earlier than at the age of 15. A complex root system and specific teething, often entailing an anatomically incorrect position, cause a high risk of complications and dental diseases.
Third molars are the only teeth that dentists recommend pulling out not as part of treatment, but as a preventive measure. Before making a decision on their removal, it is necessary to consult a specialist, objectively assess the condition of the molars, their effect on the dental arch, weigh all the risks and possible consequences after removing the wisdom tooth on the lower or upper jaw.
Content
Features of the structure of eights and indications for removal
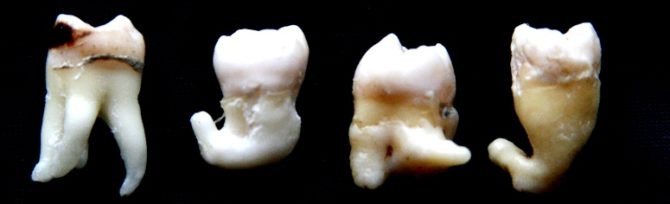
The structure of the bone tissue of the eights is no different from the neighboring teeth, the features of the third molars are in their structure. Unlike other teeth, eights erupt in youth and do not have “predecessors” - milk teeth - which prepare the gum for normal eruption. Due to such complicating factors wisdom teeth can have irregular shaped root canals, a large number of roots or fused roots.
In the photo of the extracted eights, the specific form of their root system is clearly visible:
Pathologies of the location of wisdom teeth
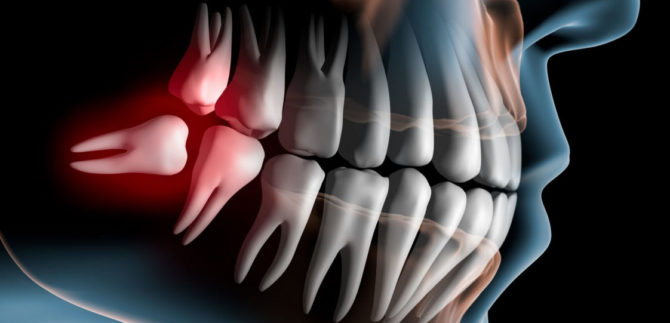
A characteristic phenomenon for the third molars is dystopia - an incorrect position of the tooth in relation to the entire jaw row. It is due to the fact that the eights erupt last. Deficit of free space in the jaw arch can cause the tooth to partially erupt or not erupt at all.
In dentistry, teeth, the cutting of which occurs with retention (delay), are called semi-retined - partially shown on the gum surface, and retined - completely hidden under the gum.
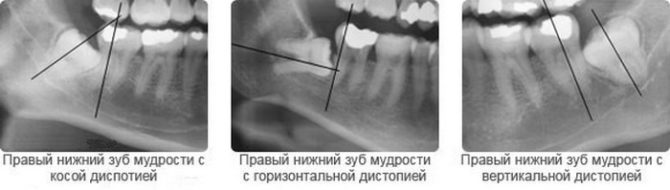
Dystopia can be accompanied by pain, swelling of the gums and cheeks, the development of internal inflammatory processes. Such a pathology is clearly visible on x-rays of wisdom teeth:
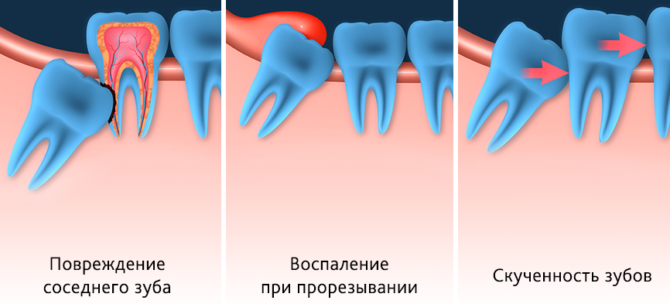
When looking for an exit to the surface, the molar can significantly deviate towards the cheek, which is fraught with injury to the mucosa during chewing. Long non-healing wounds are terrible not only because the cheek constantly hurts and swells, but also because they can transform into ulcers. If left untreated, tumor processes may begin. With advanced pathology, the figure eight is removed, and the oncologist observes the wounds.
Indications for the removal of a wisdom tooth in the upper or lower jaw
Due to abnormal eruption of a tooth, a person may experience a feeling of discomfort, an unceasing throbbing pain, worse when chewing. Abnormal teething can lead to the development of dental diseases and the displacement of the dentition up to the anterior zone.
Wisdom teeth do not carry a functional or aesthetic load, so many dentists recommend removing the eighth tooth immediately after eruption, without waiting until it becomes sick. Emergency removal reduces the risk of developing dental diseases and is less difficult.
In conservative dentistry, in order for the doctor to decide on the need for the operation to remove the eights, the patient must have indications (symptoms that threaten health). They can be direct and indirect.
Direct indications for urgent extraction are:
- sepsis;
- osteitis of the jaw;
- neoplasm development;
- periodontal inflammation;
- pericoronitis;
- destruction of bone tissue;
- destruction of the tooth crown - caries.
The conditional indications for the removal of 8 teeth from above or below include:
- pathology of the bite;
- retraction - lack of natural eruption;
- softening of the root system;
- fracture of the root or crown of the tooth;
- root bifurcation disorder;
- sinusitis;
- the need for prosthetics;
- horizontal position of the tooth with inflammation.
If the molar has not erupted or partially erupted, the doctor decides to eliminate the rudiment based on the threat of future complications and the patient’s current condition. If the patient is well, the tooth and gums near him are not inflamed, he will be recommended to see a dentist every six months. Immediate removal is indicated if there is at least one of the following symptoms:
- the occurrence of pain;
- acute and chronic inflammation;
- development of a follicular (tooth-containing) cyst.
Extraction of wisdom teeth
When removing eights, not only the tooth extraction procedure itself is important, but also the preparation for it. The procedure for simple tooth extraction takes from half an hour to an hour, a complex surgical operation can last up to 5 hours. If you plan to wrest a few eights, operations are scheduled at intervals of three weeks.
Treatment, cleaning, filling and other planned manipulations on the remaining teeth can be performed 2-4 weeks after the extraction of the third molar.
Training
Before removing a wisdom tooth, the dentist must examine an x-ray of the patient's jaw. With its help, the doctor will be able to accurately determine which removal is to be done - simple or complex, to eliminate serious complications. This information allows you to draw up an optimal work plan, study potential risks and choose the right tools and equipment.
After the patient’s medical history is collected, a surface examination of the tooth is carried out, the extraction method, anesthesia drug and tools are finally approved. To exclude suppuration and inflammation of the well after surgery, before removing it is necessary to thoroughly clean the teeth from plaque and to disinfect the oral cavity with antiseptics.
Anesthesia
The final step in preparing for surgery is anesthesia. Usually, the removal of the upper and lower eights is performed under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is relevant in situations where a local anesthetic cannot be used due to the presence of allergic reactions in the patient’s history.
Regardless of the type of anesthesia, the procedure should be painless. The patient may feel pain with the introduction of anesthetic and at the end of the anesthesia, but during the period when the doctor will remove the wisdom tooth, it will not hurt.
Removing a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw
Bone tissue of the lower jaw is denser and 3 times stronger than the upper, so it is more difficult to tear the teeth from below. But fractures in the process of removing the lower wisdom tooth are extremely rare. The main risk in the extraction of the lower 8 tooth, especially semi-reinforced or retinated, is nerve damage, which can provoke numbness of the facial muscles.
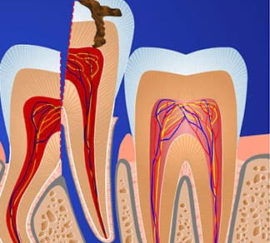 The eighth molars located below have more roots than the upper ones, so dentists resort to surgery for their painless extraction.
The eighth molars located below have more roots than the upper ones, so dentists resort to surgery for their painless extraction.
Before removing the bottom eight, the doctor conducts a detailed analysis of the x-ray to visualize the location and shape of the root system. With a large branching of the roots, it is difficult and traumatic to tear out the molar entirely, which is why these teeth are usually divided into several parts with a drill and pulled out one by one.
Removal of the wisdom tooth in the upper jaw
In most cases, extraction of the upper eights is not complicated by multiple roots characteristic of lower row wisdom teeth. The upper wisdom tooth is removed using forceps (without surgery) in cases where:
- The root is one.
- There are several roots, but they are connected.
- The root curvature is negligible, and its length is small.
- The crown is completely or almost completely cut, which allows you to grab it with forceps.
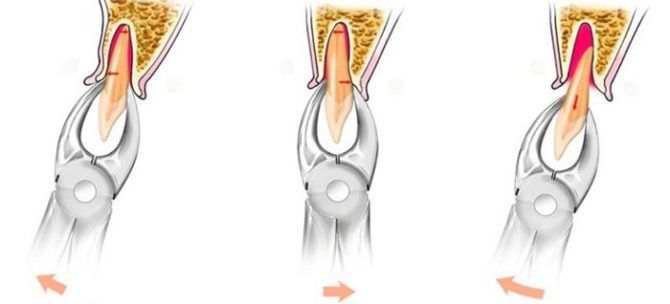
The delete algorithm looks like this:
- The forceps are superimposed on the crown or root located in the hole, then the forceps cheeks move a little deeper into the gums and are fixed.
- When the doctor is convinced that the instrument is fixed correctly, he gradually begins to swing the molar, after which it painlessly removes it from the hole.
- The last step is to apply a sterile swab to the well to stop the bleeding.
Removing complex wisdom teeth
Removing complex wisdom teeth is a full-fledged surgical operation, during which the dentist performs incisions, uses a drill, and sutures wounds. Sophisticated operations are required to extract retined or horizontal teeth. Such an intervention is performed in a surgical sterile room. To completely remove the discomfort and any pain for the entire period of the operation, stronger anesthetics are used.
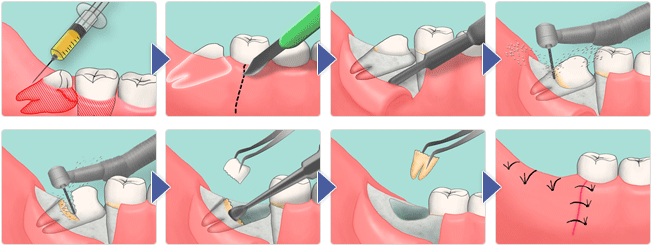
The algorithm of operations on the wisdom tooth:
- The doctor injects an anesthetic into the gums.
- Since the wisdom tooth is hidden under the gum, the surgeon makes an incision in the gum and flakes off the flap, sufficient for subsequent work size.
- In the event that a wise tooth is surrounded by bone tissue, before removing it, the doctor performs a bone resection using special cutters. To avoid bone necrosis, work is carried out at minimum speed with cooling.
- Then the eighth tooth is removed. Depending on the number of roots, the surgeon can tear out the tooth in whole or in part.
- The curettage of the hole and the disinfection of soft and bone tissues are carried out.
- When all decontamination procedures are completed, the surgeon returns the mucous flap into place and sutures. If necessary, special drugs are used to stop bleeding.
- At the end of the operation, the patient receives recommendations for postoperative wound care.
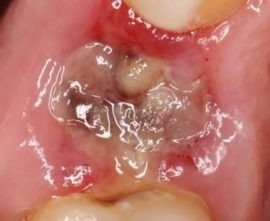
Consequences and possible complications after removing a wisdom tooth
Complications can arise due to erroneous actions of the dentist, insufficient antiseptic processing of instruments, neglect of rehabilitation measures and due to physiological characteristics.
Doctor’s errors are most often associated with improper position of the instrument and excessive force when pressing on the forceps, which can lead to a fracture of the jaw, damage to the gums, ruptures of the corners of the mouth. Due to the structure of bone tissue and the specifics of the operation, mechanical injuries are more often the consequences of removing the upper wisdom tooth.
The close arrangement of eights to large vessels not only increases the risk of severe bleeding after surgery, but also increases the risk of developing an extensive inflammatory process in the body when an infection of an extracted tooth socket is infected.The doctor can bring the infection into the hole, working with tools that have not undergone proper treatment, or the patient himself, without caring for the wound and oral cavity properly.
The most serious complications after extraction of the third molars are:
- Hematoma - severe swelling of the gums. It occurs with fragile vessels, accompanied by fever and severe pain.
- Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. It arises due to extraction with poorly processed tools or with insufficient hygiene.
-
Dry hole syndrome is a pathology of the healing process in which a blood clot that must form in the hole does not form, dissolves too soon or drops out of the hole. Most often seen in smokers. A dry hole is fraught with the development of inflammatory processes, can develop into an alveolitis. With this disease, the walls of the hole are suppurating, a specific bad breath appears, and the gums swell. General malaise, fever, and headache are possible.
- Flux is an inflammation of the periosteum resulting from postoperative infection. With pathology, there is a strong redness of the gums, swelling in the cheek, severe pain and fever.
- The formation of cysts. Fibrous neoplasms arise as a protective reaction of the body to separate healthy cells. Their appearance is not related to the quality of the operation. Antibiotic therapy is used as prophylaxis.
Rehabilitation after extraction
Depending on the type and complexity of the operation, complete restoration of the gums will take from three to twelve weeks. The patient may be assigned:
- Taking antibiotics.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Therapeutic rinses and irrigation of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions.
- Herbal applications.
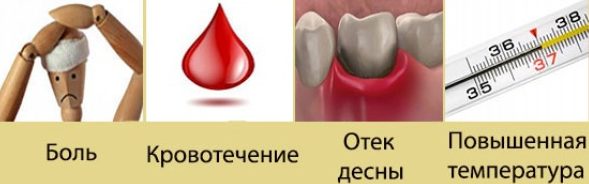
The dentist can perform the operation quickly and painlessly, but it is impossible to completely eliminate all the risks and negative consequences after removing the wisdom tooth. Normally, an increase in body temperature to 38.5 ° C, malaise and poor health, the formation of edema and bruising in the cheek area, slight bleeding, which should stop for 3-4 hours, are permissible.
The first time after surgery, you need to properly care for the wound and gum, clean the oral cavity in a gentle manner and adhere to the following recommendations:
- Postoperative pain intensifies in the evening and at night, so pain medications should be available at the ready, which will need to be taken if it becomes unbearably painful. Throbbing pain can be relieved by applying cold to the cheek. An analgesic effect and a decrease in swelling are achieved due to narrowing of blood vessels.
- Sleep on a thick, high pillow or several pillows, which will help to avoid swelling.
- Exclude solid, cold and hot foods from the diet.
- On the first day you should refrain from drinking drinks through a straw. When it is used, a vacuum is created in the mouth, which leads to a slowdown in regenerative processes.
- To avoid bleeding, do not smoke the first week after surgery, since tobacco smoke increases vascular fragility. It is especially important to exclude smoking after removing the 8th tooth from below, since the consequences in the form of bleeding are more characteristic of the lower jaw.
To find out how the surgical removal of the wisdom tooth goes, watch the video: